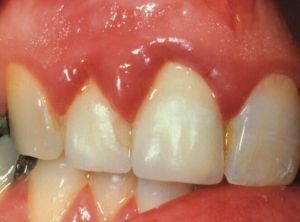
 Gingival swelling is always a sign: with this part of the oral mucosa something is unsuccessful. When the gum swells, it looks like a thickening of the edge or all of its mass, accompanied by soreness and redness. Or, there can be a transformation of all tissues into a continuous, watery-glassy massif, devoid of any sensations.
Gingival swelling is always a sign: with this part of the oral mucosa something is unsuccessful. When the gum swells, it looks like a thickening of the edge or all of its mass, accompanied by soreness and redness. Or, there can be a transformation of all tissues into a continuous, watery-glassy massif, devoid of any sensations.
Swollen gums are always alarming, causing a logical question, from what happened?
Contents
- Understand the causes of
- Our babies need special attention
- The gingiva swells after tooth extraction - the most frequent case of
- How to relieve swelling?
- On the consequences and preventive measures of
We understand the causes of
The causes of gingival edema can be very different, depending on both the traumatic situation and age - the child has its own factors, and the recent visitor to the dental office after tooth extraction - quite different. In the first case( with teething), the state of the edema is physiological, in all other variants it is a pathological process that develops both for external and internal causes.
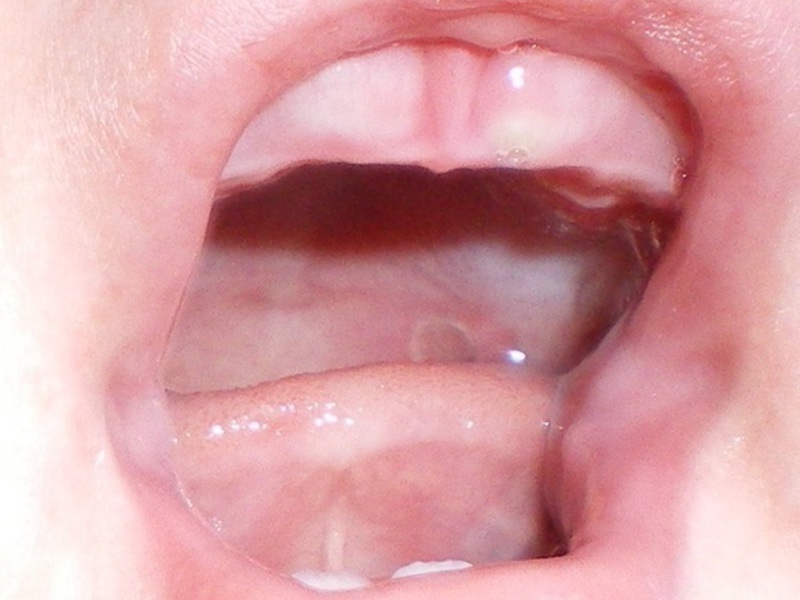
Swollen gingiva in the baby is a normal process in which you should not panic and beat the alarm
If the lightning swelling caused by the local external cause( in case of severe trauma: chemical, thermal, mechanical) is said to develop for severalseconds from the moment of impact, then the acute one requires at least an hour for its formation.
The cause of puffiness can be:
- damage( with the removal of the tooth, with a rough cleaning of the oral cavity);
- acute inflammatory, infectious or infectious-inflammatory disease involving the oral cavity;
- is an allergic process that manifests itself in addition to the general flow of the body to the local at the gum level.
Modern filling materials and other substances can also cause an allergic condition, which has the appearance of both acute and lightning fastness.
Chronic disease, accompanied by more or less destruction of tissues, leads to the development of a chronic variant of the condition with a formation period of several days to several weeks. Reasons for it may become:
- tartar;
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- pulpitis;
- periodontitis;
- periostitis of the periosteum, also referred to as flux.
Chronic injuring and leading to the development of puffiness factors can also serve as bruxism, hypertonus of masticatory muscles, improperly fitted or worn out from prolonged wearing of prostheses and similar reasons.
There is edema of the gums, as a result of excessive permeability of the capillaries of its tissues due to:
- vascular wall reaction to toxins;
- disorders of the nervous regulation of its permeability;
- disturbances of capillary wall trophism.
In view of these factors saturation of the intercellular space of tissues with edematous fluid occurs, the composition of which depends on the cause of the disease state.
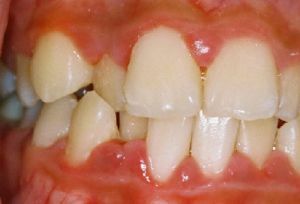
Hypertrophic gingivitis provokes swelling of the gums
In case of trauma, it is often hemorrhagic, with an allergic reaction - serous, with the development of the inflammatory process - necrotic-hemorrhagic or purulent. That is, it is either an exudate, or a transudate, or a liquid rich in protein, with a certain amount of formed elements of blood, or a liquid with a scanty protein content.
Thus, gingival edema is a local water balance disorder that has developed as a result of a local circulatory disorder, the reasons for which can be both local and general.
Local include acute and chronic trauma, general - acute and chronic conditions of the body with predominance:
- inflammatory;
- infectious;
- of the allergic component.
These can be diseases of the blood, avitaminosis C, oncological and endocrine diseases, collagenoses and other pathology.
Mucosal involvement can be general and local.
Our children need special attention to
The general causes of this condition in children are:
- unwillingness of children to practice oral hygiene or lack of ability to do it;
- high vulnerability of the mucosa;
- susceptibility of mucous membranes to damage( due to frequent viral and other oral diseases due to lack of immunity and general immaturity of the body).
Babies swollen gums signal about painful teething, beginning at the age of six months and continuing then to 2.5-3 years, as for the baby teeth. Sometimes in infants the gum swells much earlier than the appearance of the first teeth.
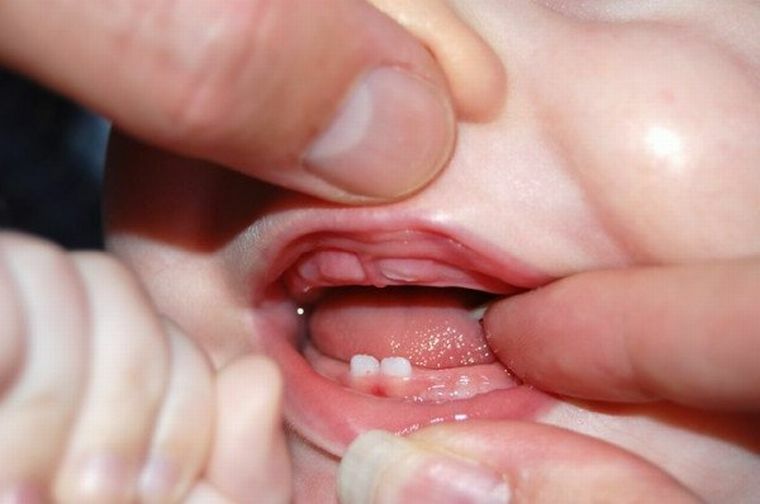
Along with the swollen gums, the early chance of a tooth incision is confirmed by the accompanying symptoms:
- drooling with a "full mouth" and during the whole time of the day;
- fierce gnawing by the child of various items, which he indiscriminately tightens into the mouth, biting the nipple of the mother's breast;
- nervousness, tearfulness, insomnia, refusal to eat and similar behavioral symptoms.
As a result of swallowing abundant saliva and mucus, diarrhea, cough, and runny nose appear. To confuse parents, leading to the thought of ARVI, is capable of raising the temperature to 39⁰ C with its preservation at this level up to 2 days.
Other reasons for swelling of the gums in infants may be:
- mucosal damage;
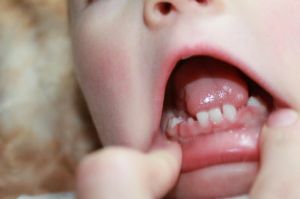
- Vitamin C deficiency with delayed and sluggish wound healing from trauma;
- dental diseases( stomatitis, caries).
Do not tighten with diagnostics for more than 2 days.
After a physical examination, teeth cutting shows minimal interference in the process: observation, facilitation of the process with the help of special medical products( teethers) or suitable for properties and easily sterilizable items, the use of lubricating-cooling gels, massage of the swollen area with a mother's finger wrapped inclean napkin.
The next period for the physiological swelling of the tissues of this area of the mucosa is the time( from 6 to 13 years) for changing dairy teeth to permanent teeth.
And for adults, by the year 21 or after it comes the time for the eruption of third molars( wisdom teeth).Puffiness and signs of inflammation with difficulty or incomplete eruption are called pericoronitis( pericoronitis).
A special moment is the period of the teeth change, when the edema is a consequence of the tension of the tissues due to the powerful pressure from the inside, which is provided by the growing tooth.
The gingiva swells after tooth extraction - the most frequent case of
. The swelling of the gums that occurs near the socket after tooth extraction is not unusual and is caused by the following reasons:
- traumatic intervention due to the difficulty of tooth extraction with long, widely divergent roots, or with an excessive amount;
- features of the structure of the gingival tissues - their high vulnerability and propensity to inflammation, for example, in diabetes mellitus.
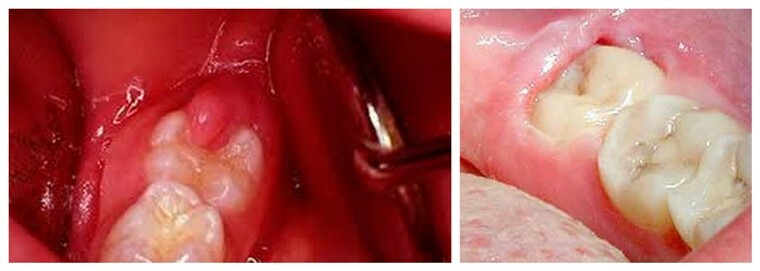
Pericoronitis is an acute inflammatory process after removal of the wisdom tooth, which provokes swelling of the gingiva
. To the same situation, leaving a fragment of the tooth or a fragment of the instrument leads to a similar situation.
The provoking factor is the development of an allergic reaction to an anesthetic or another manipulative reagent.
The onset of an acute infectious disease in the body or the exacerbation of a chronic process in it soon after extraction of the tooth also leads to greater manifestation of local inflammatory changes.
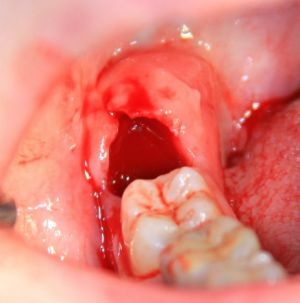
Gums after tooth extraction
The picture of a periosteal injury in the depth of the tooth socket( periostitis-flux) has the form of edema that is not accompanied by soreness and the appearance of hyperemia of the edges - the tissues are evenly pale edematous.
The emergence of the same inflammatory "edging" is a sign of involvement in the process of the microbial factor due to the creation in the wound of favorable conditions for nutrition and reproduction of bacteria. In this case, in addition to the swelling of the mucous in the patient, there is a feeling of pulsating pain in the gum and a feeling that it is hot.
The presence of these symptoms already requires a repeated visit to the dentist, not to mention more serious signs of complications of the operation:
- persistence for several days of elevated body temperature;
- involvement in the process of soft tissue of the face;
- lymphadenitis, and even more so the growing headache with nausea, vomiting and other general cerebral events.
How to relieve swelling?
Treatment of any deviations from the proper picture of the postoperative gingival socket requires agreement with the treating dentist.
In case of a postoperative period that is not complicated, the doctor can recommend rinsing of the oral cavity( with official solutions or decoctions of medicinal raw materials prepared independently), the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, local heat( strictly according to indications).
Of the most simple home remedies for rinsing, solutions of soda or common salt, or a combination thereof, a solution of hydrogen peroxide are applicable.
Do not use such products as an antiseptic disinfectant - solutions with the addition of iodine tincture in case of ingestion of  inside the body accumulate iodine in the tissues of the thyroid gland.
inside the body accumulate iodine in the tissues of the thyroid gland.
From medicinal raw materials prepare broths of chamomile, calendula, mint and eucalyptus in accordance with the recommended tips and recipes.
From drugstore rinse products, solutions of Chlorhexidine and Miramistine, diluted extract of Stomatophyte or solution of Mevalex, Givalex, are effective. Metrogyltant gel is effective.
On the consequences and preventive measures of
Swollen and painful gums are not only unpleasant in themselves, but under certain conditions they can cause varying degrees of bleeding effects, the appearance of purulent processes in the jaw apparatus, which in severe cases leads to tooth loss.
To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to pay attention to the health of teeth from the very moment of their appearance and take measures to preserve them in a natural and healthy state.
Knowledge of hygiene rules and strict adherence to them, observance of chewing biomechanics and attentive attitude towards food, refusal from alcohol and smoking of tobacco, prevention of stresses are common truths of a healthy lifestyle, known to everyone and constantly declared by medicine in the person of dentists.
The case for small: the recommendations of the dentist should be carried out impeccably, and the visits to his office - become the same rule as regular brushing your teeth!
