The blood loss during menstruation on the average is about 30-40 ml, although 80 ml can be considered the norm. Nevertheless, in some women, the loss can be much greater. Menorrhagia is a medical term that implies excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding. Loss of large amounts of blood during menstruation can lead to anemia( few red blood cells), which will affect the quality of life. But can death come from menstruation with heavy bleeding? Yes, there are life-threatening cases of menorrhagia that require emergency blood transfusion.
Normal menstrual cycle
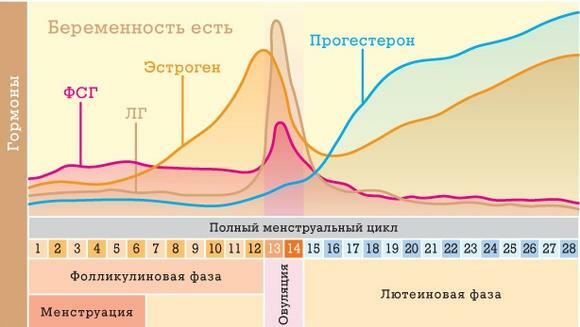
The duration of the normal menstrual cycle ranges from 21 to 35 days( an average of 28 days).Characterized by a series of changes occurring in the uterus, ovaries, hypothalamus and pituitary gland, whose purpose is to prepare the female body for pregnancy. Follicle stimulating( FSH) and luteinizing( LH) hormones that are produced by the pituitary gland play a major role in this process. In the first half of the cycle, FSH stimulates the maturation of the follicle( in it there is an ovum), which leads to an increase in the body level of estrogen, a hormone that stimulatesproliferation of the endometrium( inner layer of the uterus).All these events result in a "splash" of LH, rupture of the follicle and release of the ovum from the ovary( ie, ovulation).
The phases of the menstrual cycle
After ovulation, the ovaries produce both estrogen and progesterone. Their task in the second half of the cycle is to prepare the uterus for possible fertilization of the egg and subsequent pregnancy. Progesterone during this period helps to "stabilize" the mucous membrane of the uterus, prevents abnormal bleeding. If pregnancy does not occur, estrogen and progesterone levels decrease, endometrial rejection occurs. This process of "releasing" the uterine cavity from the mucous membrane and blood is called "menstruation."

Anovulation is a pathological condition when the ovum does not ripen and release from the follicle. Because of the absence of normal hormonal changes that are observed during ovulation, the growth and rejection of the mucous uterus is uneven, the non-decreasing levels of estrogen continue to stimulate it, it becomes thicker than usual. In turn, the amount of progesterone is not enough, there is an uneven rejection of the mucosa, which can lead to severe and / or prolonged bleeding.
Menorrhagia( profuse monthly) in adolescence, usually occur due to anovulation. Anovulatory bleeding can occur before menopause( perimenopausal period), as well as in endocrine pathologies( eg, in hypothyroidism and polycystic ovary syndrome).
Menorrhagia
During normal menstruation, women lose an average of 60 ml of blood, the duration of menstruation - 3 - 5 days. With menorrhagia, blood loss exceeds 80 milliliters, lasts more than 7 days. It should be noted that only 10% of premenopausal patients who complain of heavy bleeding( every third woman in this period comes to see a doctor with this complaint) will be diagnosed with menorrhagia.
A number of pathological conditions and diseases contribute to the appearance of menorrhagia. These include:
- Myoma.
- Uterine polyps( the most commonly diagnosed benign uterine tumor).
- Retroversion of the uterus( non-standard location, deviation of the uterus).
- Contraceptive( oral contraceptives or intrauterine device).
- Coagulopathies are pathological conditions due to impaired coagulation. The presence of coagulopathy can lead to severe menstrual blood loss. According to many studies, from 10% to 17% of cases of menorrhagia can be associated with this pathology. Von Willebrand disease( genetic disease) is a vivid example of coagulopathy, in which menorrhagia is quite common. It can be the main and only clinical manifestation of this hereditary bleeding disorder. The first description of von Willebrand's disease is associated with a patient who died of hemorrhage with menstruation at the age of 13 years.
- Uterine cancer.
- Inflammation of the uterus and / or appendages.
- Endometriosis( cells of the inner layer of the uterus expand beyond its boundaries).
- Adenomyosis( a pathological condition in which the proliferation of glandular tissue of the uterus into the muscle that causes severe bleeding, as well as pain, are observed most often in large children
- A number of diseases: thyroid cancer, systemic lupus erythematosus, diabetes mellitus
- The use of anticoagulantsand some anti-inflammatory drugs, are also capable of causing heavy bleeding
 We recommend reading the article about the treatment of menorrhagia. With it you will learn about the causes of the pathology in womensymptoms, diagnosing with abundant menstrual discharge and prescribed by doctors
We recommend reading the article about the treatment of menorrhagia. With it you will learn about the causes of the pathology in womensymptoms, diagnosing with abundant menstrual discharge and prescribed by doctors
As for menorrhagia( profuse menstruation), life-threatening blood loss is possible, but this happens very rarely. It is most often observed with hereditary coagulopathies, when the work of genes is disrupted, responsible for the synthesis of clotting factors. However, the question arises: what was the root cause of death - the absence of coagulation factors or the onset of menstruation?
To die from blood loss, it is necessary for a person with a weight of 70 kg to lose at least 2 liters of blood within 20 to 30 minutes, which is impossible with normal menstruation. If a girl or a woman has a menorrhagia, then she can not do without treatment. And at any suspicions it is simply necessary to appear to the doctor.
