The period of menopause often becomes borderline between health and illness. Many ailments with her reminiscent of themselves for the first time or exacerbated. It happens contrary to the expectations of many women who are sure that in the reproductive field they are no longer in danger. Therefore, the probability of running the disease is high. And it is important to know what kind of uterine fibroids, symptoms and symptoms are with menopause. After all, this neoplasm sometimes manifests itself in it for the first time or is activated.
More about fibroids
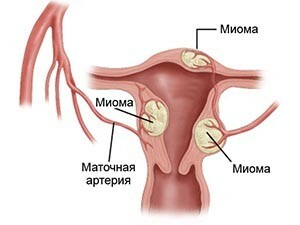 Myoma is a hormone-dependent benign tumor localized in the muscular or connective tissue of the uterus. It can be of different sizes and looks like a round knot with a shiny shell. There are several types of neoplasms, but one of the reasons for their appearance is hormonal failure. Precisely for this reason premenopause and myoma are a common combination, because in this period the fluctuations of estrogens and gestagens together with the growth of FSH volume create a necessary background for the development of the neoplasm.
Myoma is a hormone-dependent benign tumor localized in the muscular or connective tissue of the uterus. It can be of different sizes and looks like a round knot with a shiny shell. There are several types of neoplasms, but one of the reasons for their appearance is hormonal failure. Precisely for this reason premenopause and myoma are a common combination, because in this period the fluctuations of estrogens and gestagens together with the growth of FSH volume create a necessary background for the development of the neoplasm.
Among the other causes of the appearance of the tumor, which are typical for many women on the approach to menopause, experts call:
- Menstrual irregularity( this is a common sign of premenopause);
- Gynecological diseases, transferred earlier. Some of them acquire a chronic course, which is favorable for the development of fibroids. Venereal infections also create the right background for tumor growth;
- Genetic predisposition. Heredity on the female line makes the occurrence of fibroids more likely than absence;
- Early menarche and long reproductive period. If at 50 years are still regular monthly, uterine fibroids are more likely in menopause than in a woman who met menopause on standard terms;
- Often consumed alcohol, smoking. These habits affect the balance of hormones, as well as blood circulation in the most negative way;
- Lack of normal sexual life. This breaks the balance of hormones, which, as already mentioned, is the main culprit in the growth of the tumor;
- Operational interventions on reproductive organs, including abortion;
- Adverse environmental conditions, constant stress.
The fact that the menopausal period and myoma coincide in time, the woman herself is guilty and if the woman decides to take medicines with hormones herself, she is not aware of the importance of proper nutrition, preferring fat, moves little, and generally leads unhealthy life.
How the myoma occurs in menopause
Neoplasm does not necessarily occur for the first time with menopause, even in its initial period. It is found in women of reproductive age. And since they feed the myomas blood vessels, and most importantly - estrogens, you can expect that after the final arrival of menopause it will decrease in size or disappear altogether.
But seriously, it's worth it if you know which fibroids are more likely to dissolve in menopause. Because not all neoplasm reduces its activity with a decrease in the volume of sex hormones. Tears can disappear more likely:
- Intramural, that is formed inside the muscular layer of the uterus;
- Sub-serous, which grow outside the organ.

Signs during the menopause
Myoma of the uterus shows the following symptoms and symptoms in menopause if it has a long existence and a rather large volume:
- Abundant bleeding at any stage of menopause, bleeding between menstruation in premenopause;
- Aching in the lower abdomen;
- Feeling of raspiraniya in the pelvic region, pressure on the adjacent to the uterus organs;
- Painful sensations in sexual intercourse in some cases. It depends on the location and size of the tumor;
- Problems with urination and defecation. Myoma during menopause can contact the bladder and intestines, irritating or crushing on them. Hence the frequent urge to urinate and constipation. Defecation can be painful and accompanied by bleeding;
- Increase in the size of the circumference of the abdomen. Some women before that start the disease, that the tumor leads their appearance to a kind corresponding to several months of pregnancy.
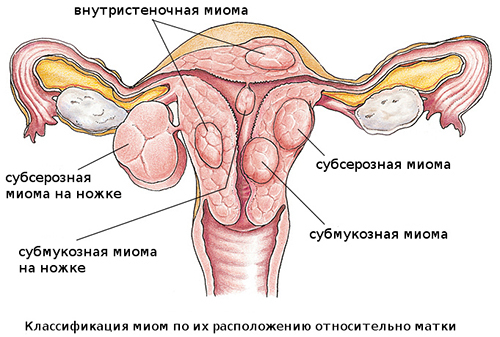
Types of uterine fibroids during menopause in women
Than a new growth in menopause
As already mentioned, small size fibroids during the menopause may not cause noticeable manifestations. But even if it does not grow, it is necessary to control it, although for the most part it does not threaten anything. In some cases, and with a small myome, the appearance of cancer cells is likely, but only 0.1% are recorded.
Prerequisites for this may be the circumstances mentioned above that cause the appearance of the benign neoplasm, and:
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Human papillomavirus;
- Overweight.

The growth of fibroids in menopause is characterized by a changeable state of health, but most importantly - intensive bleeding. They lead to less dangerous than cancer, but still a serious disease - anemia. And this means strengthening signs of menopause, constant weakness, fainting. Malignant cells can be the next step if you continue to wait and not be treated.
What to do with myoma
 If a woman herself suspected that she has a uterine myoma, with menopause symptoms and treatment should be justified by specialists. It is necessary to differentiate the disease from other ailments having similar manifestations. To do this, use hardware diagnostics, but this is already the business of physicians. And the woman herself should visit the doctor from time to time, as more often the neoplasm is revealed precisely during the examination. The choice of treatment is also the prerogative of specialists, it depends on many circumstances:
If a woman herself suspected that she has a uterine myoma, with menopause symptoms and treatment should be justified by specialists. It is necessary to differentiate the disease from other ailments having similar manifestations. To do this, use hardware diagnostics, but this is already the business of physicians. And the woman herself should visit the doctor from time to time, as more often the neoplasm is revealed precisely during the examination. The choice of treatment is also the prerogative of specialists, it depends on many circumstances:
- The age of the patient and the period of menopause;
- Degrees of severity of symptoms;
- Type of fibroids, the nature of its development( growing or not), multiple nodes or single;
- Concomitant diseases.
Drug therapy for fibroids in menopause
Conservative treatment of fibroids in menopause is indicated if:
- The nodes do not exceed 20 mm in volume;
- The presence of malignant cells in the tumor is excluded;
- Neoplasm is intramural or subserous;
- Uterine size in menopause does not exceed the size of the organ in 12 weeks of pregnancy( normal organ decreases in comparison with the previous size almost three times);
- Neighboring organs are healthy;
- Tumor grows slowly.
Since neoplasm increases with a high volume of estrogens, drug treatment should be directed to its suppression. It is also necessary to take into account the symptoms of menopause, because most of them are caused by a deficiency of this hormone.
 The preparations with menopause with myome can apply the following:
The preparations with menopause with myome can apply the following:
- Having as part of the gestagens Norkolut, Dyufaston. They suppress gonadotropic hormones, therefore, interfere with the production of estrogens. More often this treatment is indicated in the period of premenopause;
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists Buserelin, Diferelin, Zoladex. Preparations block the production of gonadotropins, thus reducing the size of the uterus and nodes;
- Includes derivatives of 19-norsteroid Gestrinone. Thanks to it, the production of estrogens and progestins is reduced simultaneously. But this drug is rarely used;
- Created on the basis of antiandrogens Androkur, Finasteride. Substances affect the processes of hyperplasia and tissue hypertrophy, which reduces the chances of fibroid growth. They are not effective in all cases, so they are also infrequently applied;
- Containing female sex hormones. These drugs have in the composition of both estrogens and progesterone, that is, used for relief of climacteric signs. But having in mind the influence on the increase in myomatous nodules, specialists choose from the media those in which progestogens from the norsteroid series, that is, Cleiogest, Trisequens and their analogues.
 We recommend reading the article about the causes of bleeding after menopause. You will learn about the diseases that cause pathological discharge during menopause in women.
We recommend reading the article about the causes of bleeding after menopause. You will learn about the diseases that cause pathological discharge during menopause in women.
Surgical treatment of
Myoma of the uterus after menopause often leads to resort to surgery. And the drug treatment in this case will be applied before the operation to reduce the tumor. Then there are several possibilities for intervention.
The most modern - embolization of uterine arteries. This is the cessation of feeding the tumor( unless it is submucous) by blocking access to blood. In the uterine artery through the femoral inject a special substance that clogs it. The tumor loses its blood supply and decreases in size or disappears.
This operation allows to save the organ, therefore it was previously considered expedient only for women of reproductive age. But now and in menopause, doctors try to keep the organ if possible, if there are no other pathologies in the reproductive system.
 Sometimes uterine fibroids give such symptoms and signs in menopause that delay in treatment is dangerous for life. This is a rapid and pathological growth, as well as painful manifestations of the woman for the neoplasm( bleeding, pain, severe emotional state), torsion of the base of the node, high risk of degeneration. All of them require intervention without prior medical therapy, and it consists in the removal of the tumor:
Sometimes uterine fibroids give such symptoms and signs in menopause that delay in treatment is dangerous for life. This is a rapid and pathological growth, as well as painful manifestations of the woman for the neoplasm( bleeding, pain, severe emotional state), torsion of the base of the node, high risk of degeneration. All of them require intervention without prior medical therapy, and it consists in the removal of the tumor:
- With the retention of the uterus and appendages. This can be done abdominal, laparoscopic or hysteroscopic. The first intervention is carried out through the incision in the abdominal wall with removal of the nodes, sewing each layer. It is risky for neighboring organs and traumatic. Laparoscopy is done through several punctures in the abdomen, through which a video camera and instruments are inserted. Here, healing is faster, but the danger of touching the organs adjacent to the uterus is preserved. With hysteroscopy, the risks inherent in the two previous methods are lower, as it is done through the vagina. But there is a danger of infection, burns, the need for re-intervention;
- With the removal of the organ, and sometimes the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Hysterectomy can be performed with or without cervix left. Here, too, there are options for intervention methods, it can be performed laparotomically( using a scalpel and incisions), laparoscopically or using a hysteroscope with a small uterus.
Climax and myoma are not a rare combination. But there are many ways to treat the tumor. Therefore, do not waste time and energy, spending them on folk methods, delaying treatment to a doctor. This increases the risk of malignant neoplasm, causes an exacerbation of climacteric syndrome.
