 Low molecular weight( fractional) heparins are often used in various thrombotic diseases. They improve blood clotting and reduce the risk of blood clots, thereby restoring the patency of the walls of blood vessels.
Low molecular weight( fractional) heparins are often used in various thrombotic diseases. They improve blood clotting and reduce the risk of blood clots, thereby restoring the patency of the walls of blood vessels.
Before you start using this group, you should find out what kind of drugs, what effect they have on the body and what indications they should be used for.
Low molecular weight heparins( LMWH) are a class of heparin derivatives that have a molecular weight of 2,000-10,000 Daltons. These drugs are used to change the coagulability of blood. Used to treat various thrombotic pathologies, with varicose veins and for the therapy of venous thromboembolism.
Approximately in the mid-70s it was found that when the physical and chemical properties of heparin change, quite useful pharmacological characteristics are obtained.
Since 1/3 of the heparin molecule causes its activity with anticoagulant flow. Approximately from the middle of 80th years began to create medicinal preparations which contain low-molecular heparins.

Contents
-
- Pharmacological properties
- Application areas
- TOP-15 most popular preparations of the
- group Mechanism of action
- For which indications is contraindicated
- Features of the
- treatment Overview of the phlebologist
Pharmacological properties of
LMWH is produced from conventional heparin by chemical and enzymatic depolymerization. Heparins of low molecular weight type have heterogeneous properties in their molecular weight and have anticoagulant activity.
The average molecular weight of heparins of low molecular weight is from 4000 to 5000 Dalton, sometimes it can vary between 1,000 and 10,000 Daltons.
All heparins of low molecular weight have a number of pharmacological properties:
- , these substances have no pronounced effect on the inactivation of thrombin, due to the small parameters of the molecule, but in spite of this they retain the ability to inactivate factor Xa;
- LMWH binds to a small extent with plasma proteins, which as a result causes their strong anticoagulant effect;
- , these components are slightly combined with macrophages and endothelial cells, which results in a long half-life and a prolonged effect;
- preparations almost do not interact with platelets and PF4, these properties cause their reduced frequency of thrombocytopenia.
Areas of Application
Low molecular weight heparins are widely used in medicine in vascular surgery and phlebology. Preparations based on these components are used to treat various thrombotic diseases of veins and vessels, thromboembolism, varicose, as well as heart disease, in particular with myocardial infarction. 
Based on this substance, a large number of drugs have been created that help in the fight against these conditions and diseases.
Drugs with low molecular weight heparins are used in the following conditions:
- during the prophylactic treatment of thromboembolism in orthopedic surgery, as well as in general surgical interventions before and after the surgery;
- in the prophylactic therapy of thromboembolism in people who have an increased risk of developing it, as well as in patients who are in bed with acute therapeutic pathologies - acute respiratory failure, respiratory infections, acute cardiac failure;
- during the treatment of unstable angina, as well as myocardial infarction without the presence of abnormal Q wave on the ECG;
- during the treatment of deep vein thrombosis in acute form;
- during the therapeutic treatment of pulmonary embolism;
- during the treatment of severe thrombosis;
- for prophylactic treatment of coagulation and thrombus formation in a system with extracorporeal circulation in the provision of hemodialysis and hemofiltration.
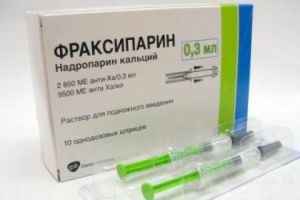
TOP-15 of the most popular drugs of the
group. Medicines containing low molecular weight heparins:
- Nadroparin calcium;
- Enoxaparin sodium;
- Hemapaksan;
- Clexan;
- Fragmin;
- Anfiber;
- Fraxyparin;

- Cleaver;
- Zertoparin;
- Eniksum;
- Reviparin;
- Dalteparin;
- Bemiparin( Cibor);
- Flenox;
- Novaparin.
Mechanism of action
All drugs with fractional heparins have highly effective antithrombotic and weak anticoagulant properties. Have a direct effect. Prevent the processes of hypercoagulation.
Drugs based on LMWH have the following properties:
- has a prolonged antithrombotic effect of , therefore it is used for various thromboembolic pathologies.
- inhibits the formation of thrombin to a small extent.
- To a small extent may have an impact on primary homeostasis, adhesion and aggregation of platelets, refer to the weak anticoagulant .These properties are due to the low impact on anticoagulant tests, as well as low hemorrhagic effects.
- The anticoagulant effect of on blood is due to the binding of plasma antithrombin and inhibition of factor Xa. When using drugs based on LMWH in small doses, they practically do not affect the bleeding period, the duration of blood coagulation and the activated partial thromboplastin time( APTT).
At which indications are contraindicated
Medicines with heparins of low molecular weight are contraindicated to use at the following indications:
- during the occurrence of an increased allergic reaction to the active element;
- for disorders in the blood clotting system, as well as hypocoagulation, hemorrhagic diathesis( hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, purpura, the presence of increased permeability of capillaries);
- during hemorrhagic stroke, encephalomalacia, traumatic injuries associated with the CNS, intracranial type bleeding in acute form, surgical interventions on the CNS, brain aneurysm of the head;
- for various surgical interventions of the ophthalmologic type;
- for retinopathy during diabetes mellitus;
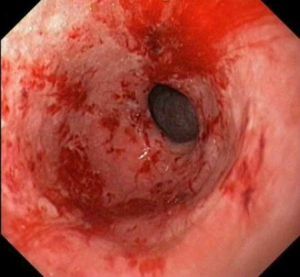
- in the presence of gastric and duodenal ulcers in acute form;
- in case of stomach and intestinal bleeding;
- during pulmonary hemorrhage, tuberculosis in active form;
- during severe kidney disease;
- severe disturbances in kidney function;
- during uncontrolled arterial hypertension in severe form;
- for bacterial endocarditis;
- any low molecular weight heparin is not used in pregnancy in the first trimester.
With special care, the agents of this group are used in the following cases:
- with an increased risk of bleeding;
- with ulcerative stomach disease;
- if there are circulatory disorders in the brain with an ischemic type;
- if there is recent traumatic injury or surgery on the brain;
- during arterial hypertension with uncontrolled course;
- during the presence of thrombosis of cerebral vessels;
- in disorders of the functioning of the liver, kidneys, pancreas;
- with intramuscular injection, epidural, spinal puncture;
- during diabetes mellitus;
- for women over 60;
- within 36 hours after delivery;
- during neuralgic and ophthalmologic surgeries.
Features of the use of
All medications with low molecular weight heparins can not be used interchangeably, they should be used only according to the recommendations in the manual.
It is impossible during medical therapy to replace one medication with LMWH on another. All agents of this type are administered subcutaneously or intravenously.
The use of these drugs by intramuscular route is prohibited. The dosage of drugs is determined on an individual basis depending on the disease and on the survey data. Treatment and use should only be prescribed by a physician.
Rules for the use of drugs of the group:
- the drug is administered by the subcutaneous route;
- during insertion, it is necessary to raise the fold between the navel and the lower abdomen;
- needle is inserted vertically;
- after insertion, the fold should be held for some time;The
- drug can be injected into the upper part of the shoulder or upper thigh area;
- after the drug has been injected, the place does not need to be ground.

If necessary, then an analysis of the functional type of anti-Xa should be carried out. In these cases, the blood is taken for examination 3-4 hours after the injection, when the anti-Xa content in the blood reaches the highest level.
The normal content of anti-Xa in the blood plasma should be in the range 0.2-0.4 IU anti-Xa / ml. The maximum allowable content is 1 - 1.5 IU anti-Xa / ml.
It is also worth remembering that all preparations of this group differ in the method of production, molecular weight, activity.
How to put an injection of NMG Clexane:
Overview of phlebologist
Opinion of a professional about NMG.
All drugs based on low molecular weight heparins are used mainly for the prevention of thromboembolic diseases and their complications.
These drugs have an antithrombotic effect, which results in the dilution of blood and the prevention of blood clots in the vessels. Therefore, these drugs are not recommended for use in the presence of a high probability of bleeding.
Use them only in accordance with the instructions depending on the disease. Do injections of this type of drugs subcutaneously or intravenously, but not intramuscularly.
Low molecular weight drugs help to eliminate various serious thromboembolic pathologies. Their use ensures the prevention of blood clots, varicose veins and other dangerous disorders of veins and vessels. They should be applied strictly according to the instructions, after an appropriate examination and a doctor's consultation.
Phlebologist, experience 24 years
