Ovarian cyst is a tumor-shaped hollow formation, in most cases filled with liquid contents. It can occur in different age periods of a woman's life, have both benign and malignant character. The cyst may be hidden for some time, as well as with various symptoms: pain in the lower abdomen, a violation of the regularity of menstruation, and so on. What is inflammation of the ovarian cyst, why does it occur and whether it threatens the woman's health?
Causes of inflammation of the ovarian cyst
Cystic formation on the ovary can be formed by variousreasons. Including as a result of the infectious process in the field of appendages.
But most often, functional cysts are formed, which are a consequence of the violation of the processes of ovulation. Thus the follicle grows, reaching at times very large sizes and thus forming a cyst.
In primary inflammation of the ovarian cyst, the signs of this process are limited by the appendages. As a rule, such conditions are well suited to conservative therapy. With secondary inflammation, the ovarian tissue becomes involved in the pathological process following the vagina and the uterine cavity. The course is more serious, surgical intervention is often necessary.
The following are the main conditions that can lead to the involvement of the cyst in the inflammatory process:
- Presence of a chronic or acute infection of the genitals. This concerns gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, urea- and mycoplasmosis, HSV and even HPV, as well as some others.
- Immunodeficiency conditions in a woman against HIV( often with a latent flow), constant stress, anxiety, vitamin deficiency, exhaustion, etc.
- The presence of a contraceptive spiral in the uterus, especially if it is not replaced on time or the woman has an active sex life with different partners. This is because the antennae and threads of the IUD are a good absorption material not only for pathogens, but also for conditionally pathogenic microbes. The latter include E. coli, diplococci, strepto-, staphylococcus and others. They can fall into the genital tract of a woman from the intestine, urinary system, etc.
- Various manipulations inside the cavity, especially abortions, scraping, hysterosalpingography, etc.
- The postpartum period is also dangerous from the point of view of the development of ovarian inflammation, as the immunity of a woman at this time is sharply reduced, and pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate into the uterine cavity and then through the cervical canal that has not yet closed.
- Similar complications can occur after purulent appendicitis, especially if inadequate antibacterial therapy is used.
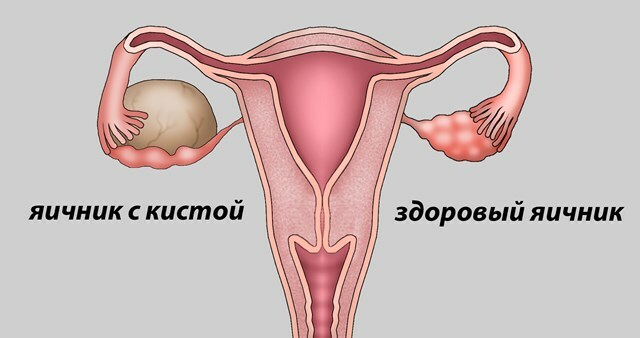
Symptoms and signs of exacerbation
Inflammation of the ovarian cyst in most cases is accompanied by at least minimal symptoms, but not always given proper attention. It all depends on the aggressiveness of the infection, which caused the pathological process, as well as the state of the woman's own protective forces. A significant role is played by the size of the cyst itself and then, both ovaries are involved or only one.

Easy degree
This condition is accompanied by the following set of symptoms:
- The general state of health does not suffer, the woman leads a practically normal way of life. In view of discomfort, women usually limit physical activity and try not to behave excessively actively.
- Body temperature remains normal.
- Disturbing pulling pains in the lower abdomen, which can concentrate more left or right( depending on the location of the cyst).Sometimes they give to the area of the rectum.
- There may be frequent urination, especially when the cyst is just behind the bladder.
- Often inflammation of the cyst is accompanied by , a violation of the menstrual cycle - delay and, more rarely, bleeding or irregular swabbing.
Moderate degree of
With progression of the previous stage, as well as in the absence of proper treatment, the inflammation becomes more active. In this case, the woman begins to feel the following:
- Abdominal pain is so intense that a girl can not lead her usual way of life, it forces her to seek medical help.
- Body temperature may rise to subfebrile values.
- Pains are intense, there may be a parallel with them the urge to defecate or urinate. They are associated with irritation of the rectum and bladder with an inflamed cyst.
Pronounced inflammation of
At this stage, the cyst and the ovary itself are so involved in the inflammatory process that this leads to the formation of an abscess. Along with this, a pyosalpinx is formed - accumulation of pus in the fallopian tubes, as well as traces of inflammation in the uterine cavity and in the vagina. This is the most dangerous condition, which in 95% of cases requires immediate surgical treatment.
Self-perforation of the cyst is possible with the release of pus into the abdominal cavity and small pelvis. This leads to the formation of pelvioperitonitis - a condition that threatens the life of a woman. The main symptoms are as follows:
- The girl is troubled by severe pain in the lower abdomen, often they are diffuse.
- Body temperature rises to 38 - 39 degrees, there are symptoms of intoxication( weakness, lethargy, pallor, rapid pulse, lower blood pressure, etc.).
- There is nausea and even vomiting, perhaps - diarrhea( due to irritation of the walls of the rectum with abscess or pus).
Look at the video about the ovarian cyst:
What will happen if you do not treat the inflamed cyst
Any inflammation of the cyst should be subjected to compulsory treatment. If it is absent, the further prognosis depends on many factors, including the reactivity of the woman's immunity, the pathogen that caused the disease, etc.
The outcome can develop in several directions:
- With mild uncomplicated inflammation, an independent cure is possible. But in any case, there are consequences. It can be just a soldering process in a small pelvis, which will constantly give drawing pains in the lower abdomen. Possible the development of tubal obstruction and infertility. After inflammation, ovarian cysts are also characterized by various malfunctions of the menstrual cycle.
- Progression of the process with the development of pelvioperitonitis. This is a very serious situation that requires immediate surgical treatment. In 80% of cases, removal of the uterus and appendages is carried out in the complex due to pronounced inflammation. After this, a long period of rehabilitation follows.
Any infectious processes of genital organs, including inflammation of the ovarian cyst, must be treated in a timely and competent manner. Otherwise, the consequences can not be avoided: in most cases all this affects the reproductive function of the woman, she subsequently has problems with pregnancy.
Diagnosis of cyst status
Diagnosis of such conditions is not always unambiguous, since many pathological processes, not only gynecological, can behave in this way.
The main surveys are aimed at addressing the choice of conservative or operational treatment tactics at the moment. They are as follows:
- A general blood test, in which leukocytes, ESR, are elevated, anemia may appear.
- Urine examination allows to establish whether the process is associated with the pathology of the urinary system.
- An extensive biochemical blood test in which CRP( C-reactive protein, an inflammatory marker in the body) will be elevated, possibly other enzymes.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, according to the results of which it will be possible to establish volumetric formation in the small pelvis, if there is - fluid in the fallopian tubes and abdominal cavity.
- If the process has a subacute current, it is possible to additionally define oncomarkers - CA-125, HE-4, the ROMA index to exclude the malignant process.
- If there is a delay, it is necessary to exclude pregnancy. You should perform a test or donate blood to HCG.
The general examination of the abdomen and gynecological examination are of fundamental importance. If there is a suspicion of pelviperitonitis or an acute process in the small pelvis, which will be confirmed laboratory, there is a need for surgical treatment.
Treatment of inflammation of the cyst
Tactics in these situations begin with conservative therapy. The question in its duration is maybe an hour or two, or several days. In the most favorable course of the pathology, conservative therapy avoids emergency surgical intervention. In this case, the question of removing the cyst is already in the planned order, if it does not disappear after the course of therapy.
Conservative treatment
The following medicines are used:
- Antibacterial drugs .As a rule, this is a combination of several serious drugs with different directional effects. For example, often in a complex go cephalosporins and metronidazole, and also effective carbapenems and aminoglycosides, etc. Ideally, if the drug is selected taking into account the sensitivity, which is revealed during sowing( for example, vaginal secretions).
- Anti-inflammatory and analgesic therapy. This group includes NSAIDs( diclofenac, ibuprofen and others), antispasmodics, analgesics.
- Vitaminotherapy for strengthening immunity. Usually it is group A, E and C.

Surgical treatment
Operation is necessary in the following situations:
- for suspected ovarian cyst abscess;
- in case of development of pelvioperitonitis;
- in case of ineffectiveness of conservative therapy;
- if after a successful drug treatment the cyst remains after the expiration of 2 - 3 months.
The scope of surgical intervention depends on many factors. But two of all the most significant:
- The woman gave birth or not. Often the question arises about the need to remove the uterus due to a pronounced inflammatory process, which involved all the organs of the small pelvis. If the girl has not yet given birth, if possible, the doctor can take certain risks and remove only the cyst or appendages from the affected side. Preservation of the body of the uterus and part of a healthy ovary allows in future( with the help of ECO-technologies) a girl to become pregnant.
- How serious is the condition on admission. If this is an easy inflammation, the volume is less. The more pronounced the process, the more tissues will be removed, as there is a "melting" of their pathogens with the formation of pus, and there is nothing to save.
In most cases, an abdominal operation is performed with access through the anterior abdominal wall( median or Pfannenstil incision).If the process of inflammation was suppressed, laparoscopic removal of formations is possible. The following surgical options are possible:
- removal only cysts;
- resection of the cyst with part of the ovary;
- removal of appendages with one or two( in the case of a parallel process) parties;
- amputation or extirpation of the uterus with contiguous structures( ovaries, etc.).
Prognosis for a woman
The prognosis depends on how pronounced the process of inflammation of the cyst was. In rare cases, recovery is possible without consequences for health and reproductive function. Typically, the following problems occur:
- periodic or persistent abdominal pain that is caused by the adhesion process in the small pelvis after acute inflammation of the ;
- problems with conception, up to infertility( with obstruction of the fallopian tubes or after removal of the uterus);
- a woman can "lose" the ovaries, and then she will have to take hormone replacement therapy for the rest of her life.
 We recommend reading an article on the treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery. From it you will learn about the types of cyst and its symptoms, the dangers to the body, the treatment and effectiveness of folk remedies.
We recommend reading an article on the treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery. From it you will learn about the types of cyst and its symptoms, the dangers to the body, the treatment and effectiveness of folk remedies.
Inflammation of the ovarian cyst is a serious pathology, which requires a fairly long and competent treatment. In case of untimely request for medical assistance and failure to comply with all the recommendations of a doctor, a woman can put her reproductive health in serious danger.

 We recommend that you read an article on the monthly for an ovarian cyst. From it you will learn about the cyst and its effects on the menstrual cycle and the monthly, signs of rupture of the cyst, the peculiarities of its treatment.
We recommend that you read an article on the monthly for an ovarian cyst. From it you will learn about the cyst and its effects on the menstrual cycle and the monthly, signs of rupture of the cyst, the peculiarities of its treatment.