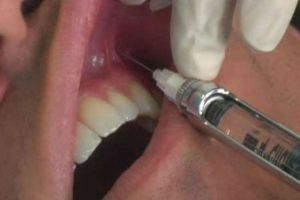
 One of the most effective methods for conducting local anesthesia is conductive anesthesia( conductive anesthesia).The principle of its action is to install the unit on nerve impulses, responsible for the transmission of information about the appearance of pain directly to the brain.
One of the most effective methods for conducting local anesthesia is conductive anesthesia( conductive anesthesia).The principle of its action is to install the unit on nerve impulses, responsible for the transmission of information about the appearance of pain directly to the brain.
Once the lock is set, the pain threshold for a specific time is minimized. After this, you can proceed with the operation.
This type of anesthesia is characterized by good tolerability and a high degree of effectiveness. Immediately after surgery, pain remains at the same minimum level.
Contents
- General description
- Application in dentistry: features, indications
- Methods used in dentistry
- Technique for the procedure
- Possible complications
General description
Conductive anesthesia is one of the types of local anesthesia. Anesthetic solution is injected directly into the area where the nerve responsible for the operated area is located. This method is widely used and is actively used in the field of dentistry.
Anesthesia can be anesthetized with virtually any part of the human body. For the procedure, special preparations are used, but in most cases a solution of novocaine is used.
Conductive anesthesia is contraindicated in the following cases: 
- a number of operations in children under 12 years of age;
- marked disturbance of the emotional background;
- diagnosis of infection of the skin in the area of operation;
- confirmed allergy to antiseptic drugs;
- congenital deaf mute, lack of contact with the patient.
The patient during anesthesia can feel a slight discomfort, comparable to the analysis of blood from the vein. There may be fever, a feeling of heaviness, in the abdomen. But all this passes as quickly as it appears.
Dental application: features, indications
Anesthesia is performed by injecting an anesthetic into a region slightly remote from the surgical site.
There are two types of conductive anesthesia:
- Central .The main nerve trunks of the trigeminal nerve are determined and the drug is injected into one of them.
- Peripheral .In this case, the anesthetic is injected into one of the branches of the main stem nerve.
 For anesthesia to be successful, it is necessary to deliver the solution to the target point, as a rule, this channel is the bone orifice, through which the nerve trunk passes.
For anesthesia to be successful, it is necessary to deliver the solution to the target point, as a rule, this channel is the bone orifice, through which the nerve trunk passes.
The conductor method has significant advantages over other types of anesthesia in dentistry:
- an opportunity to anesthetize a large portion of the jaw, after which to remove several teeth at once, to open abscesses;
- requires a small amount of solution compared to other types of anesthesia.
Indications for use:
- removal of several teeth at once;
- removal of inflamed roots;
- extraction of teeth with abnormal germination;
- implant implantation;
- surgical intervention on lower molars;
- inflammation in the maxillofacial region;
- inflammation of soft tissues and mucous membranes;
- complex form of caries, periodontitis;
- a negative reaction to general anesthesia.
Methods used in dentistry
Anesthesia with this method is characterized by high efficiency. A positive result is achieved due to the blockage of the nerve, in some cases, a whole group of nerves responsible for pain impulses.
So, when irritated, the signal received in the brain is processed and given to the person as a strong pain. The location of the operation, where it is required to block nerves, is the main source of pain.
Conduction anesthesia is carried out by different methods, in dentistry it depends on which jaw the intervention will be performed on.
For anesthesia of the upper jaws, the following procedures are used:
- Palatine .This method anesthetizes completely the sky, reducing its sensitivity to zero. Along with it, the alveolar
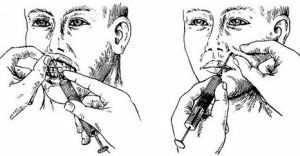 is anesthetized.
is anesthetized. - Tuberal .To this method, dentists resort to treatment or removal of molars.
- Infraorbital .It is used in cases when the treatment of canines, incisors, premolars is required.
- Cutting tool .Anesthesia is carried out in part of the mucosa between the canine teeth and incisors.
In order to anesthetize the lower jaw, the following methods are used:
- Mental .Anesthesia for anesthesia of canines, incisors and premolars.
- Mandibular .Anesthesia succumbs to all teeth from the side where the solution is injected.
- Torus .The anesthetic is introduced into the torus( mandibular cushion), blocking the combat pulse of the region of molars and premolars.
- According to Bershe Dubov .This is a more serious method and is used in maxillofacial surgery. Anesthesia affects all teeth on one side.
Two methods of needle insertion are used: extraoral and intraoral.
Technique for the procedure
The technique of this procedure is quite simple. In the region of the nerve, whose impulses must be muffled, a special solution is introduced. The doctor can do with one injection, and may need a few injections of the syringe. To anesthetize the effect, the anesthetic must be introduced a few millimeters from the nerve.
The procedure will be safer if you use ultrasound or a neurostimulator during it.
Using ultrasound, anesthesia is performed under full control with the help of vision. Previously, this procedure was conducted only blindly, which is now often found.
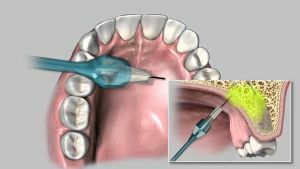 When using an ultrasound machine, the doctor sees well the needle and the nerve, in the area of which it needs to get to, while not hurting the nerve itself. Accordingly, this at times precludes the possibility of improper administration of an anesthetic.
When using an ultrasound machine, the doctor sees well the needle and the nerve, in the area of which it needs to get to, while not hurting the nerve itself. Accordingly, this at times precludes the possibility of improper administration of an anesthetic.
With the help of the neurostimulator it is determined at what distance the needle is located from the nerve that gives out the pain impulse.
Thus, it becomes clear that the use of devices such as ultrasound and neurostimulator for anesthesia in dentistry reduces all risks to minimum values.
The main advantages are the following:
- minimal probability of neuropathy;
- exclusion of accidental ingress of solution inside the vessel;
- significantly increases the success in performing neural blocking;
- qualitative, effective and absolute anesthesia.
Possible complications of
The most serious and dangerous complication that can result from improper injection of an anesthetic is neuropathy. In some cases, the human body can adversely react to the injected anesthetic.
Side effects are most often manifested as an allergic reaction, and in some cases, a disorder of other body systems.
Accidental ingestion of a solution in a blood vessel leads to functional disorders of the body, resulting in the following symptoms:
- general weakness;
- heart palpitations;
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness.
Neuropathy develops as a result of disruption of the nervous system. Can manifest in varying degrees. The main signs: 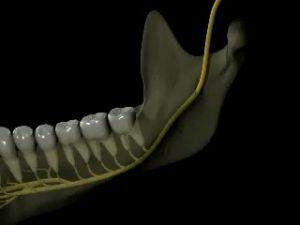
- sensation of goosebumping all over the body;
- numbness;
- pain;
- weakening of muscle tone in the anesthetized area.
The incidence of such symptoms is quite small and is no more than 1% for all cases of the procedure. If this still happens, it will take several months to one year to completely repair the damaged nerve.
The development of new technologies in the modern world allows us to speak about the minimum probability of development of various complications.
In most cases, surgical interventions require appropriate anesthesia. Without anesthetics, modern medicine simply can not exist. And the use of a neurostimulator or ultrasound will help to correctly administer an anesthetic injection and thereby prevent the possibility of complications after the procedure.
