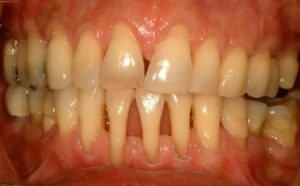
 Parodontium refers to gum retaining tissues, bones, ligaments and mucous membranes.
Parodontium refers to gum retaining tissues, bones, ligaments and mucous membranes.
The development of periodontal disease is associated with periodontal damage. As a rule, this disease is of a dystrophic nature and manifests itself in adulthood.
Contents
- Mechanism of the disease
- Causes of the development of the disease
- Symptoms and signs of the disease
- Stages of the development of the disease
- Treatment is difficult but possible
- Surgical intervention
- Orthopedic treatment
- Physiotherapy
- Laser therapy
- A word for patients
- Preventive measures
- Cost of treatment
- Frequent
Mechanisms of the development of the disease
Periodontal disease disrupts nutrition of periodontal tissues, as a result of chegincorrect exchange occurs proteins and mineral salts. As a result, tissue growth and regeneration are delayed.
Such changes are associated with a chronic non-inflammatory course of the disease, leading to atrophy called alveolar dentition of dental cells. In the absence of treatment, pathology can result in a violation of the mobility of the teeth and their loss.
Characteristic sclerotic changes in bone tissue are visible on the results of X-ray examination. On the pathological violations indicates the presence of a fine-celled bone pattern and reduced bone marrow spaces, foci of osteoporosis. Also, the decrease in the height of the interdental septa is clearly noticeable.
Causes of the development of the disease
To date, the exact cause of the development of periodontal disease is not completely determined. But it is possible to list the following factors that increase the risk of development of pathology:
-
 hereditary predisposition of ;
hereditary predisposition of ; - the presence of the pathological pathologies contributing to the dystrophic processes in the form of diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, abnormalities of the digestive tract, changes in the reactivity of the organism, hypovitaminosis;
- disruption of nutrition surrounding the teeth of tissue and blood circulation in affected areas as a result of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels;
- effect on the periodontium of pathogenic microorganisms .
As the main possible cause, a cluster on the gums and teeth of bacterial plaque is considered as a colorless sticky film.
In case of untimely removal of such a deposit as a result of its hardening, a porous coarse substance - tartar - is formed.
Symptoms and signs of the disease
For periodontal disease is characterized by non-inflammatory character with a gradual exposure of the necks of teeth as a result of destruction of the surrounding tissues of the tooth. At the same time, a good fixation of the teeth persists for a long time.
Because of the slow development of pathology, the initial stage proceeds without the appearance of pain or other unpleasant sensations. However, against the background of asymptomatic development of the disease, the structure of the periodontal tissue is disrupted.
Therefore, attention should be paid to the following changes:
-
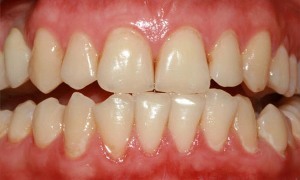
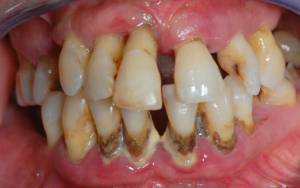
In the photo, the initial stage of the
disease is the pallor of the gums without signs of inflammation;
- gradual retraction of gum tissues and exposure of the necks of the teeth( the elongation of the tooth is visually noticeable);
- appearance of lesions of non-carious type, namely, erosion of enamel, wedge-shaped defect, tooth erasure;
- formation of minor dental deposits.
These signs, as a rule, are not accompanied by gingival hemorrhage. Pathologies may be accompanied by disruption of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems.
As the disease develops, the following symptoms begin to appear:
-
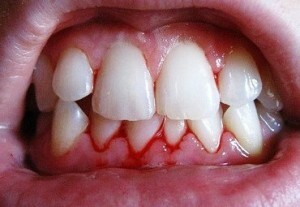 sensation of burning and itching, pain;
sensation of burning and itching, pain; - pulsation in the gums;
- slight swelling of the gums;
- bleeding in the process of eating and cleaning teeth;
- appearance of bad breath;
- fan-shaped divergence of teeth, their loosening and prolapse.
A so-called parodontic tooth is formed - an absolutely healthy tooth with a bare neck, which can not perform its function due to loosening. In the absence of treatment, signs of inflammation in the soft tissues of the oral cavity up to sepsis can be added.
The causes and symptoms of periodontal disease will be told by the dentist:
Stages of the development of the disease
Dentists determine the degree of development of this pathology, based on the depth of the gingival pockets and estimated in the gum bleeding index, as follows:
- 1 point - bleeding point appears during the sensation of the apexpapillas between teeth;
- 2 points bleeds the contact line of the gingival papilla and tooth;
- 3 points - bloody contents collected in the interdental space;
- 4 points - the gingival papilla bleeds profusely, several dental spaces and the gum margin fill with blood.
Depending on the condition of the gums, the following stages of periodontal disease are distinguished:
- Initial .The gums become swollen, the sensation of itching appears, the area of the tooth becomes too sensitive. The ingestion of solid foods can lead to bleeding.
- First .The teeth are slightly mobile, but the dentition is not broken. There is an exposure of the necks of the teeth and the appearance of tartar, a slight thickening of the gums and their puffiness near the tooth.
- The second .The roots of the teeth are strongly exposed, which leads to the formation of a dentogingival pocket with serous-purulent exudate and blood. There is strong mobility of the teeth in the lateral direction, slight bleeding of the gums, the mucosa of which is stained with a bluish tinge. In the course of the radiographic examination, a shortening of the bone tissue of the root is detected in half.
- Third .The roots of the teeth are exposed half the length, while the open part is covered with solid deposits. Deepened
 dentogingival pocket, with pressure on the edge of the gums appears purulent contents. The mobility of teeth is aggravated. The amount of bone tissue of the tooth is less than half.
dentogingival pocket, with pressure on the edge of the gums appears purulent contents. The mobility of teeth is aggravated. The amount of bone tissue of the tooth is less than half. - Fourth .Fixation of the tooth is carried out only due to soft tissues due to the complete atrophy of the bone support. The depth of the dentogingival pocket reaches the apex of the root, the teeth can be rotated in any direction. For severe stages of the disease is characterized by the development of periodontitis, which is an inflammation of the gum tissue.
Treatment - difficult, but possible
Is this pathology treated? Sadly, it is not possible to effectively cure periodontal disease in most cases. However, thanks to modern technology, it is still possible to partially restore the gum.
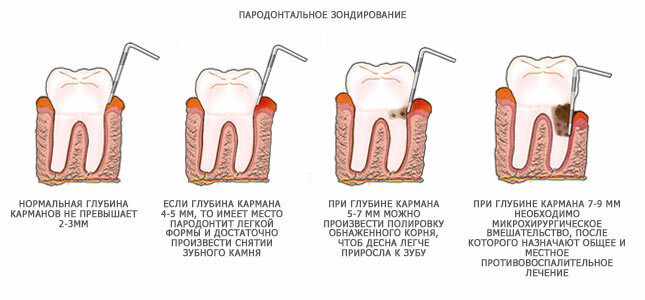
Treatment depending on the depth of the periodontal pocket
Among the treatment activities are widely distributed:
- Gum massage, physiotherapy , symptomatic treatment for pain relief, hypersensitivity of teeth.
- Also, prescribe preparations that stimulate the immunity of , strengthen the body as a whole and contribute to the improvement of regenerative processes. At the discretion of the dentist, consultations of the neurologist, immunologist, endocrinologist and therapist can additionally be prescribed.
- Due to the connection of periodontal disease with a significant decrease in immunity, treatment of this pathology implies the mandatory reception of of vitamin complexes and immunomodulators , which restore protective functions and increase the body's resistance. The choice of drugs is due to the severity of the pathological process. Also, with acute periodontal disease, antibiotic therapy can be used to eliminate the inflammatory process.
- High efficiency is provided by administration of drugs into the gum through injection of .As preparations, extract of aloe, FIBS( shown in case of acute inflammatory process), Lydase is chosen. Usually the course consists of 20-25 injections, administered with a daily interval.
-
 Additionally, gaseous oxygen can be injected into the gingival tissue. The procedure is carried out in dental clinics to improve blood flow in the tissues.
Additionally, gaseous oxygen can be injected into the gingival tissue. The procedure is carried out in dental clinics to improve blood flow in the tissues. - Also, ribonuclease, methyluracil, antitoxic serum, biogenic stimulants may be prescribed.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment for periodontal disease is often a priority. For restoration of tissues, substitute materials, membranes and regenerating cell cultures in the form of fibroblasts, platelet growth factor, stem cells are used.
Currently, the most widespread membrane technology, in which the interdental spaces are filled with self-absorbable membranes, which promote the rapid "engraftment" of the attached structures and the early regeneration.
The main types of surgical intervention are:
-
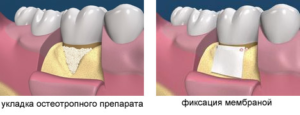 Curettage. Granulation formations are removed under the gum, gingival pockets are eliminated, into which synthetic bone substitutes are introduced.
Curettage. Granulation formations are removed under the gum, gingival pockets are eliminated, into which synthetic bone substitutes are introduced. - Patchwork operation ( pictured right).
Simultaneously with the activities typical for curettage, remove the thin adjacent to the tooth gum layer, in which there were pathological changes. Before both types of interventions, anti-inflammatory and antibiotic therapy is carried out.
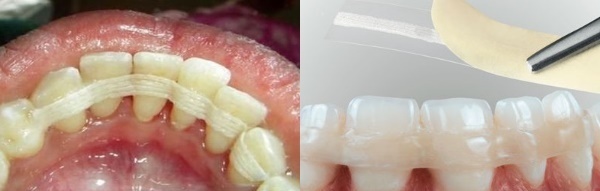
Orthopedic treatment
One of the common methods of treatment of periodontitis is splinting or installation of prostheses. To fix the tires to loose teeth, use crowns, pins, rings and caps, which serve to limit mobility.
This fixation of the teeth along with the prosthesis allows you to distribute the gum load and make up for the loss of the lost teeth.
Use of physiotherapy
Among the variants of physiotherapy used for periodontosis to improve the filling of periodontal tissues with oxygen and nutrients, it is possible to extract electrophoresis, treatment of affected areas with ultrasound and laser treatment, which should be considered in more detail.
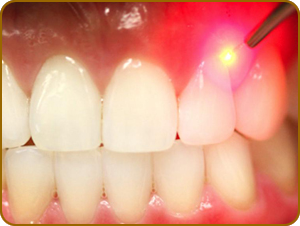
Laser therapy special feature
A special dental laser can effectively fight infection spreading in the gingival pockets, cleaning them, activating the processes of tissue healing and their regeneration, which contributes to the restoration of the periodontal function.
Laser treatment is indicated in the following situations:
-
 gum bleeding when brushing teeth;
gum bleeding when brushing teeth; - change in the color of the gums and the appearance of plaque on them;
- appearance of sensation of itching and soreness of the gums;
- presence of periodontal pockets;
- exfoliation of gum tissue from tooth;
- appearance on mucous signs of an abscess;
- frequent stuck food in the interdental spaces.
Thanks to the use of the laser, the following results can be achieved:
-
 destruction of pathogenic microflora;
destruction of pathogenic microflora; - evaporation of dead tissue sites;
- stop bleeding;
- sterilization of the periodontal pocket;
- acceleration of the regeneration process;
- removal of calculus and smoothing of the gingival surface.
At the same time, healthy gum tissue and tooth enamel are not injured, so recovery is as quick as possible.
Laser therapy can be performed according to one of three methods:
- closed curettage of ( the most remote places of periodontal pockets are cleaned, after which a dressing is applied to the treated areas);
- gingivectomy ( used if gingival tissue grows and false pockets are formed);
- de-epilation of ( due to slowing down of the restoration process, the root surface is smoothed and the damaged tissues are completely restored).
A word for patients
The effectiveness of laser treatment of periodontal disease can be judged by the following reviews.
For a long time I suffered from periodontal disease, so the situation was aggravated by loosening of the teeth. Specialists, who were treated, offered to completely rip out teeth, perform prosthetics, and only one doctor offered laser treatment.
During the procedure, the anti-inflammatory agent produced in Germany was embedded in the periodontal pockets, after which the upper tissues were laser treated.
After 5 sessions the pain was gone, the bleeding stopped, the mobility of the teeth decreased, so eating stopped being an anguish. Now I conduct such procedures every year for several sessions.
Elizabeth, Moscow
The circumstances demanded laser therapy. It should be noted that the high cost of such treatment is fully justified. During the procedure, there is no uncomfortable sensation, and the result is pleased with the effectiveness.
Andrey, Kirov
Preventative measures
To prevent periodontal disease include:
-
 systematic examinations at the dentist;
systematic examinations at the dentist; - rational nutrition with the intake of vitamins;
- quality oral hygiene;
- regular performance of special gymnastics for teeth.
Separately, it should be noted the importance of the presence in the diet of a complex of micronutrients affecting the periodontal state, which include:
- Copper ( present in sufficient quantities in wheat, liver, potatoes, coffee, tea, lentils, bakery products and is well digested with the simultaneous use of cottage cheese, sour cream, prunes, soy, egg yolks, cheese).
 Poor absorption of copper is observed with excessive intake of vitamin C.
Poor absorption of copper is observed with excessive intake of vitamin C. - Iron ( rich in beef, dark poultry meat, buckwheat, liver, apples).It is well absorbed when there are vegetables, nuts, leeks, peas in the diet. Disrupts the absorption of excessive consumption of tea, foods rich in calcium, phosphorus.
- Zinc ( present in cereals, beef, egg yolks, oysters, beans, cheese).
Cost of treatment
Laser therapy of parodontosis is the highest cost. The price varies in a fairly wide range - from 4 to 10 thousand rubles or more - and depends on such criteria as the scope of the intervention, the severity of the process, the status of the medical institution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What interests people who have experienced this disease.
Can I completely cure the periodontal disease?
The answer to this question can only be affirmative if complex therapy is applied from the very beginning of the development of the process. In the case of diagnosis of periodontal disease in the first and subsequent stages should be prepared for periodic exacerbations and the need for permanent preventive measures.
Is this pathology safe?
Parodontosis itself is not contagious, but if pathogenic microorganisms get into the oral cavity at the initial stage of the disease development, a significant aggravation of the situation may occur.
