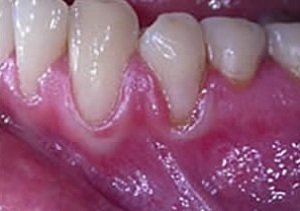
 Desmodontosis( periodontitis, juvenile periodontitis) is a serious and very rare disease in which a patient lyses periodontal tissue. It is characterized by a chronic course, lasting for many years and occasionally exacerbated.
Desmodontosis( periodontitis, juvenile periodontitis) is a serious and very rare disease in which a patient lyses periodontal tissue. It is characterized by a chronic course, lasting for many years and occasionally exacerbated.
The first exacerbation of the disease usually occurs at the age of 2-3 years, and the second - at 9-10 years.
The etiology and pathogenesis of desmodontosis remains unknown to this day, but scientists suggest that pathology is inherited by autosomal recessive type( the probability of transmission of disease in the presence of one healthy parent is small).Also today it is not known how to save a child from periodontal disease.
Contents
- Forms of the disease
- Clinical picture
- Diagnostic methods and criteria
- Treatment and prognosis
Forms of the disease
Dentists distinguish two forms of desmodontosis:
- localized - the periodontal lesion does not occur throughout the oral cavity, but only in the area of the incisors and the first permanent molars;
- generates - the pathological process involves the periodontium in the entire oral cavity.
The latest form of the disease is the most dangerous. With her, the patient loses all his teeth by the age of 15.
Clinical picture
Patients suffering from juvenile periodontitis, from birth have poor immunity. They often suffer from acne, furunculosis and nonspecific pneumonia. The skin is usually pale. 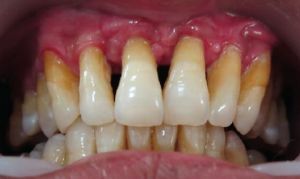
The first symptom of desmodontosis is the appearance of excessive mobility of teeth combined with a change in their position( with places in the oral cavity sufficient).In the future, with an unchanged appearance of the gums, a very deep gingival pocket is formed in a person.
After a while, an inflammatory process joins all of this. At this stage, juvenile periodontitis becomes similar to periodontitis.
In this case, the patient retains the characteristic features of the pathology: the absence of pain during intake of hot, cold and sweet food, the roots remain covered with plaque, and caries are absent. Quite often, patients have hypoplasia of enamel.
After removal of the tooth, the gum is healed easily and quickly enough.
Periodontalysis is often accompanied by dyskeratosis on the palms and soles of the feet. Hyperkeratosis can be as pronounced and spread from the palms to the elbow joint, and insignificant and manifest as a slight dryness and roughness of the skin.
Diagnostic methods and criteria
Diagnosis of pathology occurs on the basis of patient complaints, examination and the results of X-ray examination, laboratory blood analysis.
 The latter almost always shows a slight decrease in the amount of hemoglobin. In addition, disproteinemia can be observed by increasing the level of globulins in combination with a decrease in albumin blood.
The latter almost always shows a slight decrease in the amount of hemoglobin. In addition, disproteinemia can be observed by increasing the level of globulins in combination with a decrease in albumin blood.
In this case, some patients have a flattening of the sugar curve and there are slight deviations in the metabolism of tryptophan. Any changes that make it possible to characterize the pathology formed are not found.
With a localized form of the disease, periodontal damage always occurs symmetrically. The x-ray image clearly shows osteoporosis and destruction of the alveolar bone, which is of limited or diffuse nature. These changes usually do not correspond to the clinical picture.
Treatment and prognosis
The prognosis of this disease is unfavorable. It is completely impossible to get rid of him. Treatment of desmodontosis is exceptionally symptomatic. As a rule, its essence is as follows:
- The patient is regularly held professional dental cleaning in the dentist's office. During it, the tooth stones are removed and the surface of the teeth is leveled. The procedure is carried out using a sandblast or ultrasound machine.
- The patient is taught the rules of hygienic measures in the oral cavity.
- The patient is explained what foods( tea, coffee, red wine) and pathological factors( smoking) can cause rapid formation of plaque on the teeth.
- In the event of an inflammatory process, baths and applications with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory substances are prescribed. In advanced cases, antibiotics can be used in tableted form.
- To accelerate the process of tissue regeneration in the oral cavity, various keratolytic agents are recommended( rose hips or sea buckthorn oil, Solcoseryl paste, AEVit vitamins).
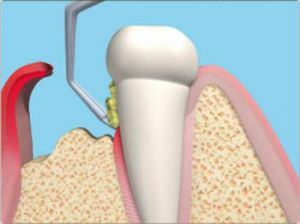
- Use of drugs and dietary supplements that strengthen the body as a whole. These include various vitamin-mineral complexes, adaptogens, immunostimulants, antioxidants and agents for the normalization of metabolic processes.
- When filling the gingival pockets with pus, curettage, depulpation of the teeth and the introduction of drugs that trigger the process of bone repair are performed.
Regardless of the stage of development of the disease, the patient is recommended to use the means that reduce bleeding gums. In addition, after each intake of 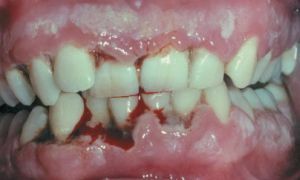 food mouth can rinse with infusion of sage or chamomile. This will help to destroy the pathogenic microflora and to remove the inflammatory process.
food mouth can rinse with infusion of sage or chamomile. This will help to destroy the pathogenic microflora and to remove the inflammatory process.
All this time the patient must comply with a strict diet, the essence of which is the total refusal of hard and rough food.
If the full loss of teeth has already begun - orthopedic treatment is performed. With complete loss of teeth, a removable or non-removable denture( upper and lower jaw) is installed in the oral cavity, and in the case of partial teeth - bridges.
