 Modern dentistry is impossible without anesthesia. Many types of manipulation require anesthesia. In this way, comfort is achieved for the patient and convenience for the operation of the doctor.
Modern dentistry is impossible without anesthesia. Many types of manipulation require anesthesia. In this way, comfort is achieved for the patient and convenience for the operation of the doctor.
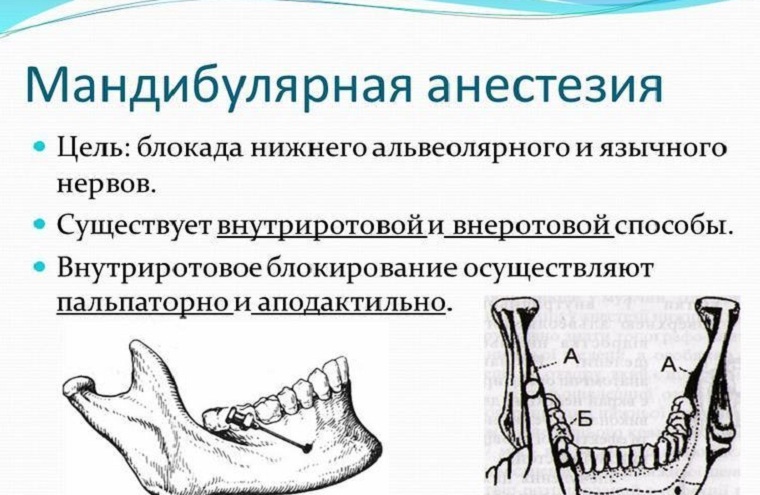
Mandibular anesthesia is a kind of conductive anesthesia on the lower jaw. As a result, the lingual and lower lunar nerves are blocked.
The technique is not simple. To accurately achieve an effective and safe result, the physician must clearly visualize all the anatomical guidelines.
Contents of
- Where is the sensitivity lost?
- Goals for use in dental practice
- Complex of available techniques
- Technique for performing the palpation method
- What complications can occur?
- Advantages and tacts of the tactile method
- Apodactile intraoral method
- Pros and cons
- Extraoral methods
- Subclavian method
- Procedure with a prick below the lower jaw
- Over-jaw method
- Possible errors
Where is the sensitivity lost?
An anesthetic zone will include:
- teeth of the half of the jaw from the side of the anesthetic procedure;
- bone tissue of the alveoli;
- the gingival mucosa;
- half of the lip;
- the tip of the tongue and the sublingual area;
- the skin of the chin area.
The purposes of application in dental practice
. To situations where the application of this type of anesthesia is necessary, all manipulations that can cause painful sensations are included in the case of treatment of the following diseases:
- caries;

- root canal treatment;
- extraction of teeth, including retinas;
- autopsy of purulent foci;
- operation to remove sequestration;
- excision of mucous hood with teething;
- removal of the cyst of the tooth;
- removal of tumors and tumor-like formations in the body or branch of the lower jaw;
- splinting of jaws in fractures.
Complex of available techniques
There are intraoral and extraoral methods of conducting mandibular conductive anesthesia. The first types are as follows:
- palpation method;
- apodactyl method;
- apodactyl method in the modification of A.E.Verlotsky.
Extraoral methods:
- subcutaneous method of anesthesia in modifications by Egorov, Uvarov, Bersh or Bershe-Dubov;
- submandibular technique;
- is a mandibular procedure.
Let's look at each method separately with photos and video explanations.
Technique for performing the palpation method
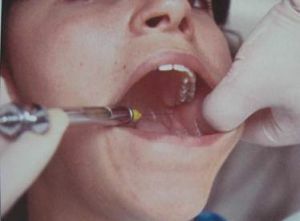 With this method, the physician first palpates the future site of the injection to determine the position of the mandibular orifice. In this area, the nerve leaves the lower jaw.
With this method, the physician first palpates the future site of the injection to determine the position of the mandibular orifice. In this area, the nerve leaves the lower jaw.
The approximate period of the onset of the effect of injection is 10-15 minutes. The duration of anesthesia depends on the amount of substance administered and can be 2-3 hours.
Technique:
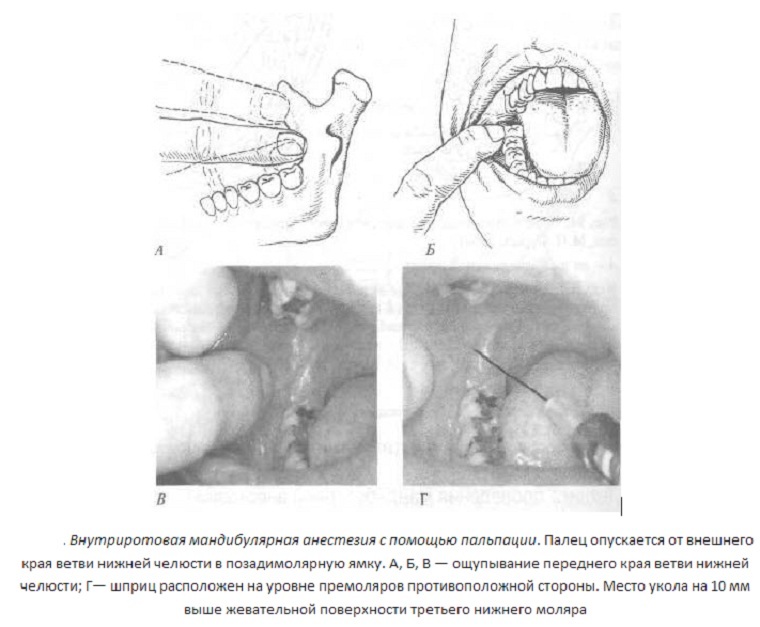
- The patient should open his mouth as far as possible.
- After this, the doctor puts the index finger behind the molars. At the same time, the inner surface of the mandible branch is felt.
- The syringe is located on the second premolar on the other side.
- The needle enters the tissue 1 cm behind the index finger and 1 cm above the teeth.
- First the injection is made 1-1.5 cm deep into the tissues. As a result, the tongue will be anesthetized first. The volume of the produced anesthetic is approximately 0.2-0.3 ml.
- Next, the needle is inserted up to the bone.
- If the doctor felt it, then it transfers the syringe to the incisors and goes 2-2.5 cm deep.
- It is compulsory to perform an aspiration test to exclude the trauma of the blood vessel. If the sample is negative, then the bulk of the anesthetic is administered.
- At the end, the needle is carefully removed from the soft tissues.
If everything went well, the patient will develop a feeling of numbness, tingling and cold on the corresponding half of the lip.
The anesthetic zone is as described above.
What complications can occur?
If the needle has entered more medially than necessary, that is, the risk of rupture of the pterygoid muscle fibers.
In case of damage to the blood vessel with a needle, there is the possibility of developing bleeding with its subsequent organization in the hematoma. In the future, an infection can join her. The result will be an inflammatory process that can not be treated on an outpatient basis.
If the vessel is damaged, besides bleeding, there is a likelihood of an anesthetic entering the bloodstream. This is fraught with the development of ischemic zones on the lips and chin. There is also a risk of systemic effects of epinephrine, which is part of the anesthetic. There is a spasm of blood vessels and increased blood pressure.
Possible damage to the very mandibular nerve. This will be manifested by a sensation of numbness that will persist 8-12 hours after anesthesia.
One of the very rare complications is the disruption of the normal operation of the face facial muscles. This is possible with damage to the branches of the facial nerve, if the technique of the procedure was grossly violated.
Advantages and disadvantages of tactile method
The following advantages of this method stand out: 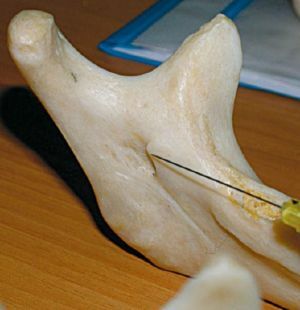
- the risk of complications is less, since anatomical landmarks are determined palpation;
- anesthesia occurs even in the most painful situations;
- long duration of anesthesia;
- completely turns off half of the jaw, which allows the doctor to engage in the work of several anatomical zones.
Cons of the palpation method:
- high traumatism in the event of a violation of technology;
- discomfort for the patient, since half of the jaw and tongue do not move;
- bite of soft tissues until the moment of departure from the action of the anesthetic;
- , even if performed correctly, the procedure can be very painful.
Apodactyl intraoral method
To use this method of anesthesia, the physician must clearly know the location of all anatomical landmarks. 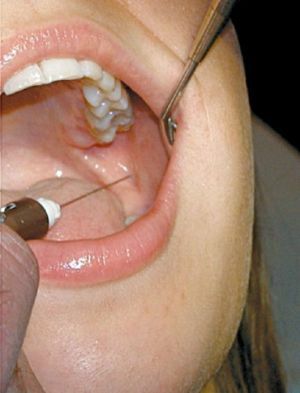
The first is the pterygo-mandibular fold that passes behind the molars of the lower jaw. It is she who is guided by the dentist in order to clearly locate the point of entry of the needle.
The duration and duration of anesthesia is the same as for the palpator method.
Technique:
- injection is made in the medial rim at the border between the upper and middle third;The
- needle should go perpendicular to the bone;
- the syringe cylinder is also located on the premolars of the opposite side;The
- needle moves 1.5-2 cm to the bone, where the first portion of the anesthetic is injected;
- then the syringe is transferred to the incisors, and the needle advances 2-2.5 cm further;
- an aspiration test is performed;
- if the sample is negative, then the remaining drug is administered.
The area of anesthesia and possible complications are the same as for the palpation method of execution.
Pros and Cons of
Positive and negative sides are almost the same as in the previous method. The only difference is a greater risk of complications, since the site of the nerve exit from the bone may not correspond to the structure of the pterygo-mandibular fold.
Apodactyl mandibular conductive anesthesia according to A.E.Verlotsky is carried out in the same way as the standard apodactyl method. The only difference is the place where the injection takes place. In this case, the needle enters the tissue in the middle between the upper and lower molars.
Visual technique for mandibular anesthesia with video explanations( first for foreign language experts, second in Russian):
Extraoral techniques for
There are several extraoral techniques for mandibular anesthesia.
Subcrown way
The first method was used by Bersche. Such anesthesia is used if there is a spasm of chewing muscles. According to his technique, 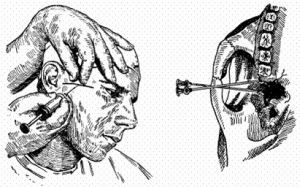 injection is carried out under the zygomatic arch, retreating 2 cm from the tragus of the ear. The depth of needle insertion is 2-2.5 cm.
injection is carried out under the zygomatic arch, retreating 2 cm from the tragus of the ear. The depth of needle insertion is 2-2.5 cm.
Uvarov's modification consists in deeper insertion of the needle to block the nerve at the site of his exit from the skull.
The technique of Dubova also differs by a deeper introduction of the needle by 3-3.5 cm.
According to the Egorov technique, the needle entry point is located 1 cm in front of the articular tubercle under the cheekbone. The needle advances to the temporal bone.
This distance is fixed by a special stopper. Then the needle is displayed several times. Further, it enters at an angle of 90 degrees to the skin at a marked depth.
Maxillary anesthesia according to Bershe-Dubova:
Technique for under-jaw incision
With this method, the doctor puts the index finger behind the mandible and the large one at the angle of the mandible. Then the needle enters the tissue, receding 2 cm from the thumb forward. It moves 3-4 cm in depth according to the direction indicated by the index finger.
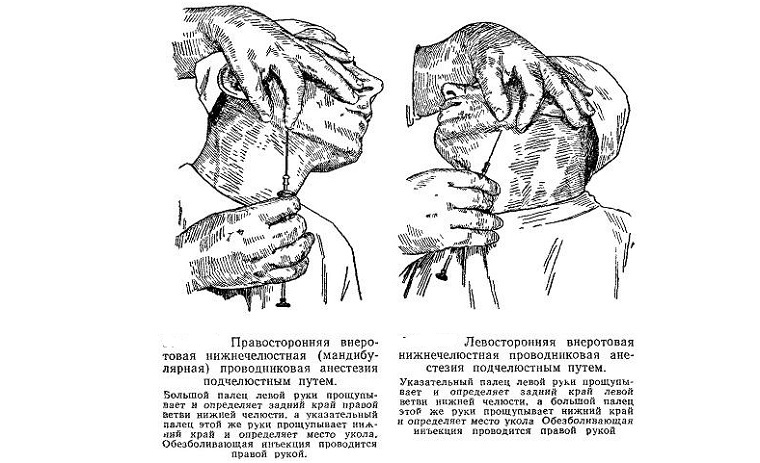
Post-jaw method
The injection should occur in the region of the mastoid process of the temporal bone behind the lower jaw. The length to which the needle is immersed is 1 cm.
Possible errors of
Even modern dentists recognize that mandibular anesthesia is very difficult in the technique of carrying out, in particular possible such errors:
- After the needle has moved 0.5 cm, it begins to abut the bone .If you enter at this time an anesthetic completely, then only one of the branches of the mandibular nerve is anesthetized. To avoid this, you need to move the needle slightly back and move the syringe barrel to the incisors. After that, you can continue to insert needles into soft tissues.
- Another option is the advancing the needle to a depth of more than 2-3 cm without contact with the bone .This is possible,
 if the corners of the jaw are strongly deployed. Or the needle moves parallel to the bone, not along the length. In this case, you need to partially pull out the needle and maximally push the syringe cylinder onto the opposite rear teeth.
if the corners of the jaw are strongly deployed. Or the needle moves parallel to the bone, not along the length. In this case, you need to partially pull out the needle and maximally push the syringe cylinder onto the opposite rear teeth. - If the needle is incorrectly inserted, it is possible to break it .This happens if its original position was very sharply changed, and the end was at a great depth in soft tissues or located between the muscle fibers and bone. Most often, a fracture occurs at the junction of the needle with the cannula, so you need to use tools from proven manufacturers and clearly follow the procedure. Treatment of this condition is carried out in a hospital under X-ray control.
Conductive mandibular anesthesia is one of the most common methods of anesthesia in dentistry. High effective this method allows you to use it in almost all situations. And thanks to the long time of the anesthesia, the doctor can perform any necessary manipulations in the proper amount.
