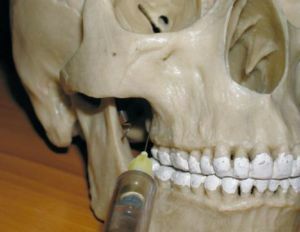
 In tuberal anesthesia, the posterior upper lunar and alveolar nerves that participate in the formation of dental plexuses are blocked.
In tuberal anesthesia, the posterior upper lunar and alveolar nerves that participate in the formation of dental plexuses are blocked.
This anesthetic is made for the possibility of painless interference in the area of the upper molars, more known to people as molars.
Also tuberal anesthesia is included in the complex of possible options for blocking the nervous activity in the place of the body where the operation will be performed. Therefore, this type of anesthesia can occur under a different name - conductive anesthesia or peripheral anesthesia.
Contents
- Anesthetic area
- Restrictions on the use of
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Preparations and instruments
- Extraoral introduction of anesthetic
- Intraoral method
- Possible consequences and dangers
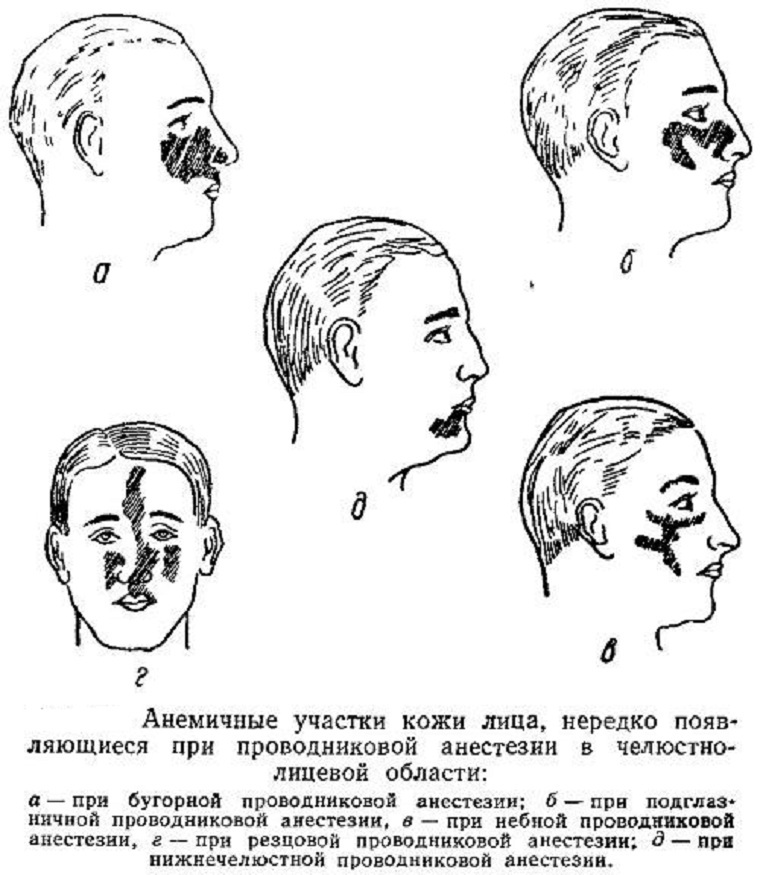
Anesthetic zone
This type of anesthesia has an effect on the areas from the gums of the first small molar to the gums of the first largetooth. The needle is inserted into the depth between the optic nerve and the thickness of the fat body. With some features of the innervation of this part of the jaw, it is possible to spread to a larger, or vice versa, smaller area.
Anesthesia is administered near the alveolar nerve, which is located on the posterior surface of the upper jaw bone. Anesthesia is exposed to the mucous membranes of neighboring areas, the posterior part of the alveolar process and the molars themselves, that is, the molars.
Restrictions on the use of
Conductive anesthesia is contraindicated for use in people who have inflammatory processes and bruises at the site of application. In such circumstances, use alternative methods of introducing a substance or change the method of anesthesia.
Also contraindicated in people who are allergic to certain types of anesthetics. In this case, an allergic reaction to the potent anesthetic used in this procedure is possible. An unfavorable allergic reaction appears rarely - a chance of occurrence of about 0.00002%.
Advantages and disadvantages of
The main advantage of this technique is clear consciousness with no pain. Modern medicine uses such methods of tracking the location of the needle and nerve:
- Ultrasound .Special ultrasound equipment allows you to see the exact position of the needle inside the bone of the upper jaw. Visualization of the whole process makes it easier for the doctor to solve the problem, providing an accurate determination of the location of the alveolar nerve. This reduces the chances of injury.
- Neuroimmimator .It makes it possible to determine the position of the nerve, by tracking the distance of the needle from the selected nerve trunks. Used in conductive anesthesia, as a method of safe localization of nerve plexuses.

With tuberial anesthesia, even despite the current practice of facilitating this procedure, there is a high chance of damage to nerves, rupture of blood vessels, getting the drug into the blood vessels.
The practice of using ultrasound and neurostimulants is not universally used. Anesthesia is often done blindly, relying only on the possible location of the nerves.
Drugs and tools
The syringe and dental spatula are used by the doctor. Injection of local anesthetics is made:
- Lidocaine .This substance has a low price segment and it is sold as a solution of low concentration - 1-2%.Lidocaine
 is contraindicated in people who have liver problems.
is contraindicated in people who have liver problems. - Trimecaine .More effective than lidocaine, it acts faster and more durable. However, there may be side effects - dizziness, nausea, weakness.
- Ultracaine .Highly effective foreign analogue of domestic local anesthetics. Has a long period of time and has a high analgesia, which allows the drug to be used even in orthopedic dentistry.
Extraoral injection of anesthetic
Patient's head turns sideways. The zone of anesthesia is treated with alcohol, then the left hand probes the surface of the cheek-alveolar ridge. A thumb and forefinger stretches the skin and presses soft tissues to the jaw.
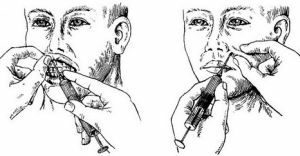 Next, at a right angle, a needle is inserted along a straight trajectory, driven under the cheekbone to a depth of 2-2.5 cm. Then, the syringe is stretched slightly, the blood gets caught. If there is no blood in the syringe, an anesthetic is slowly injected. After that, the injection site is massaged with a finger. Anesthesia occurs within 5-10 minutes.
Next, at a right angle, a needle is inserted along a straight trajectory, driven under the cheekbone to a depth of 2-2.5 cm. Then, the syringe is stretched slightly, the blood gets caught. If there is no blood in the syringe, an anesthetic is slowly injected. After that, the injection site is massaged with a finger. Anesthesia occurs within 5-10 minutes.
The patient may have an unpleasant tingling in the area of the injection, numbness. When grazing a large blood vessel, a hematoma is formed. If the injection has been done at insufficient depth, then anesthesia will not have an effect, since the substance will simply dissolve in the fatty layer.
Intraoral method
Patient's mouth should be relaxed and half open. The cheek is pushed aside by a dental spatula. The injection is made just below the junction of the mucosa of the cheek and the shell of the alveolar process. The needle is inserted over the second molar, pressed into the bone and directed upward along the surface of the upper jaw.
In the event of a deviation from the trajectory, the risk of damage to the internal group of large blood vessels is high. The syringe is deepened in the same way as with the extraoral method, by 2-2.5 cm. The further procedure does not differ from the extraoral method.
Tuberial anesthesia according to Egorov:
Possible consequences and dangers
Tuberial anesthesia is the most traumatic risk due to the high probability of mechanical damage to blood vessels and nerves. 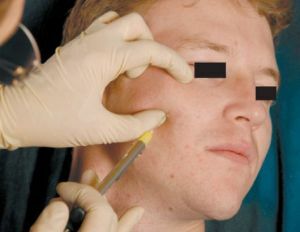
If the needle is pressed further than the required distance, the venous plexus will be damaged. Damage to these blood vessels forms a large hematoma.
Also, in case of such damage, an anesthetic may enter the blood, which is a great danger in view of an instant increase in the toxicity of anesthetics. It is fraught with loss of consciousness, shock, convulsions.
In case of damage to the alveolar nerve itself or directly to the nervous plexuses, neuropathy develops. Neuropathy - mechanical damage to the nerve, which disturbs its operation. Signs when it is damaged:
- numbness;
- pain in the anatomical area of the injection;
- rudimentary reflex( sensation of "goosebumps") when injected;
- muscle weakness.
Restoration of the full working capacity of a damaged nerve takes time from several months to six months, less often about a year. The practical frequency of cases of development of neuropathy due to incorrect application of conductive anesthesia is about 1%.
Modern medicine uses either advanced methods of conducting this procedure, or other methods of anesthesia when it is necessary to surgically interfere with the space of molars of the upper jaw.
