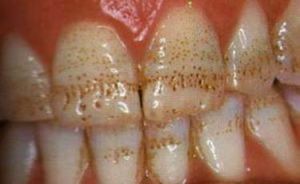
 Necrosis is a pathology of tissues of a living organism, manifested in the death of cells without subsequent regeneration and with the complete cessation of their functioning.
Necrosis is a pathology of tissues of a living organism, manifested in the death of cells without subsequent regeneration and with the complete cessation of their functioning.
This deviation develops under the influence of strong stimuli and can be accompanied by swelling or, conversely, dehydration of the tissues.
content
- Feature of pathologic process in the oral cavity
- factors dieback
- gums cells Precipitating
- Properties clinic
- Diagnosis and treatment
- Necrotic changes tooth hard tissue
- Classification destructive process
- Diagnosis and treatment
- Summarizing
Feature of pathologic process in the oral cavity
Necrosishard tissues of teeth and gums - a dangerous phenomenon that eventually leads to a complete loss of chewing gumfunctions. Dying of dental tissues in the oral cavity is a process of gradual necrosis of dentin and enamel cells. Such a dental disease is difficult to treat.
The death of gum cells and hard tooth tissues can be caused by various factors - both external( direct exposure from outside) and internal( diseases of internal organs, changes in the state of the body).
The pathological process affects several teeth at once. When the disease progresses, the tissues are quickly erased and the damaged teeth are loosened.
Gingival cell death
Gingival necrosis is an abnormal process that manifests itself in the dying of the soft tissues of the oral cavity. The development of the disease is associated with impaired blood circulation. Affected areas are not restored even during medical treatment.
Aggravating factors
The structure of the gum is destroyed due to such factors:
- lack of proper care of the oral cavity, which leads to inflammation of the gums;
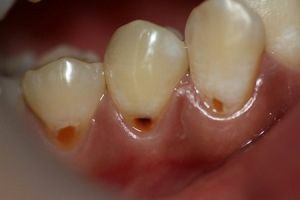
- the patient has gingivitis or periodontitis in neglected form;
- mechanical gum disease caused by burns, the action of medical instruments, frostbite;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- hormonal disorders, changes in the hormonal background( the provoking factor including pregnancy is also provoking);
- reduced immunity;
- patient use of drugs;
- the effect of radiation on the body, the conduct of radiation therapy;
- getting into and developing an infection that affects the tissues;
- disturbance of metabolic processes.
Separately it is worth noting the harm for gingival tissue from a material such as arsenic, which is sometimes used in the dental field to eliminate pulp from the bowels of the tooth. Arsenic has a destructive effect on soft tissue and can lead to the development of gingival necrosis.
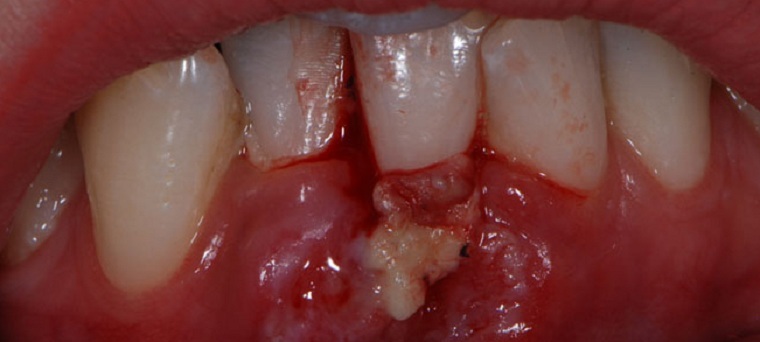
On the photo, gingival necrosis, developed from pulp of arsenic
Features of the
Clinic The necrosis of the gum tissue is expressed in the following signs, which become more pronounced as the pathology progresses.
The first thing that should alert a patient is severe bleeding of the gums for no apparent reason. Other signs of the disease are:
- loss of gloss enamel;
- discoloration and surface roughness of the teeth;
- appearance of bad breath;
- reddening of the gums and puffiness, a slight lag of their surfaces from the tooth;
- enlargement of the lymph nodes.
As the death of tissues progresses, there is an increase in body temperature, as well as increased bleeding of soft tissues, the appearance of a gray coating on the surface of the teeth and their gradual blackening, loosening.
Against the background of the described symptoms, the patient experiences constant headaches, loses sleep and appetite.
Diagnosis and treatment of
Diagnosis of the deviation is based on the identification of the following criteria:
- presence of an unpleasant odor coming from the oral cavity;
- color of gum tissues, their structure;
- tenderness of soft tissues, the presence of bleeding;
- the presence of signs indicating the intoxication of the body - insomnia, benign pain, upset stomach.
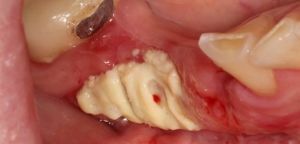 In addition to the methods of visual inspection of the oral cavity, the dentist assigns the patient an X-ray examination and instrumental diagnostics.
In addition to the methods of visual inspection of the oral cavity, the dentist assigns the patient an X-ray examination and instrumental diagnostics.
The first method produces a picture of necrotic tissue destruction and possible complications caused by this.
X-ray examination allows us to establish the stage of the pathological process.
Methods of instrumental diagnostics presuppose a microscopic examination of soft plaque. The result is getting information about the composition of microflora, the number of leukocytes, the definition of fungi.
The dentist also examines the likelihood of concomitant oral diseases.
Regarding the treatment of the destructive process, the effectiveness depends on the stage of its development, the presence or absence of other soft tissue diseases. Already affected areas can not be treated, because necrosis is irreversible. Dead cells can only be removed surgically to avoid further destruction and spread of infections.
There are two ways to stop the pathology:
- Treatment of affected tissues with antiseptics and restoration of normal circulation, surgical removal of completely deadened areas. This method of treatment is used for dry necrosis.
- Conversion of wet necrosis into a dry stage followed by treatment of affected areas with disinfectants, opening of purulent areas and draining them.
Since death leads to the rapid spread of infection and causes intoxication of the body, the patient, along with the described procedures, is prescribed antibacterial and detoxification therapy.
With timely treatment, while necrosis is in the early stages of development, the prognosis of the disease is favorable: special measures restore normal blood circulation in the gum area, help stop bleeding and eliminate pain and unpleasant odor.
If the treatment does not work, as observed in the late stages of necrosis, the chewing function may be lost. In addition, the gums and teeth are completely destroyed.
To prevent the destructive process, it is recommended to provide a full and regular care of the oral cavity, timely contact the dentist in case of problems, fully eat, treat chronic diseases.
Necrotic changes of hard tooth tissues
Necrosis of enamel and dentin of teeth arises from the presence of provoking factors of internal and external nature: 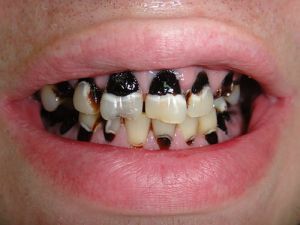
- The first group of unites such causes as a violation of the activity of organs and body systems: these are malfunctions in the central nervous system and gland functioninternal secretion, genetically malfunctions. Also, the death of cells of hard tissues is observed during pregnancy, when a serious hormonal restructuring takes place in the woman's body.
- The reasons for the external nature of are unfavorable factors directly affecting a person. These include the effects of chemicals, radioactive radiation, as well as electromagnetic influence. Often necrosis of teeth occurs in representatives of those professions, whose activities are associated with these harmful substances.
Classification of the destructive process
In the dental field, such types of dental necrosis are considered:
- Cervical necrosis. He got his name because the defeat extends to the neck of the teeth. These areas are covered with white spots, and then the loss of enamel gloss is observed, the bone tissue becomes loose and crumbles. Necrosis quickly spreads, destroying enamel en route. This type of pathology is typical for patients with hormonal disorders( including those in pregnant women).
- Acid .This type of disease arises from the inhalation of a person with vapors saturated with acids. Such substances wash calcium out of the body and actively destroy hard tooth tissues. With acid necrosis of the teeth, characteristic symptoms are observed, such as the roughness of the tooth enamel and its graying. Teeth become very sensitive to temperatures. As the pathology progresses, the affected tooth is erased to the gum surfaces.
- Post-beam .This type of necrosis is a reaction to the effect of radioactive radiation. Characterized by the gradual destruction of enamel, the color of which varies from gray to black. The process of necrosis spreads over large areas with the patient not feeling sick or uncomfortable. In the absence of post-radiation treatment, necrosis causes destruction of the whole dentition.
- Computer necrosis of teeth. This type of pathology was discovered relatively recently, about twenty years ago. The development of this form of illness is associated with ionizing radiation emanating from computers. Its influence disrupts the functions of cells and destroys the hard tissues of dentin and enamel. With computer necrosis, the teeth acquire a dark brown or black color, a matte surface.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnostic measures to accurately identify the disease include examination of the patient, collection of anamnesis, differential methods. Polarization microscopy in diagnosis can detect changes in the subsurface layer of the enamel.
The choice of treatment method depends on what type of necrosis was detected:
- When treatment of a prishechnogo pathology initially eliminate the sensitivity of the teeth, then cover their surface with special materials, fill the carious cavities.
- In the destruction of tissues caused by by computer exposure or by irradiation of , necrotic masses are removed and the cavities are filled with calcifying material. After a lapse of a month and a half, the affected tissues of the teeth are removed and reinforcements are applied again. The last stage of treatment is filling with special cements.
- In the case of acidic necrosis, it is first necessary to stop the effect of harmful substances on the tooth. Further, a long course of remineralization of enamel is carried out.
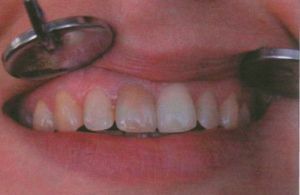
 The consequence of a neglected form of the disease is the loss of the whole dentition.
The consequence of a neglected form of the disease is the loss of the whole dentition.
To prevent exposure to harmful enamel in production environments, it is important to observe safety techniques using personal protective equipment and rinsing the oral cavity with alkaline water every two hours.
Another important condition for prevention is oral hygiene.
Summing up
Necrosis is a dangerous phenomenon that contributes to the destruction of hard and soft tissues. In dentistry, this pathology is seen as a condition that can not be cured completely. Nevertheless, it is possible to stop the destructive process and eliminate already dead areas.
Dying of gum tissue and hard tooth tissues requires different diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Depending on the form and stage of the disease, it can have both favorable and unfavorable outcomes.
In order to prevent pathology, it is important to comply with a set of prescribed measures, especially if a person's professional activity is associated with harmful substances - acids, chemical elements.
