 Periodontitis refers to inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, in which changes occur in the condition of periodontal tissues. The disease can bring a lot of discomfort to the patient, especially in severe stages, when only maintenance treatment is possible.
Periodontitis refers to inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, in which changes occur in the condition of periodontal tissues. The disease can bring a lot of discomfort to the patient, especially in severe stages, when only maintenance treatment is possible.
Therefore, timely diagnosis of periodontitis and differentiation from other diseases that are similar in the clinic, at the very beginning of its development, is very important.
Contents of
-
- history
- history
- assay
- Instrumental and other research methods
- Differential diagnosis
History of
The first thing a dentist does when he sees a patient is collecting an anamnesis. The doctor specifies the following data: 
- the presence of general somatic pathologies, for example, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, bronchial asthma;
- earlier manifestations of the disease and their frequency;
- manifestations of late;
- how daily hygiene of the oral cavity is carried out;
- usefulness of the diet;
- profession;
- patient complaints.
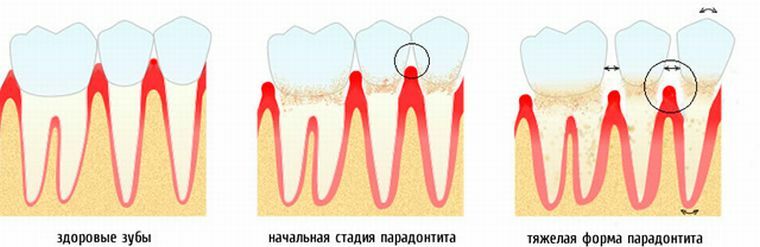
Determination of the severity of the disease at the
After the history is collected, a thorough examination of the entire oral cavity begins. For each of the stages of periodontitis will be characteristic of its manifestations:
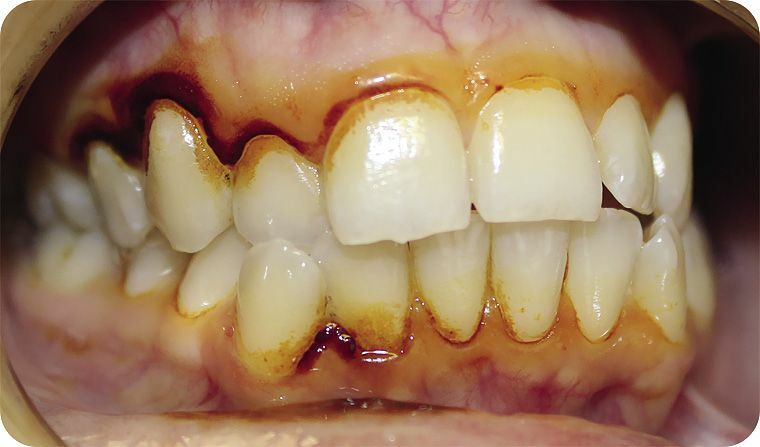
- Disease with a light current .In this case, the patient has a feeling of discomfort in the oral cavity. There is bleeding gums during daily brushing of teeth, with the use of solid foods. The gums and papillae between the teeth look cyanotic. The main feature is the presence of a pathological pocket having a depth of up to 4 mm. The teeth are still motionless.
- Disease with an average severity of .With periodontitis of medium degree, the gingival margin of the gingival margin will be somewhat larger. There is a constant unpleasant odor from the mouth, and teeth become mobile in the horizontal direction. Gums are edematic and hyperemic. When probing, periodontal pockets with a depth of 5 mm are determined.
- Heavy stage .This degree of severity is characterized by a violation of chewing and closing of the teeth, which are mobile in all directions. There will also be signs of inflammation of the gingival margin. Pathological pockets have a depth of more than 5 mm. Quite often they can detect a purulent discharge.
In all cases, dental deposits will be present.
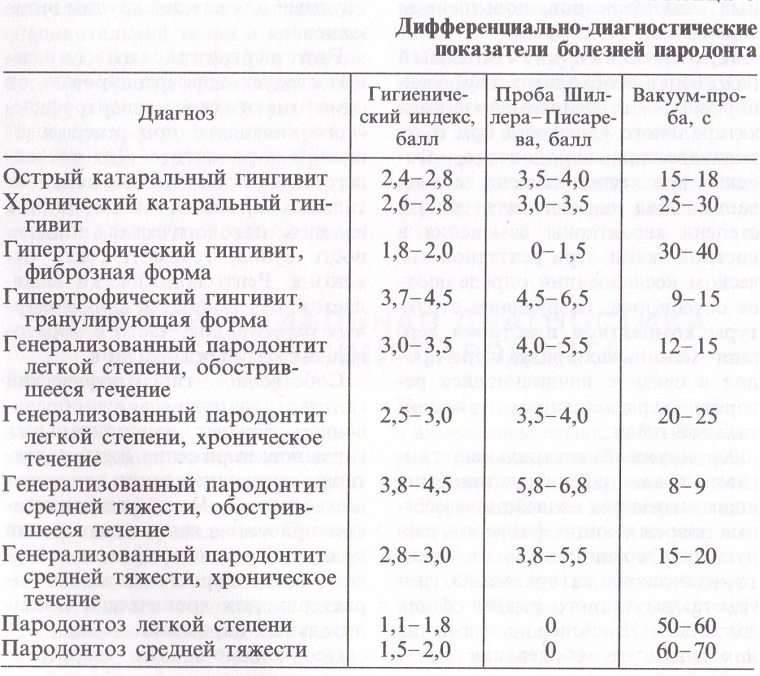
Schiller-Pisarev assay
This study is based on the staining of glycogen, deposited in the periodontal inflammatory processes, with an iodine solution. Depending on the intensity of staining, the extent of the changes that occur is determined.
The more brighter, the more pronounced inflammation. For evaluation, the following gradation is used:
- straw-yellow color - absence of inflammation;
- light brown color - mild inflammation;
- dark brown color - a strong inflammation.
The Schiller-Pisarev test is not specific. With its help, you can determine the dynamics of the treatment.
Periodontal index
This index allows you to take into account all the signs of periodontal pathology.
Grading grades:
- 0 - complete absence of any changes;
- 1 - an easy flow of gingivitis;
- 2 - inflammatory gum disease without periodontal pocket;
- 6 - the appearance of the periodontal pocket, accompanied by a disruption of the periodontal function, the tooth does not move;
- 8 - the deterioration of the condition of periodontal tissues is expressed significantly, the tooth begins to shift from its place.
The condition of the tissues around each individual tooth is assessed. The calculation of the index is carried out according to the formula: PI = the sum of all the estimates submitted / total number of teeth.
Interpretation of the results:
- 0.1-1 - initial tissue damage;
- 1,4-4 - moderate severity;
- 4-4,8 - severe course of the disease.

Kulazhenko sample
Used to determine the stability of capillaries to the action of vacuum. In the process of research, Kulazhenko's apparatus is used. It leads to the formation of a hematoma on the gum, the time of its appearance and the degree of damage to the walls of the vessels.
Normal values:
- front teeth - 50-70 s;
- premolars - 70-90 s;
- lower molars - 80-100 s;
- upper molars - 80-90 s.
The formation of a hematoma with periodontitis occurs 8-9 times faster.
Instrumental and other research methods
One of the most informative studies in periodontitis is panoramic radiography or orthopantomography. X-ray examination allows you to more accurately assess the degree of bone tissue changes and clarify the diagnosis.
 With a mild degree of periodontitis, the resorption of the interdental septum is 1/3.The average degree is associated with a decrease in the amount of bone to ½.In severe disease, bone is absent already by 2/3.
With a mild degree of periodontitis, the resorption of the interdental septum is 1/3.The average degree is associated with a decrease in the amount of bone to ½.In severe disease, bone is absent already by 2/3.
Depth measurement of pathological pockets also allows to determine the degree of tissue damage. For this, a buttoned graduated probe, gutta-peristal pins and contrast solutions are used.
A biopsy of the gingival tissue will be informative. As a result, an accurate diagnosis will be obtained that will confirm the changes corresponding to rheumatic, hereditary and autoimmune diseases.
For greater effectiveness of treatment, microbiological and cytological examination of the contents of the dentogingival pockets is carried out. In the same way, the degree of changes that occur in the periodontal tissues is determined.
Investigation of the gum liquid composition will give an idea of the severity of inflammatory phenomena. A large number of immune cells indicate a far-gone process.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of periodontitis is necessary with the following diseases:
- Gingivitis .In this case, a common symptom is inflammation of the gingival margin. Differences will be visible on the roentgenogram. With gingivitis, the loss of bone tissue and the development of periodontal pockets will not occur.
- With periodontal disease , pathological pockets and signs of inflammation are absent. There is only a withdrawal of bone tissue.
- Premature atrophy of bone tissue .In this case, the changes will be for young people. Inflammation of periodontal tissue is absent, and the decrease in bone tissue occurs evenly.
Diagnosis is easy enough. For this, you need to carefully collect anamnesis and conduct a complete examination of the patient.
