In the article - about the types of bleeding and ways of stopping them. This knowledge can save someone's health and life.
Contents
- Types of bleeding and first aid for bleeding
- ( adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []). Push({ });
- General algorithm for emergency care for bleeding
- First aid for bruises, fractures and bleeding.
- VIDEO: First aid for fractures. Training film
- Emergency care for capillary bleeding
- Venous bleeding, signs and first aid
- First aid for arterial bleeding
- Assisting with nosebleeds
- VIDEO: How to stop nasal bleeding?
- First aid for gastric bleeding. First aid for intestinal bleeding
- How to properly assist with bleeding: tips and reviews
- VIDEO: First aid for bleeding
How to provide emergency first aid for bleeding, everyone should know. After all, from the speed and adequacy of actions in some situations, which, unfortunately, are not uncommon, his own life or the life of one who is near can depend.
Types of bleeding and first aid for bleeding
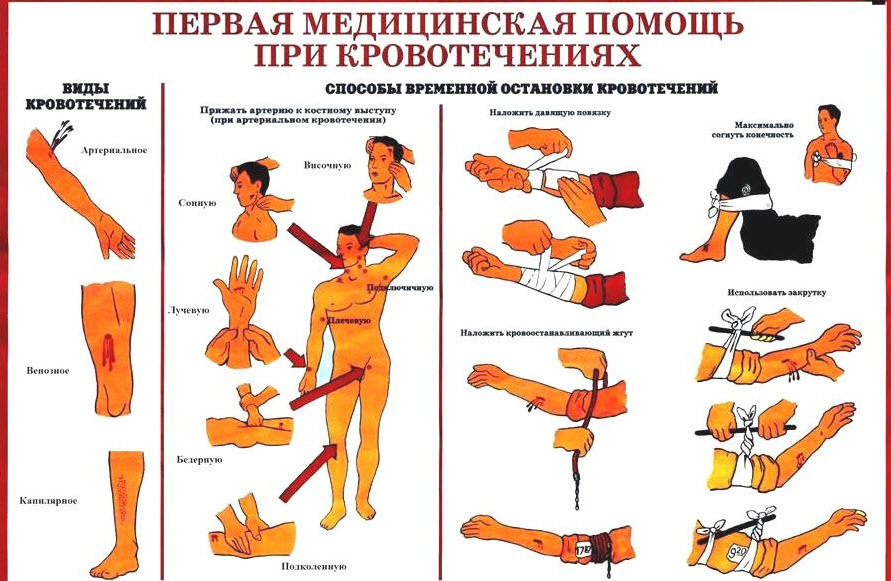 Before giving first aid, it is necessary to determine the type of bleeding
Before giving first aid, it is necessary to determine the type of bleeding Bleeding refers to the flow of blood from a vessel or heart because of their damage. Usually, it happens due to trauma or internal illness.
Classification of bleeding is carried out by several criteria.
By which vessel is damaged, distinguish:
- Arterial bleeding occurs when the integrity of the walls of large blood vessels, carrying blood and arteries to tissues and organs is increased. Such damage to the medical profession is considered the most dangerous, because because of the higher pressure in the arteries, the body loses blood too intensively. It is colored in a scarlet color, comes out throbbing, fountains
- Venous bleeding occurs when the integrity of vessels carrying blood enriched with carbon dioxide, veins is violated. This kind of trauma can be distinguished by the dark cherry color of the blood, which evenly flows out of the damaged vessel
- . Capillary bleeding is a weak blood loss due to disruption of the integrity of small vessels. As a rule, it does not pose a threat to life, but is the most common type of
IMPORTANT: It is possible that when a trauma occurs, a violation of the integrity of several types of blood vessels occurs at once. Then there is a bleeding called mixed
. Depending on where the blood flows from the damaged vessel, bleeds are different:
- external - blood enters the environment
- internal - blood enters the body cavity or inside the hollow organ( eg hemothorax, in whichblood accumulates in the pleural cavity)
The following several techniques should be known to everyone. With their help, you can stop bleeding.
- Maximum limb bending. It is used in the case when the damage to the blood vessel happens below any mobile joint, usually an elbow or knee joint. When flexing the joint, a natural clamping of the vessel occurs
- Direct pressure on the wound. It is used for the purpose of artificial restoration of the integrity of a small artery, vein or capillaries. In extreme conditions, a pressure bandage is made from improvised means - a bandage, folded several times, gauze, but more often from ordinary laminated fabric
- Overlapping the harness. This assistance is provided before the arrival of the physician to the victim with severe damage to the veins or arteries, usually on the extremities of the
IMPORTANT: The tourniquet may have a different design. To impose it it is necessary skilfully
The general rules of imposing of a roof-fixing plait-design are that:
- A blood-stopping procedure of this type is performed only with arterial bleeding
- The position of the damaged artery may be different, but the tourniquet is always superimposed between this place and the heart.
- There should be a layer between the harness and the body. If there is no clothing there, a piece of cloth or bandage
- should be placed under the harness. There should be nothing above the harness. Physicians should always see it
- It is possible to squeeze the artery with a tourniquet for no more than half an hour. As a rule, under it put a piece of paper with the designation of the time of imposition. If this is not possible, this time is written by the victim's blood directly on his body
- If for half an hour the physicians do not arrive, the tourniquet is weakened( for 10-15 minutes), at this time they perform blood-resurfacing procedures of a different kind. After the tourniquet is again tightened
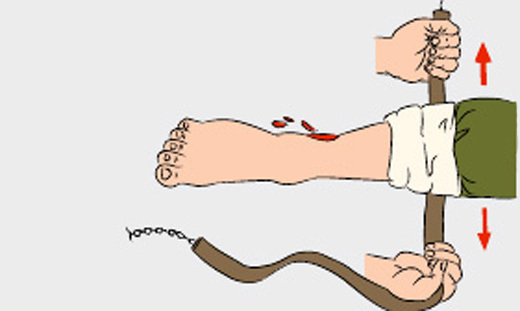
 Attaching the harness to the lower extremity
Attaching the harness to the lower extremity General algorithm for emergency relief for bleeding
If a person finds himself in a situation where it is necessary to help the patient with bleeding, the following should be done:
- Evaluate the situation: try to find out what constitutes a source of danger,whether it is liquidated
- Take measures to protect yourself and the victim in the event of a source of danger
- Try to assess the severity of the conditionostradavshego: to determine whether it is life threatening anything other than bleeding. For example, a patient may have heart or respiratory arrest, pneumothorax, open fractures, etc.
- Try to determine if the victim has internal bleeding other than external
- Attempt to determine the type of bleeding and, depending on him, the way of assisting. If the blood is low, most likely, the integrity of the capillaries is broken, it is enough to rinse and disinfect the wound, put a bandage on it. If there is a lot of blood, it is dark and flowing, you can suspect a venous bleeding. It is necessary to impose a bandage and hand over the injured physicians for further assistance. If there is a lot of blood, it is scarlet and pulsating, it determines a life-threatening arterial bleeding. In order to stop it, a tourniquet is placed and waiting for professional medics.
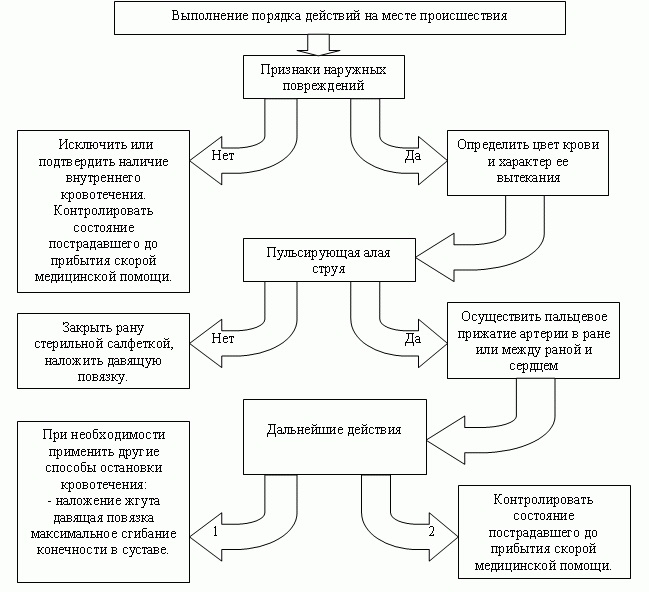 General algorithm for emergency care for bleeding
General algorithm for emergency care for bleeding
IMPORTANT: Indications of internal bleeding should be known to everyone. The victim begins to feel weakness suddenly or on an increasing, his head is spinning, he wants to drink, flies before his eyes, there may be a faint. Skin covers of the affected pale or cyanotic, it can become covered with a cold sweat. Pulse and pressure in the victim weaken, with the breathing quickening
First aid for bruises, fractures and bleeding.


VIDEO: First aid for fractures. Training film
Emergency care for capillary bleeding
Capillary bleeding often becomes a result of domestic trauma. It happens in a child, for example, who fell and squeezed his knee. As a rule, with this type of bleeding, small subcutaneous capillaries are damaged. Injury is not a danger to human life.
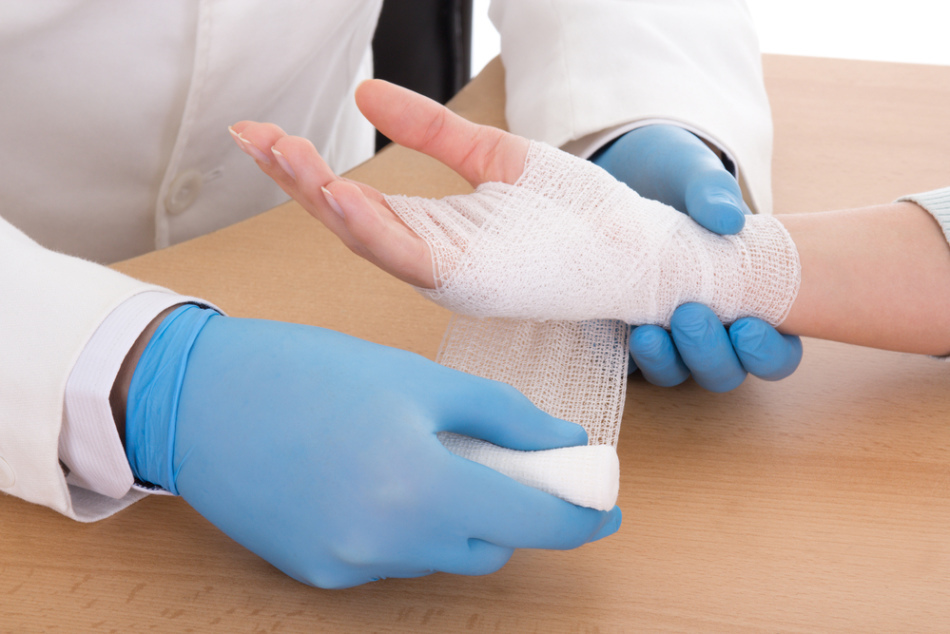 As a rule, capillary bleeding can be stopped easily.
As a rule, capillary bleeding can be stopped easily. IMPORTANT: The very capillary bleeding is not dangerous. But there is a risk of infection of the wound. Before applying the dressing, the place of damage must be disinfected.
Algorithm for helping with capillary damage, wound:
- is washed with a flowing, necessarily pure water
- is treated with an antiseptic - alcohol, vodka, hydrogen peroxide, calendula alcoholic infusion, other
- covered with a bandage of pure bandage or gauze
. As a rule, the doctor's help in bleeding thiskind of superfluous. There is a need to make a visit to the clinic only if the infection still got into the wound.
Venous bleeding, signs and first aid
Smooth, pulse-free dark blood flowing out of the wound is a sign of venous bleeding.
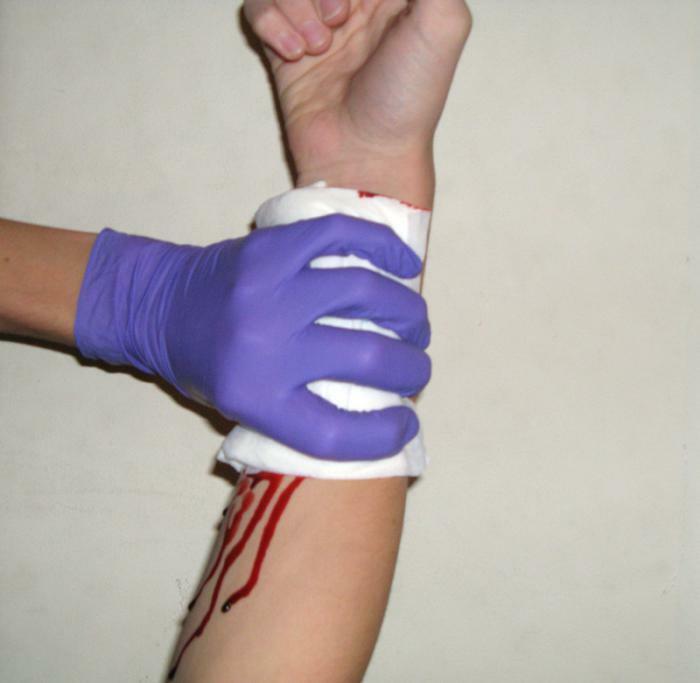 In venous bleeding, a pressure bandage is applied.
In venous bleeding, a pressure bandage is applied. It is necessary to assess how much the vein is damaged.
IMPORTANT: If a large vein is damaged, a tourniquet is applied. Be sure to lower the place of injury!
In case of violation of the integrity of the medium vein, a pressure bandage is sufficient.
- The injured person is seated or laid in such a way that the injured limb is raised
- If possible, free the damaged area from visible contaminants
- Apply a pressure bandage
- Wait physicians
First aid for arterial bleeding
It is necessary to stop scarlet blood from the artery by a fountain very quickly.
- The injured person is seated or laid so that the injured limb is raised
- If possible, try pressing the artery with your fingers. The vessel must be pressed directly to the bone, otherwise blood loss will continue
- Apply a tourniquet. It can be improvised - a belt, a towel, a cloth flap
- Wait doctors
IMPORTANT: The tourniquet can not be overstayed longer than the allotted time. Otherwise, blood circulation may be disturbed in the limb, necrosis will begin.
Assisting with nasal bleeding
Nasal bleeding may occur due to many circumstances. Most often the cause is:
- high blood pressure
- blood vessel integrity disorder
- blood composition disorder
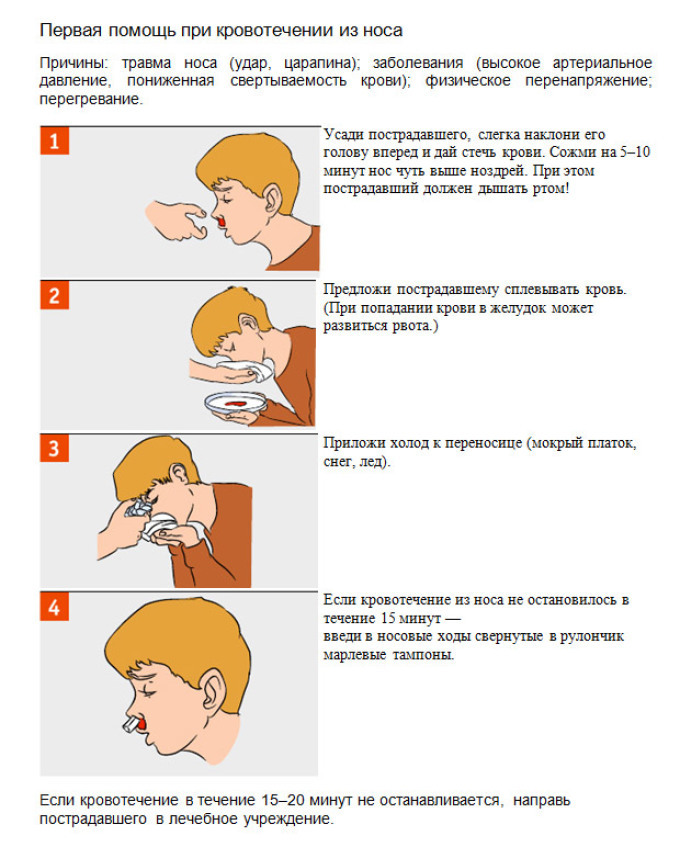 Assisting with nosebleeds.
Assisting with nosebleeds. To determine if bleeding from the nose was physiologically, traumatic or caused by any disease, only a physician can. Everyone should know how to render first aid in this situation.
- The victim is planted so that his head and body are slightly tilted down
- If the cause of the bleeding is clearly not the injury of the nasal skeleton, slightly press the wings of the nose for 5 minutes
- Insert a cotton swab soaked in pure water or 3% perhydrol
- into the nasal passage. Ifbleeding is strong, you can attach cold to the nose area - ice from the freezer, a cold bottle, even frozen vegetables. It is necessary to take care of that in a nose thus the infection has not got. Cold applied to a maximum of half an hour
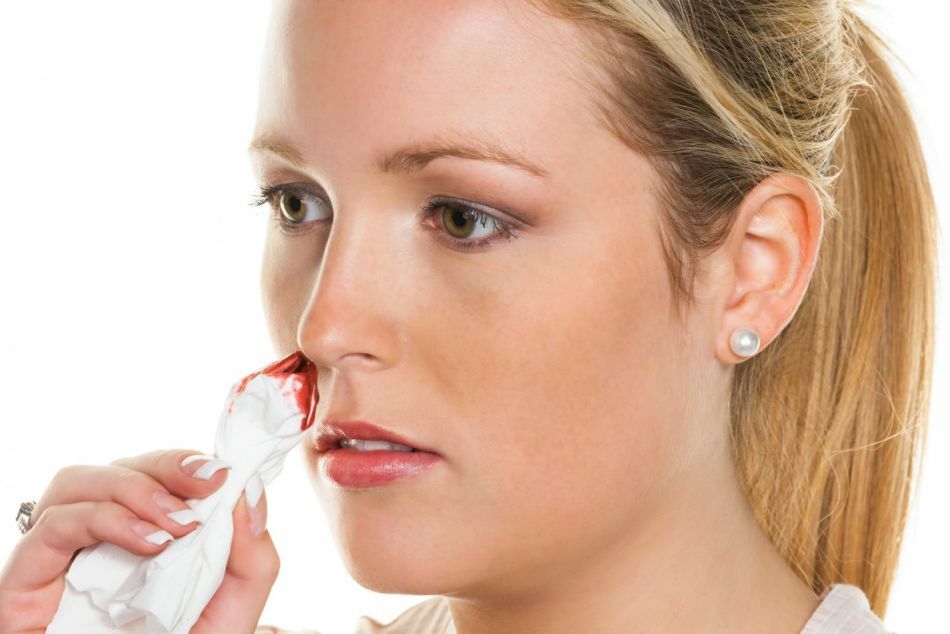 With nosebleeds, the head can not be thrown back.
With nosebleeds, the head can not be thrown back. IMPORTANT: It must be ensured that the blood from the nose does not flow through the nasopharynx. If this occurs, the victim may vomit. That's why with nosebleeds you can not toss your head or lie on your back.
If the blood from the nose does not stop within 30 minutes, you need to call an ambulance.
VIDEO: How to stop nasal bleeding?
First aid for gastric bleeding. First aid for intestinal bleeding
Gastrointestinal, intestinal or gastrointestinal bleeding is a condition in which blood gets into the cavity of the esophagus, stomach, or intestine due to damage or destruction of the vascular wall of the digestive organ.
 Gastrointestinal bleeding is a very dangerous condition.
Gastrointestinal bleeding is a very dangerous condition. The severity of the condition of the affected person is determined by the following factors:
- degree of damage to the vessel wall of the
- body by the bleeding intensity
- blood pressure level
- by the blood coagulation system condition
The causes of these internal bleeding
- erosive and ulcerative diseases of the digestive tract
- varicose veins of the esophagus
- benign and malignant stomach and bowel formations
- prolonged vomiting, due to which the vessels in the stomach or esophagus burst
- injury
- foreign body in the stomach
Symptoms of bleeding in the stomach or intestines are pallor, nausea, upset stomach, feces with red or black veins, vomiting of blood, abdominal pain.
IMPORTANT: If you suspect a gastrointestinal bleeding, you must call an ambulance.
The following should be done:
- to lay the victim, to create rest for him
- to raise the patient's legs at an angle of 15 degrees
- put a cold on the stomach
IMPORTANT: In a patient with gastrointestinal bleeding, breathing and palpitation may stop, so these functions need to be monitored. A patient can not be left alone. He should not be allowed to eat or drink.
How to properly assist with bleeding: tips and reviews
The safety of life safety is studied at school. But, unfortunately, many schoolchildren are not serious about this subject, they miss lessons or are simply inattentive to them. Therefore, they do not know how to help with injuries and bleeding. Such ignorance can cost anyone health or life.
How to properly assist with bleeding should everyone know!