 Gingivitis, periodontitis - behind these incomprehensible names there is a dangerous tooth disease associated with inflammation of the gums, which, if untreated, can lead to tooth loss.
Gingivitis, periodontitis - behind these incomprehensible names there is a dangerous tooth disease associated with inflammation of the gums, which, if untreated, can lead to tooth loss.
What are the causes of this disease and how to deal with it correctly?
Today, more than half of humanity suffers from gum disease, and the reasons are very different - from the wrong way of life to bad heredity or disabilities due to hormonal changes.
In this case, inflammatory processes may differ in the nature of the course and methods of treatment. To properly determine the therapy and know what to do, you should familiarize yourself with all possible nuances.
Content
- Causes inflammation
- Common factors
- Local factors
- Gingivitis - trouble that we will survive
- catarrhal gingivitis
- Ulcerative Gingivitis
- Hypertrophic gingivitis
- inflammatory processes in the oral region
- Periodontitis
- inflammatory process during pregnancy
- Prosthetics and installation of crowns
- negative impactwisdom teeth
- Comprehensive approach to treatment
- Consultation and initial examination of a specialist
- Protand
- Treatment of inflammation caused by trauma
- Features of toothpaste and brush selection
- Preventative measures
Causes of inflammation
Causes of development in the gingival inflammation can be both external and internal. In addition, they differ in the scale of the impact. It is the correctly diagnosed cause of inflammation that becomes the key to effective treatment.
Common Factors of
Problems with gums may result from:
- smoking;
- lacks in the body of minerals and vitamins;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system;
- of diabetes;
- hormonal failures;
- infectious processes;
- use of certain medications( eg, antidepressants, contraceptives or nasal drops may have a negative effect);
- reduced immunity.
Local factors
These include:
- teething;
- trauma, thermal or chemical gum burns;
- development of calculus;
- poor-quality oral hygiene, congestion, releasing toxins, microorganisms;
- improper prosthetics or sealing, in which the gum injures the overhanging edge of the crown or a seal( there is a localized within one or two teeth inflammation).
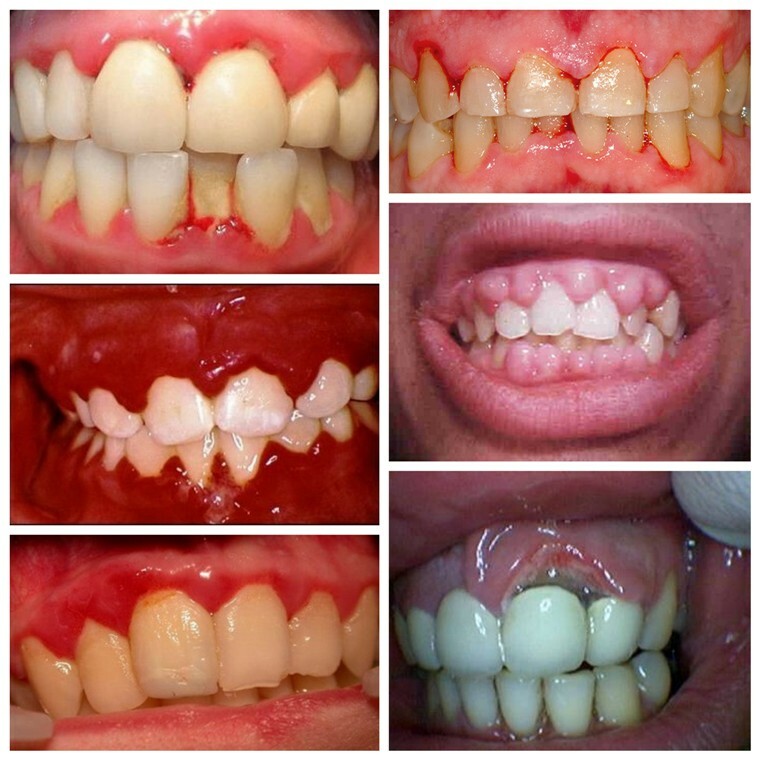
In the photo examples of gum disease
Gingivitis - this trouble we will survive
These factors often lead to the development in the gums of such dangerous inflammatory processes as gingivitis and periodontitis. In this case, there is a generalized nature of inflammation, implying damage to the entire oral cavity.
Catarrhal gingivitis
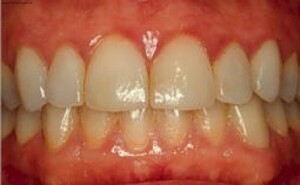
This form of inflammation is most common. Both general and local factors can provoke the disease.
For this type of inflammatory process, the following symptoms are typical:
- slight puffiness, bleeding and redness of the gums;
- change in the acute form of the gingival papillae to a domed papilla;
- appearance of unpleasant odor and taste, sensation of itching;
- soreness of the gums on contact with food;
- fever, general weakness;
- formation of copious plaque( at the initial stage).
The mild form of the disease( only the gingival papilla is affected) can be replaced by medium and severe forms with damage to the free portion of the gums and their entire space, respectively.
The photo shows a chronic process, for the cure of which requires a comprehensive approach.
Ulcerative gingivitis
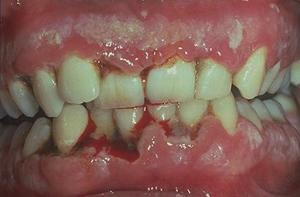
In this case, inflammatory processes affect the mucous membranes of the gums, provoking the development of tissue necrosis near the gingival margin and inflammation of the regional lymph nodes.
The most likely cause of this process, along with hypothermia, infectious diseases and reduced immunity is poor oral hygiene.
Symptoms typical for catarrhal gingivitis are:
- , the presence of a dirty gray plaque on the top of the gingival papillae , the removal of which leads to bleeding gums;
- temperature rise with increased pulse, pale skin and loss of appetite.
With the development of this form of the disease, it is extremely important to start treatment in time.
In the photo, a severe form of the disease with purulent inflammation, which requires antibacterial and surgical treatment.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
A feature of this form is the reactive proliferation of connective fibrous tissue and epithelial basal cells, caused by chronic inflammation of the mucous membranes of the gums. Most often, these disorders are caused by changes in the endocrine system, a lack of vitamins and a metabolic disorder.
In this case, the following symptoms appear:
- epithelial thickening( in the absence of treatment, keratinization is possible);
- a significant increase in gingiva in size, a change in its color to dark red( granulating flow of hypertrophic gingivitis);
- strong compaction of gum tissue, the appearance of painful sensations during palpation( fibrotic development).
Inflammatory processes in the oral area of the
In addition to generalized inflammation of the entire gingival surface, local processes are possible in certain areas due to the development of periodontitis, gum injuries to the crown, eruption of wisdom teeth.
Also, inflammatory processes in the gums of pregnant women stand apart. We will talk about these situations.
Periodontitis
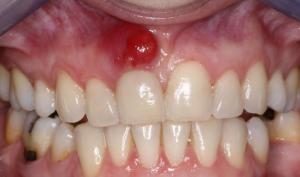
Fistula with periodontitis
A characteristic feature of periodontitis is the formation of a cyst in the top of the root of the affected tooth in the form of a pouch filled with pus, which is the cause of swelling, swelling and tenderness of the gum.
In this case, the swelling is unstable, then appearing, then disappearing.
The cause of the development of the disorder is caries started developing into pulpitis, or poor-quality root canal filling during pulpitis treatment or at the stage of preparation for prosthetics.
Inflammation during pregnancy
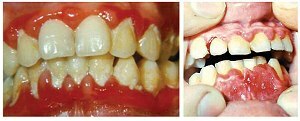
A change in the condition of the gums with the development of bleeding and swelling is very often observed during pregnancy.
A provoking factor, dentists call - a change in the hormonal background of a woman who, with impaired hygiene of the oral cavity, leads to the development of gum disease.
Especially attentive to the state of the oral cavity, one must be in the second and third trimesters( the hypertrophic process presented in the photo is typical for these terms).
In the absence of timely treatment, inflammation can quickly progress, not only aggravating the general condition of the future mother, but also provoking premature birth and the appearance of babies with a body weight deficit.
Prosthesis and installation of crowns
Wrong prosthesis with the installation of crowns or prostheses with overhanging edges, is the cause of permanent gum injuries, in which, as a result, a large-scale inflammatory process develops.
In such a situation, the periodontal pocket of a sufficiently large depth in which the inflammation develops can form in the interdental space.
Negative influence of wisdom teeth
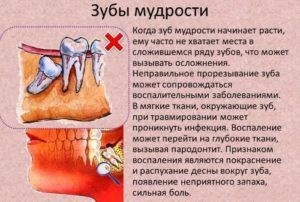 Cutting eights is one of the possible causes of inflammation of the gums, which swell and become painful in the area of the tooth.
Cutting eights is one of the possible causes of inflammation of the gums, which swell and become painful in the area of the tooth.
It is normal to have a small edema, but if the inflammation acquires a large scale, you should immediately call a doctor because of the risk of infection of the wound.
The most frequent variant of gum disease with the cutting of wisdom teeth is pericoronaritis, associated with the ingestion of food particles under the mantle covering the molar gingiva and the development of pathogenic microorganisms there.
In this case, not only the gum around the tooth, but also adjacent tissues can be inflamed, which is fraught with a purulent abscess.
It is possible to cope with the disease only with the assistance of a specialist who will prescribe appropriate therapy with the use of antiseptic solutions for rinsing, rinsing or, if necessary, dissecting the hood that creates trouble or completely removes the wisdom tooth.
Complex approach to treatment
To begin treatment of inflammatory process is necessary from the moment of detection of the first symptoms. The therapy directed on elimination of an inflammation is multifaceted enough thanks to what it is possible to stop on the most suitable way of treatment.
Consultation and initial examination of a specialist
 First of all, a dentist visually assesses the condition of the oral cavity and the degree of inflammation.
First of all, a dentist visually assesses the condition of the oral cavity and the degree of inflammation.
One of the first measures for such complaints is complete sanitation of the mouth, followed, as a rule, by the removal of deposits on the teeth with a special ultrasound unit.
Sanitation of the oral cavity by the treatment of caries-affected teeth allows eliminating the acute inflammatory process( in particular, to alleviate the condition with ulcerative necrotic gingivitis).Also, this measure is necessary to reduce the risk of re-development of inflammation.
The removal of deposits from the teeth makes it possible to eliminate one of the main causes of inflammation - the effect of pathogenic microorganisms.
After ultrasonic cleaning, the teeth are polished, forming a smooth surface on which plaque will not collect. If the gingiva is highly inflamed and bleeds, polish is performed when the process becomes less acute.
Anti-inflammatory therapy
Anti-inflammatory treatment of gum disease is performed using a variety of drugs: antiseptic solutions for lavage from a syringe, medical periodontal dressings and applications.
Depending on the cause of the inflammatory process, the following therapy methods are used:
- If is diagnosed with catarrhal gingivitis , therapy can be performed at home using a holilac gel for applications and a chlorohexidine solution of 0.05% rinse concentration.

- Treatment of periodontitis has its own characteristics, as it is required to reduce the mobility of teeth, eliminate purulent processes. Within the framework of complex therapy, antibiotic treatment, surgical intervention or splinting of groups of teeth that have acquired mobility can be prescribed.
- In pregnant women, is treated in the same way as in other patients, choosing drugs that are allowed in a particular trimester. To treat catarrhal gingivitis, rinse with chlorhexidine, decoctions of chamomile or calendula.
If antibacterial therapy is required, the drugs are selected from the macrolide group( Sumamed, Azithromycin), cephalosporins( Efodox, Cefazolin) and penicilins( Augmentin, Amoxiclav).
With the development of hypertrophic gingivitis, surgical intervention at the discretion of the dentist may be required.
Antibiotics( in tablet form) are prescribed for all patients with ulcerative necrotic gingivitis and with persistent flow of acute gingivitis. The most commonly used drugs are: Clindamycin, Ofloxacin, Augmentin, Azithromycin, Lincomycin.
The course of antibiotic therapy is chosen by the doctor on an individual basis.
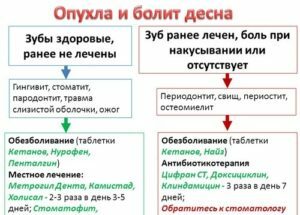
Scheme for the treatment of gum disease in the home
In addition to antibiotics, for the removal of inflammation, oral irrigation can be prescribed with Proposol spray, lubrication of affected areas with dental ointments, such as Metrogil or Solcoseryl. The use of drugs in the form of a gel is preferable, since its base facilitates the absorption of the active substance into the gum.
Vitamin - ascorbic acid or ascorutin can be prescribed to improve immunity. If desired, they can be replaced with rose hips.
The tactics of action at home with inflammation and soreness of the gums are presented in the diagram.
Treatment of inflammation caused by trauma
If the cause of the inflammatory process is the injury of the gums with the overhanging edge of the seal, firstly, the cutting of the interfering site or complete replacement of the filling material is performed.
In case of unsuccessful prosthetics, drug therapy similar to gingivitis may be prescribed first, after which, depending on the result, the need to replace the crowns for complete cure is considered.
Features of the choice of toothpaste and brush
 Inflammation of the gums requires an integrated approach to treatment, therefore, along with properly selected drug therapy, you must carefully consider the choice of toothbrush and toothpaste.
Inflammation of the gums requires an integrated approach to treatment, therefore, along with properly selected drug therapy, you must carefully consider the choice of toothbrush and toothpaste.
As part of the paste should be present:
- anti-inflammatory components ( extracts of ginseng, sage, chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, cloves);
- antibacterial substances ( which acts on gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria - triclosan, used in conjunction with a copolymer prolonging the action of the component);
- regenerating gum tissue means( oil solutions of vitamins A and E, carotolin, some enzymes).
The only option that is suitable for daily use and has not only a curative, but also a preventive effect, are toothpastes with such a natural component as tea tree oil.
A brush suitable for cleaning an inflamed oral cavity should be soft enough that the mucosa and gum do not experience excessive pressure. You can use the brush for no longer than one month.
 Can not get an appointment with a dentist? All about treating gingivitis at home in this article.
Can not get an appointment with a dentist? All about treating gingivitis at home in this article. Read more about what to rinse your mouth with gum disease read here.
Do you prefer traditional medicine? Treatment of gum disease with folk remedies by reference: http: //dentazone.ru/ bolezni-desen /gingivit/ lechenie-desen-narodnymi-sredstvami.html
Preventive measures
To save gums and teeth healthy will help:
-
 Introduction to the diet of calcium-rich products - fish, greens, dairy products, nuts, which will strengthen bone tissue and teeth.
Introduction to the diet of calcium-rich products - fish, greens, dairy products, nuts, which will strengthen bone tissue and teeth. - Saturation of the body with vitamin C , responsible for reducing bleeding gums.
- Healthy lifestyle, rejection of bad habits ( smoking, excessive consumption of coffee, tea).
- Thorough and regular oral hygiene of the with tooth cleaning twice a day and the use of dental floss after each meal.
Inflammation of the gums, especially in the acute stage, requires long and complex treatment, so you should remember about preventive measures that will significantly reduce the risk of such an ailment and do not postpone a visit to a doctor if anxiety symptoms appear.
