 Although both children and adults suffer from stomatitis, the disease is considered childish, especially when it comes to aphthous stomatitis, called "dirty hand disease".
Although both children and adults suffer from stomatitis, the disease is considered childish, especially when it comes to aphthous stomatitis, called "dirty hand disease".
Aphthous stomatitis, which is one of the most common forms of inflammation of the oral cavity in childhood, provokes staphylococcal, streptococcal and diplococcal infections.
In kindergartens, the disease often acquires an epidemic character and can develop simultaneously with influenza, measles, diphtheria.
Contents of
- What is it?
- Features of the clinical picture in the child
- Causes of the development of inflammation
- Types of the pathological process
- Approach to therapy - a set of measures
- Medical prescriptions
- Gels and antiseptic rinses
- Traditional medicine recipes
- Homeopathic remedies
- Preventive measures
What is it?

In the photo, aphthous stomatitis of the lower lip
With aphthous stomatitis, the mucosa of the oral cavity is affected by an infection that causes the inflammatory process with the appearance of characteristic rashes in the form of small sores of yellow-white color surrounded by inflamed reddened areas. Such formations are shortly called afts.
Most often, the localization of aft( as a rule, the total number - no more than 3) becomes the inner side of the tongue, cheeks, lips or sublingual space.
In a number of cases, large-scale lesions are observed with simultaneous formation of the order of 10 ulcers that merge into extensive painful foci.
For the diagnosis of the disease, a physician should conduct a visual examination of the patient and interview him, forming a clinical picture. In order to differentiate this form with ulcerative necrotic and herpetic stomatitis, laboratory tests can additionally be prescribed.
Clinical features of the child
Aphthous stomatitis in children can occur with the following symptoms:
-
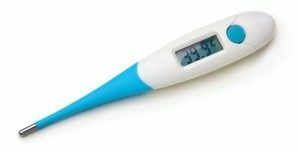 temperature rise to critical values (39 degrees);
temperature rise to critical values (39 degrees); - excessive salivation;
- appearance of bad breath;
- appetite impairment;
- increased irritability and tearfulness( especially in young children);
- presence in the oral cavity of redness, passing into the sores.
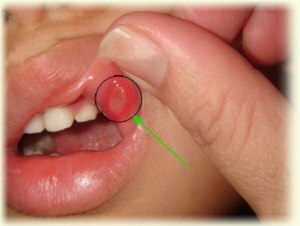
Afts appear simultaneously, provoking a temperature jump, after which the condition stabilizes a little, but the child at the same time feels obvious discomfort due to soreness of the mucosa. After a couple of days, rashes may appear again with another increase in temperature. Against the background of such symptoms in the acute course of the disease, the submaxillary lymph nodes become enlarged and painful.
Often the diagnosis is made with a significant development of inflammation, which is due to the characteristic for the initial stage of the course similar to the usual cold. From the moment of the emergence of aphthus to the full recovery, no less than 10 days pass. All these days, there are strong painful sensations that make speech and eating difficult.
Causes of inflammation development
To date, dentists and pediatricians can not give an accurate definition of the causes of development of aphthous stomatitis.
But there are a number of factors that significantly increase the risk of this pathology:
-
 the child has an allergic reaction of any type( for food, dust, drugs, oral hygiene products);
the child has an allergic reaction of any type( for food, dust, drugs, oral hygiene products); - disorders of functioning of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract in the form of erosion of mucous membranes, dysbacteriosis, inflammation of the esophagus or pharynx;
- deviations in the functioning of the central and autonomic nervous systems;
- frequent diseases of ENT organs of an inflammatory nature;
- hypovitaminosis;
-
 mechanical trauma to the oral mucosa;
mechanical trauma to the oral mucosa; - development of carious processes;
- availability of chipped, tartar, poorly installed seals;
- inadequate oral hygiene.
According to experts, the ailment is practically unrelated to the development of acute respiratory disease in the child, but with accompanying high blood pressure and respiration through the mouth( due to nasal congestion), the mucosa becomes over-dried, so saliva is unable to perform its protective function. As a result, favorable conditions are created for the penetration of viruses and bacteria.
The causes and symptoms of stomatitis will be told by the doctor dentist of the children's clinic:
Types of the pathological process
The type of aphthous stomatitis is determined by the nature of its course:
- Acute .It is characterized by a sharp soreness of the sores. Pain can increase when contacting affected areas with hot, spicy or sweet food, during a conversation due to movements of the tongue. The child raises the temperature, there is a headache, there is a violation in the work of the digestive tract( often stomatitis is accompanied by diarrhea due to intoxication of the body).
- Chronic recurrent .Usually this type of disease is manifested in children who are already 4 years old. A characteristic feature is a prolonged course of about 2 weeks. Exacerbations occur in the autumn and spring periods and develop under the influence of mucous injuries, fatigue, stress or a viral infection.
Approach to therapy - a set of measures
If you have any suspicious symptoms that indicate the possible development of aphthous stomatitis in a child, you should immediately contact a doctor( pediatric dentist or pediatrician) to choose an effective adequate treatment. Usually, therapy consists of local and general activities.
Medical prescriptions
 Therapy is carried out using antihistamines( Suprastin, Tavegil or Claritin), drugs to eliminate viral infection, vitamin complexes and drugs-immunomodulators.
Therapy is carried out using antihistamines( Suprastin, Tavegil or Claritin), drugs to eliminate viral infection, vitamin complexes and drugs-immunomodulators.
Local immunomodulators in the form of toothpastes with lysozyme, lactoferrin, glucose oxide are especially effective. These enzymes increase the local immunity of the oral mucosa and make it resistant to the action of bacteria and viruses.
Older children may be prescribed Imudon in the form of lollipops( within two weeks every day you need to dissolve about 6 pieces).In severe cases, steroids and antibiotics may be prescribed.
Gels and antiseptic rinses
Preparations for local treatment are prescribed, based on the severity of the process. At the initial stage, it is effective to irrigate the aphids with antiseptic Miramistin, which provides bactericidal action. It is indicated to children of any age in the absence of allergy to the components of the drug. During the day the procedure is carried out 4 times.
 The first stages of the disease are effectively eliminated and thanks to the use of holisal gel, which not only removes the symptoms of inflammation, but also effectively anesthetizes the affected areas. The treatment is carried out 3-4 times a day. In severe pain syndrome, the gel should be used before meals. Restriction to use is a child's age of up to a year.
The first stages of the disease are effectively eliminated and thanks to the use of holisal gel, which not only removes the symptoms of inflammation, but also effectively anesthetizes the affected areas. The treatment is carried out 3-4 times a day. In severe pain syndrome, the gel should be used before meals. Restriction to use is a child's age of up to a year.
If aphthous stomatitis is at the healing stage and pain sensations are completely absent, it is possible to accelerate the recovery process with Actovegin-gel, which is an epithelizing agent.
Traditional medicine recipes
Along with medicines to ease the condition of the child with aphthous stomatitis, herbal decoctions help:
-
 Mix chamomile flowers, peppermint leaves, sage( 3 teaspoons) and fennel ( 1 teaspoon), pour the mixture with a glass of water and put on a slow fire for 20 minutes( the time is indicated from the boiling point of the broth).After the infusion has cooled, it is filtered and used for rinsing in a warm form. Daily it is necessary to carry out the procedure at least 5 times;
Mix chamomile flowers, peppermint leaves, sage( 3 teaspoons) and fennel ( 1 teaspoon), pour the mixture with a glass of water and put on a slow fire for 20 minutes( the time is indicated from the boiling point of the broth).After the infusion has cooled, it is filtered and used for rinsing in a warm form. Daily it is necessary to carry out the procedure at least 5 times; - Make a calendula tincture of , pouring a teaspoon of dried flowers with a glass of warm boiled water and brewing the broth on a water bath.
Homeopathic remedies
Among effective for aphthous stomatitis funds are:
- Arsenium album - to eliminate severe pain, anxiety and thirst( combined with warm drinking);
-
 Sulfur - with severe pain, if the child prefers cold drinking;
Sulfur - with severe pain, if the child prefers cold drinking; - Natrum muriaticum - if the child's lips are over-dried, aggravation of the process provokes a stay in the open sun, there is a craving for eating salty foods;
- Borax - if aphthous stomatitis develops concomitantly with candidiasis and bleeding lesions occur;
- Natrum phosphoricum 6X - promotes fast( within 2-3 days) healing of sores and is a means of prevention, if aphthous stomatitis occurs in chronic form, is considered a universal drug.
The doctor should choose the homeopathic remedy, focusing on the manifestations of the disease in the child in a particular case.
And, of course, we must not forget about the quality of oral hygiene.
Preventive measures
Prevention of aphthous stomatitis in children is, first of all, regular oral and hand hygiene, cleanliness of the surrounding environment, timely treatment of caries affected teeth, balanced nutrition.
 If the disease has already manifested itself repeatedly and the diagnostic form of aphthous stomatitis has been established, prevention means a number of measures that can prevent relapses:
If the disease has already manifested itself repeatedly and the diagnostic form of aphthous stomatitis has been established, prevention means a number of measures that can prevent relapses:
- revealing chronic disorders of internal organs;
- assessment of the correct formation of the dentition and bite;
- obtaining advisory opinions of an immunologist, gastroenterologist, dentist and otolaryngologist.
The disease is easily treatable if the disease is diagnosed in a timely manner. Complex therapy and adherence to the doctor's recommendations can ensure a lasting result, supported by a thorough care, attentive attitude to the child and compliance with preventive measures.
