There are many reasons for menstrual irregularities in women, and a delay in menstruation often occurs with the ovarian cyst. Similar changes are characteristic for formations that are prone to the production of hormones or are a consequence of their imbalance. In the latter case, it is difficult to establish what was the root cause. How are the monthly and cysts interconnected, can this problem be independently suspected?
Signs and symptoms of cyst
Cyst is a cavitary formation on the ovary. Allocate true and false, acquired and congenital. Visually they can not always be distinguished even during an operation to remove, finally all hypotheses are confirmed or disproved by the histologist. For whatever reason, education has not developed, very often it causes disturbances in the menstrual cycle. Most often these are various delays, which lead to the absolute acyclicity of any bloody discharge in a woman.

The main signs of ovarian cysts include the following:
- Periodic pulling or aching pains in the lower abdomen at the site of localization of the neoplasm. They can be on the right or left, from below or at all simply to give in a loin or a sacrum.
- Unpleasant sensations and even pain during sexual intercourse. If the cyst is large enough, its displacement with active physical exertion will cause soreness.
- Feeling of "something superfluous", heaviness in the lower abdomen. This is more typical for formations of large sizes. For example, 5 to 7 cm of education, as a rule, do not give such complaints.
- Disorders of the menstrual cycle, most often this delay, after which come a very plentiful monthly.
- Pronounced premenstrual syndrome.
- Problems with conception. The fact is that the cyst is formed against a background of altered hormonal background, inflammation and some other causes that also cause difficulties in fertilization.
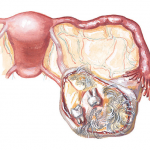 We recommend that you read an article on the monthly for an ovarian cyst. From it you will learn about the types of cysts and their effect on the menstrual cycle and the nature of the monthly, the consequences of the rupture of education and the need for treatment.
We recommend that you read an article on the monthly for an ovarian cyst. From it you will learn about the types of cysts and their effect on the menstrual cycle and the nature of the monthly, the consequences of the rupture of education and the need for treatment.
Causes of development of
The following ovarian formations lead to disorders of the menstrual cycle:
- follicular and luteal cysts,
- endometrioid,
- polycystic ovary,
- hormone-producing tumors.
Despite the similarity of the clinical picture, they all have different causes of occurrence. We can identify the main risk factors for women in the likelihood of such disorders:
- frequent inflammatory diseases of the genitals of various etiologies,
- hormonal disorders,
- abortions and pathological pregnancies( miscarriages, undeveloped, etc.),
- illiterate use of hormonal drugs( oral contraceptives,emergency contraception, etc.),
- premenopausal period and the onset of puberty.

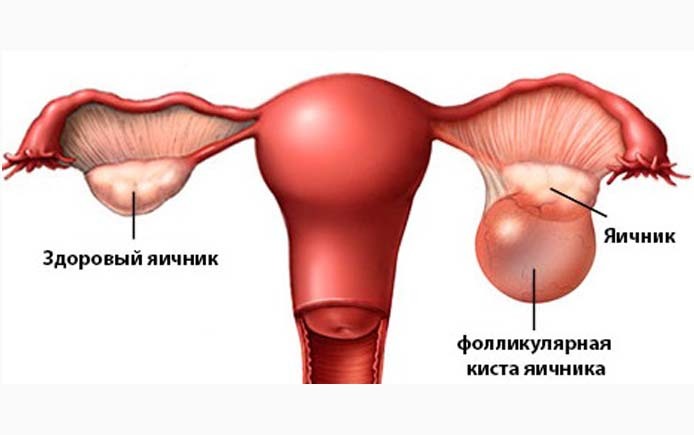
Follicular cyst
From the first day of the cycle, under the influence of estrogens and FSH, one of the follicles grows, in which the oocytes mature for subsequent fertilization. To its 14 - 21 day( for all women in different ways), it reaches its maximum size, about 20 mm. At this point, a surge of other hormones leads to rupture of the follicle, which allows the egg to exit and meet the sperm. But for some reason this does not happen, and this education has two ways of further development: to continue its growth, then a cyst is formed, or atrophy without a trace.
Follicular cysts are very common in women during the period of extinction of their reproductive function: on the eve of menopause, as well as with frequent abortions and emergency contraceptive pill methods. Constant fluctuations of hormones lead to similar excessive growth of follicles, sometimes they reach sizes up to 10 and more centimeters.
Such formations close the pathological circle, stimulating the formation of estrogens. As a result, the follicular cyst of the ovary arises and the delay of the menstrual cyst on its background. Sometimes these are very significant failures - up to 2 - 3 months.
Luteal cysts
After the ovulation occurs, a yellow body forms on the site of the bursted follicle, which produces progesterone. But for some reason, a cystic formation is formed at this site. Often this is accompanied by pregnancy, then the luteal cyst goes to 12-16 weeks of gestation. The yellow body cyst also intensively produces gestagens, which causes failures - delays( if the fact of the occurred conception is excluded).
Against the backdrop of luteal cysts, a woman observes more pronounced symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. This is engorgement of the mammary glands, frequent mood changes, pasty, etc.
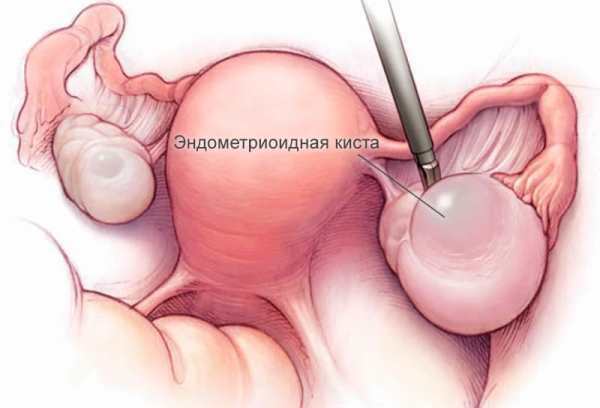
Endometrioid cysts
Endometrioid cysts themselves do not cause a malfunction of the menstrual cycle. But in 90% of cases not only the ovaries are affected, but also the muscular layer of the uterus, peritoneum and other parts. And this already entails various violations of the cycle: an increase in the volume of menstrual blood, soreness, and daub. In more neglected cases, there are delays.
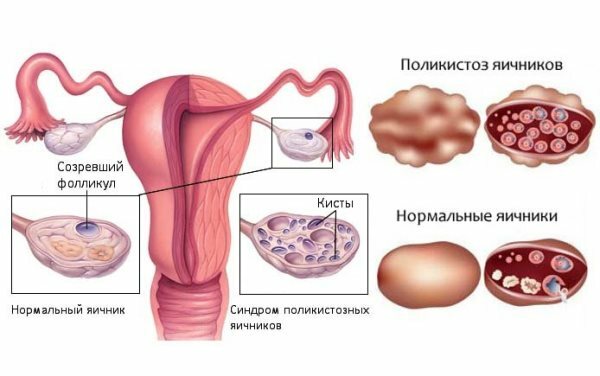
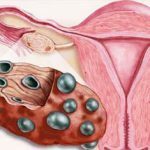
Polycystosis
Polycystic is a separate and rather serious disease, which is based on endocrine disorders. One of the symptoms of the pathology is numerous cysts on the ovaries. But they have a completely different structure and causes compared to follicular and lutein. Such cysts are represented by immature follicles, i.e.pituitary and hypothalamus signals are sent for the next growth of the egg, but hormonal disorders "stop" this process. As a result, many( more than 10) small cyst-like formations are formed on the ovaries.
With polycystic changes in the hormonal background, women can be so serious that periods of amenorrhea can go up to a year or more. A delay of several weeks - this is already the usual thing. In such situations, monthly after removal of the ovarian cyst or even resection of its part is not restored or normalized only for a short period.
Hormone-producing tumors
At any age, a woman can develop on the ovaries not just a cyst, but a malignant tumor that produces sex hormones, most often the estrogens .Against the background of the determined formation, there are significant violations of the cycle - delays, acyclic bleeding. Sometimes it is possible to establish that this is a malignant tumor, only after removal of the cyst and its subsequent histological examination.
Look at the video about the disease:
Interrelation of menstruation and cysts
Do you have a monthly ovarian cyst, what are they? The menstrual cycle can both not suffer at all, and undergo significant changes, which leads the woman to the doctor for examination.
How the monthly
goes The most common cysts are characterized by delays of menstruation from several days to a month or more. And this can occur against the background of imaginary well-being - nothing disturbs the woman.
After such delays, in most cases there are very abundant, with clots of secretion. This is due to the fact that during this period the endometrium is growing, the risk of its hyperplasia and polyps is increasing.
There are also cases when on the supposed days of monthly there comes a small daub, then again a delay. But scanty menstruation with ovarian cysts are much less common than abundant.

Causes of failures and deviations
So why do failures occur? Education itself does not affect the nature and amount of excreta. The thing is that similar cysts almost always additionally allocate a portion of hormones - estrogens, gestagens, and in the case of malignant - even androgens. This brings changes in the work of the pituitary, hypothalamus and ovaries, and as a result, failures of a different nature - delays, bleeding, etc.
In 90% of cases after removal of the tumor on the ovaries, the menstrual function normalizes, especially if the hormonal therapy is correctly selected.
Ovarian cyst is a serious condition that requires a woman to carefully perform all prescriptions of the physician. After all, until the moment of removal and histological investigation, one can never be sure that this is a benign entity. Against the background of cysts, there are often various irregularities in the menstrual cycle that occur when they are removed. But only the expert can finally understand the causes of failures.

 We recommend to read an article on the monthly for polycystic ovaries. From it you will learn about the disease and its effect on the monthly, duration and regularity of the menstrual cycle, the methods of diagnosis and treatment.
We recommend to read an article on the monthly for polycystic ovaries. From it you will learn about the disease and its effect on the monthly, duration and regularity of the menstrual cycle, the methods of diagnosis and treatment.