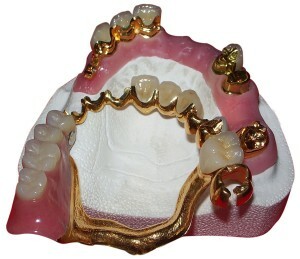
 In modern dentistry, a large number of designs of clasps( staples, clamps) are used that help fix dentures in difficult clinical situations.
In modern dentistry, a large number of designs of clasps( staples, clamps) are used that help fix dentures in difficult clinical situations.
The main task that currently faces dentists is to address the issue of qualitative fixation of the prosthetic construction while minimizing its negative impact on the teeth in which the prosthesis is attached and the mucous membrane.
Content
- Features
- Requirements shoulder
- body
- Scion
- Modern classification
- Feature popular types
- single-armed bracket
- retaining structure Jackson
- Continuous bracket
- dentoalveolar clasp
- gingival design
- cast supporting-holding clasp
- Klammer system Ney
- bracket type 1
- Type 2 fasteners
- Retaining bracket 3 types
- Fastening element 4 types
- Type 5 construction
Konstrsu- features
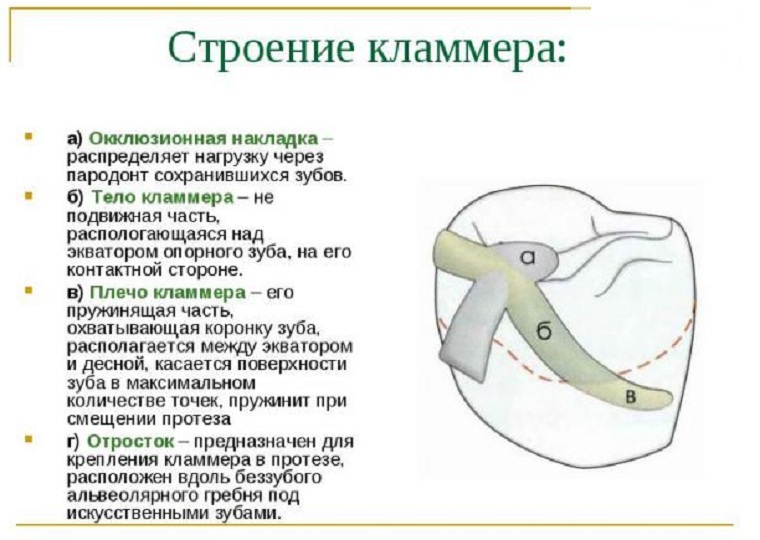
Despite the large number of varieties, all have a common clasp parts: the shoulder, the body and bone. Some types of clamps are complemented by an occlusal lining.
Shoulder requirements
The shoulder is the part of the clasp that is responsible for springing properties. It surrounds the crown part of the tooth. The position of the shoulder will depend on its structure. 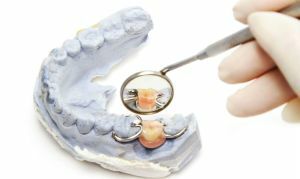
Requirements that should be remembered when modeling the shoulder:
- it should be located on the vestibular side, the optimal position is between the equator and the gingival margin;
- shoulder touches the crown in the largest number of dots;
- , when moving the prosthesis, the shoulder should spring, - the wire frame is the most compliant, and the least - cast;
- pressure applied to the tooth surface, passive;
- should not have any sharp ends that can injure the mucous membrane of the lips and cheeks.
Body
The body of the clamper is the basic mobility-free part. It is placed on the contact surface of the main tooth.
Completely eliminates the location of the body between the equator and the neck, as the prosthesis simply will not be worn. The only exception can be the front teeth. In this case, the body is moved to the gum to increase the level of aesthetics.
Scion
The scion is responsible for fixing the clamp in the prosthesis. It is under the plastic parts of the design in the base. It is not recommended to place it on the palatal or lingual side, because the risk of fracture of the prosthesis increases.
Modern classification
All clasps are divided by the type of material from which they are made:
- Metal .It can be gold, gold platinum alloy, stainless steel.
- Plastic .This kind of material is used less often. Its use is justified only in aesthetic significant areas.
- Combined versions of made of metal and plastic.
In addition to the material separation, different designs are distinguished depending on the method of their production:
- bent , which are produced by bending wire;
- cast , which are cast during the manufacture of the prosthesis.
By function, the following are distinguished:
- holding;
- support-retaining.
Split by the principle of connection with the prosthesis:
- rigid;
- spring-loaded;
- is labile.
Staple Fitting Options:
- gingival;
- gingival;
- dental.
There is also a separation according to the type of coverage of the tooth surface by fasteners:
- single-shoulder and two-shoulder;
- change-over;
- multi-link;
- ring-shaped;
- T-shaped;
- double.
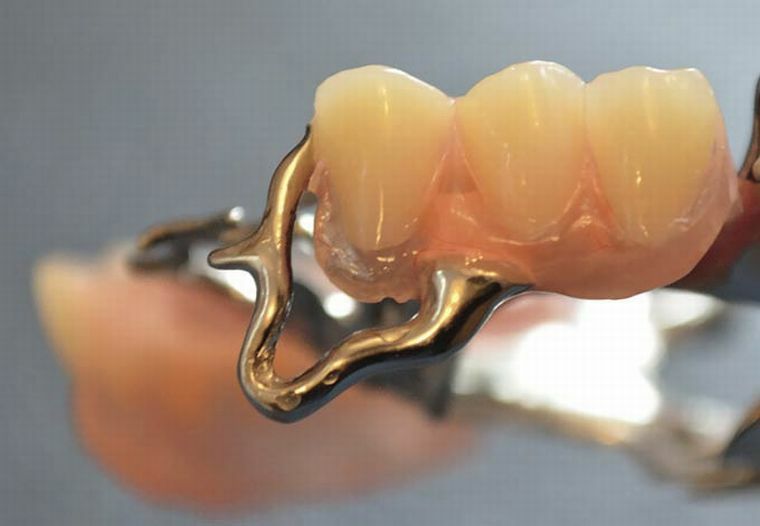
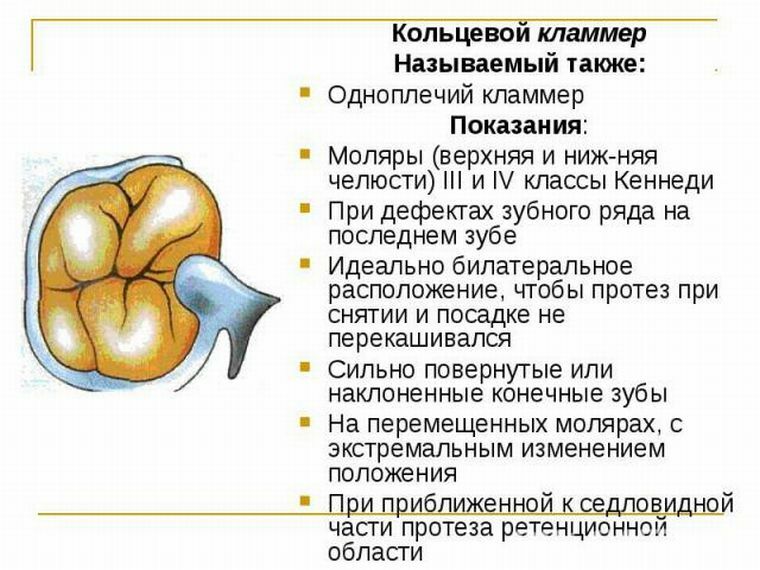
T-shaped clasp
Now the most widely used:
- single-hose;
- extended;
- dentoalveolar;
- gingival.
Characteristic of the popular
types Consider the most popular clips for prosthetic designs.
One-piece clamp
A single-arm clammer made of wire surrounds the tooth only on one side. Therefore, he needs to give such a bend that he manifested his elasticity only when passing through the equator.
All negative properties will manifest themselves when it is not fitting properly to the tooth. It should be as accurate as possible, but passive at the same time. In the case of violations, the supporting tooth will be subjected to a greater load, which will lead to an overload of periodontal disease.
Jackson Retainer
Jackson's flip-up clasp has a loop-like shape. This element is thrown across the space between the teeth and comes out on the front surface.
To give the optimum level of elasticity, the shoulder is sawn in the middle after the prosthesis is completely manufactured.
Continuous brace
Another name - multi-link. From extended it differs in that it creates a special uninterrupted system. You can arrange this type of element on both the front and back surfaces of the teeth.
Now it is made only by casting. The use is indicated for periodontal diseases and tooth splinting after trauma. As a result, it acts as a holding, supporting, stabilizing and sealing element.
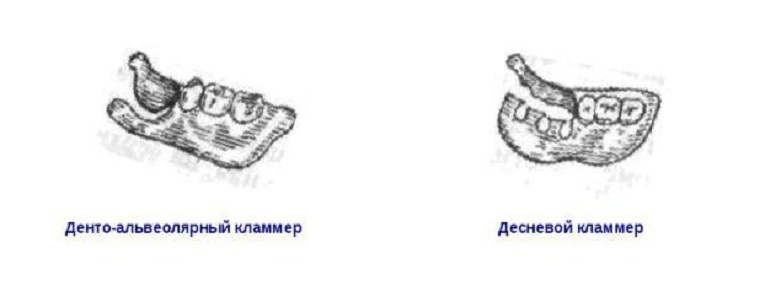
A dentoalveolar clasp
One of two types of dental prosthetic fasteners that can be made from plastic. Apply it in aesthetically significant areas, namely the frontal group of teeth.
The processes of such elements are located on the vestibular side and directed towards their teeth. They are located below the equator.
To reinforce them, they are reinforced. This means that a wire is inserted into the clamp from the metal. The downside of this method is the deterioration of the mechanical properties of plastics.
The drawbacks of this type of retention will be:
- the lip may protrude slightly;
- inability to use for teeth with a low clinical crown;
- overhanging alveolar process is also a contraindication to their use;
- such brackets can not be reactivated.
Desert construction
The gum clamp is the outgrowth of the base plastic and is located in the region of the transitional fold. The fixing properties of this option are not high. This is due to the fact that the plastic is practically not elastic.
Indication for use is the inability to use other types of fixatives. Also such fixtures are used in the unsatisfactory state of supporting teeth.
Molded support-retaining clasp
This is the most effective option. The main component of such clasps is a patch on the chewing surface of the teeth, which will act as a support. It is at her expense that the prosthesis is held on the jaw.
With end defects, the load is redistributed to the teeth, which reduces the baseline pressure. If the area to be restored is limited, then the vertical load on the supporting teeth is reduced. This kind of fixation redistributes the pressure and makes it more physiological.
The overlay can be different. Most often it looks like a paw. Regardless of the large number of forms, the basic requirement for everyone is the rigidity of the structure. Only this way the overlay will fully perform its functions.
Location is equally important. On the teeth with a pronounced occlusal surface, the patch will be located in the fissures, and on the fangs - in the region of the blind fossa. If it does not allow the teeth to close normally, then a special bed is created. They can be performed in a seal or tab. Possible variants of such cavities:
- weakly oval;
- is oval;
- box-type.
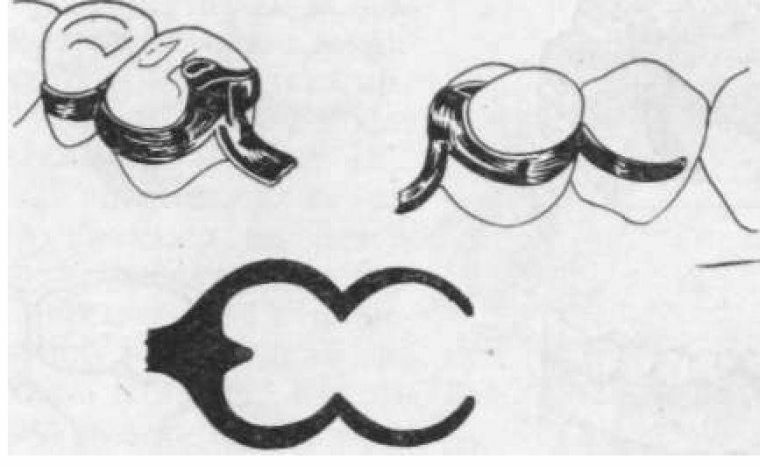
The first 2 species do not contribute to the transfer of horizontal forces. The box-shaped cavity improves stabilization.
If it is not possible to make a tab or deepen a seal, then artificial crowns are made.
How the clasp fixes the clasp prosthesis:
Clamper system Ney
The cast brackets have advantages over the bent prosthesis. They distribute the pressure better. Unfortunately, the optimal form was not immediately revealed. Only in the 50s of the last century new clasps of the Ney system were developed. They differed in that the body and all the parts adjacent to it became more massive. Thanks to this, the most severe stabilization was achieved.
The type of fastening is selected depending on the supporting tooth. Each of them has its own special line of division, which divides it into 2 parts: support and holding. Its position changes when the slope of the support changes. It rarely coincides with the equator.
The occlusal, or support, lining is located on the occlusal surface, and the retaining patch is located between the separation line and the marginal gum.

Bracket 1 type
Another name is the Akers clammer. Its use is shown when passing the dividing line in the middle of the crown area.
Rigid shoulders prevent lateral shifts. Thus, the prosthesis stabilizes in the oral cavity. They must be located between the occlusal surface and the line of separation. The position close to the gingival margin should be ruled out.
The use of this option is not possible with the tilting of the teeth, when the separation line passes high on the approximate surface. If necessary, you can use an artificial crown coating.

Fastener type 2
Another name for it is Klachmer Roach. It contains: an
- occlusive overlay that connects to the body;
- shoulders, having a T-shape.
Its application is shown with an atypical location of the separation line. In this case, it will go high in the area adjacent to the defect and low in the remote.

Bracket 3 of type
Is a combination of 1 and 2 types of latches. One of his shoulders has a T-shaped shape, and the second - is close to the chewing surface. The use of this type of fastener is indicated by the uneven course of the separation line. Basically, it occurs with the tilts of large molars.
According to its characteristics, this option of the Ney clader is not inferior to the first one. A rigid lining guarantees a qualitative stabilization, and shoulders - a support.
Fastening element 4 type
Or inverted. It is used when tilting small molars and canines or with a low clinical crown. The rigid part should be located on the side where the support will be larger. Next, the bracket surrounds the distal tooth contact, and the occlusal patch enters the fissure.
The body is located on the oral or vestibular side of the baseline.
Construction type 5
Another name - single-ring. It is used for inclined molars, which stand alone. In this case, the dividing line from the slope side is high, and from the opposite - low.
This name was given to this clammer from its position. His body is located on the supporting surface and completely grasps the tooth.
A disadvantage of this type is poor fixation of the prosthesis.

In modern dentistry is used a large number of types of clasps. It can not be said that one is better than another. Each of them is used in a specific clinical situation.
