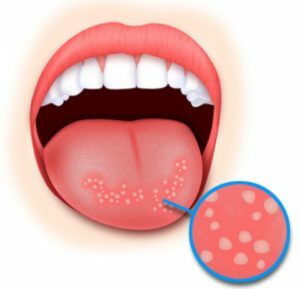
 Inflammatory diseases of the mucous membranes of the child's oral cavity are most often manifested as white plaque, painful ulcers and erosions. This state delivers a lot of unpleasant sensations to a sick kid and a lot of hassle to his parents.
Inflammatory diseases of the mucous membranes of the child's oral cavity are most often manifested as white plaque, painful ulcers and erosions. This state delivers a lot of unpleasant sensations to a sick kid and a lot of hassle to his parents.
Stomatitis should be taken very seriously. At first glance, ordinary child illness can actually arise because of the presence of other, more serious health problems.
Table of Contents
- Aftstatic stomatitis
- Symptoms of
- How to treat the disease?
- Bacterial stomatitis
- Signs of the development of the disease
- How to quickly rid the child of a disease?
- Fungal stomatitis
- How does the disease manifest in the oral cavity?
- Features of therapy
- Traumatic stomatitis
- Than the disease is shown?
- Medical therapy
- Herpetic stomatitis
- Clinic of the disease depending on severity
- What to do in viral pathology?
Aphthous stomatitis
The most common form of the disease in young children. This lesion of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity with the formation of whitish-yellow rashes in the form of ulcers( aphthus).
Aftosny stomatitis in most cases occurs as a result of the reaction of the weakened immune system of the child to pathogens. Frequent precursors of the disease are influenza, diphtheria, measles, adenovirus and other viral diseases.  The reasons for the appearance may be:
The reasons for the appearance may be:
- vitamin deficiency;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- genetic predisposition;
- trauma and infection of the oral mucosa.
The exact causes of this type of disease are not established by specialists.
Symptoms of
At the initial stage, manifestations are very similar to those in an acute viral or respiratory disease. With aphthous stomatitis, the following symptoms are characteristic:
-
 general weakness, lethargy, malaise;
general weakness, lethargy, malaise; - irritability, tearfulness;
- appetite impairment, refusal to eat;
- increase in temperature to 38-39 degrees and above;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck and occiput;
- appearance of redness on the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- formation in the oral cavity of single or grouped painful ulcers( aft), covered with a gray or yellow coating, along the edge of which there is a bright red rim, in the diameter of the formation reach 5-10 mm.
How to treat the disease?
Aphthous( ulcerative) stomatitis certainly requires treatment. In its absence, aphthae( ulcers) begin to merge, increasing in size, and spread to other areas of the oral cavity. At the same time, the pain sensations are greatly enhanced, the child becomes difficult to eat and even speak.
 Local and general therapy is prescribed for treatment. Local treatment includes mouth rinsing and the use of drugs in the form of sprays and gels. Rinse can be carried out with a solution of hydrogen peroxide or soda, with a tincture of calendula or chamomile .From pharmacy funds, Miramistin or Holilasal is suitable.
Local and general therapy is prescribed for treatment. Local treatment includes mouth rinsing and the use of drugs in the form of sprays and gels. Rinse can be carried out with a solution of hydrogen peroxide or soda, with a tincture of calendula or chamomile .From pharmacy funds, Miramistin or Holilasal is suitable.
General therapy involves the use of antihistamines such as Tavegil, Suprastin .To increase the protective functions of the body doctor can recommend a vitamin complex or immunomodulating medications. With a significant increase in body temperature, it must be reduced with antipyretic drugs( Paracetamol, Nurofen ).
 Aphthous stomatitis does not appear immediately after entering the body of pathogens, the incubation period usually lasts about 3-5 days, sometimes longer. After the appearance of the first signs of the disease begins to develop very rapidly and requires emergency treatment.
Aphthous stomatitis does not appear immediately after entering the body of pathogens, the incubation period usually lasts about 3-5 days, sometimes longer. After the appearance of the first signs of the disease begins to develop very rapidly and requires emergency treatment.
Usually during illness the child's body temperature rises up to 39 degrees. All the symptoms of stomatitis in most cases completely go away in 10-14 days, and a full recovery comes.
Bacterial stomatitis
 Its second name is "Dirty Hand Disease".Most often occurs when the bacteria in the body activate streptococcus and staphylococcus. These pathogens are present in the body of even a healthy person, and with the weakening of the immune defense they "wake up".In addition, they can exist in the oral cavity of the child, if he suffers from chronic tonsillitis, caries, laryngitis and so on.
Its second name is "Dirty Hand Disease".Most often occurs when the bacteria in the body activate streptococcus and staphylococcus. These pathogens are present in the body of even a healthy person, and with the weakening of the immune defense they "wake up".In addition, they can exist in the oral cavity of the child, if he suffers from chronic tonsillitis, caries, laryngitis and so on.
If the integrity of the mucous membranes of the mouth is not disturbed, then these bacteria are not dangerous. But in the case of even small damage, they rush to the wound, from which the bacterial process develops in this place.
Signs of the development of the disease
This type of disease can be distinguished from others by external manifestations. When bacterial stomatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
-
 redness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
redness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity; - soft tissue swelling in the mouth;
- appearance of cracks and ulcers;
- increased salivation;
- poor appetite or lack of it;
- unpleasant smell of rot from the mouth;
- weakness and high fever;
- in some cases there are signs of intoxication of the body.
How to quickly rid the child of an illness?
Given the nature of the disease, its treatment should be carried out using antibacterial agents. For local treatment of the oral cavity, you can use Tantum Verde, Miramistin, Hexoral, Metrogyl denta , rinse with solution Furacilin .
With a severe form of the disease, a purulent complication can develop, which will require the child to take antibiotics for oral administration.
 The incubation period is 2-10 days. The disease is contagious primarily for other children. Transmitted by airborne and by contact. An adult person can become infected, but only if they use shared utensils and have sores or microcracks in their mouths.
The incubation period is 2-10 days. The disease is contagious primarily for other children. Transmitted by airborne and by contact. An adult person can become infected, but only if they use shared utensils and have sores or microcracks in their mouths.
The child's body temperature rises on the first day of illness and lasts up to 3 days. If we talk about how long external manifestations of the disease last, they usually go through 7-14 days, then the full recovery also comes.
Fungal stomatitis

In the photo, candidal stomatitis in a newborn
Most often occurs in children of the first year of life, but also occurs at an older age. Other of its names are "thrush" and candidiasis. The disease begins to develop with a decrease in immunity and the ingress on the mucous membranes of the mouth of Candida fungi.
Usually the reason is inadequate hygiene, unwashed hands and the use of non-sterile nipples and bottles. Another provoking factor may be taking antibiotics.
How does the disease manifest in the oral cavity?
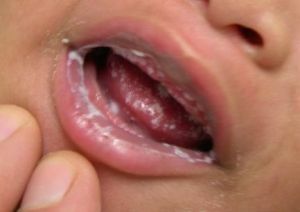 Fungal form of the disease differs from others. It manifests itself in the form of curdled white grains in the tongue, causing damage to the tongue, as well as the inner surface of the cheeks, gums. After some time can spread and on the surface of the lips. If the treatment is not started immediately, the grains merge, forming a loose film, easily detached from the mucosa and covering fairly large areas. The areas under it blush and become inflamed.
Fungal form of the disease differs from others. It manifests itself in the form of curdled white grains in the tongue, causing damage to the tongue, as well as the inner surface of the cheeks, gums. After some time can spread and on the surface of the lips. If the treatment is not started immediately, the grains merge, forming a loose film, easily detached from the mucosa and covering fairly large areas. The areas under it blush and become inflamed.
In addition, the child has moodiness, irritability, poor sleep. His appetite disappears, salivation increases, with a severe form of the disease, fever and weakness may occur.
Therapy features
 Quickly cure an easy form using a weak soda solution. They irrigate the oral cavity of the child. It is also possible to treat the affected areas with a mixture of borax in glycerin. The solution helps Candid , a clotrimazole-based agent that is approved for topical use in infants.
Quickly cure an easy form using a weak soda solution. They irrigate the oral cavity of the child. It is also possible to treat the affected areas with a mixture of borax in glycerin. The solution helps Candid , a clotrimazole-based agent that is approved for topical use in infants.
If local treatment is not effective enough, the patient is prescribed generic drugs: Nizoral, Diflucan .
 The incubation period can last up to 8 days. The disease is contagious and can be transmitted by using shared dishes by both children and adults.
The incubation period can last up to 8 days. The disease is contagious and can be transmitted by using shared dishes by both children and adults.
In "thrush" in children, a fever may occur, but more often the disease runs without it. Fever occurs only with severe disease, in which case it can last up to 3-5 days.
How long does fungal stomatitis take?
With appropriate treatment, the disappearance of symptoms occurs after 7-10 days. But the use of local drugs after this must continue for another 5-7 days, since candidiasis is characterized by relapses.
Traumatic stomatitis
 The name of this type of disease speaks for itself. It occurs due to any injury to the oral mucosa in a child of 1-2 years. Damage can be either mechanical, chemical or physical. Usually occurs during the cognition of the world "through the mouth."
The name of this type of disease speaks for itself. It occurs due to any injury to the oral mucosa in a child of 1-2 years. Damage can be either mechanical, chemical or physical. Usually occurs during the cognition of the world "through the mouth."
This can be a burn during the reception of hot food or some injury to hard objects, such as a sharp edge of the tooth or a toy.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Mucous membranes swell, blush and become inflamed, later in these places ulcers appear. There are painful sensations when opening the mouth, chewing food. In the event of an acid burn, a film appears in the lesion site. With the advanced form of the disease, there may be a rise in temperature, weakness, lethargy.
Medical therapy
 Treatment should begin with the elimination of the cause of the disease. Then, antiseptic treatment of painful areas with a solution of furacilin, peroxide, with decoction of camomile or calendula is prescribed.
Treatment should begin with the elimination of the cause of the disease. Then, antiseptic treatment of painful areas with a solution of furacilin, peroxide, with decoction of camomile or calendula is prescribed.
In complex form of the disease, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agents are prescribed: Holisal, Rotokan, Miramistin, Lugol and others.
Traumatic stomatitis is not contagious. During it, a fever can occur in the baby, but usually it happens only in the absence of timely treatment. Recovery in mild form takes about 7 days, with complex injuries this can take up to 10-14 days or more.
Herpetic stomatitis
The child's disease is possible when the virus first enters the body( HSV-1).Usually, the disease manifests itself in severe form at the time of a decrease in its protective functions and a weakening of immunity. And once having got into the body of a child, the herpes virus can from time to time manifest itself in the form of acute periods.
Clinic of the disease depending on the degree of severity
Appears in the form of painful sores and small vesicles in the mouth and lips of the child. Difficult, medium and mild forms of the disease are distinguished.
With severe form of , the patient's temperature rises sharply up to 40 degrees and extensive inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity appears. There are numerous eruptions that can spread to the area around the lips, the wings of the nose and even the eyelids. The general state of health worsens, there are signs of acute intoxication of the body, severe head and muscle pains, nausea, resulting in vomiting. The child has lymph nodes in the neck.
The average shape of the is characterized by an increase in temperature to 37.5-39 degrees. There is weakness, chills, headache, inflammation of the lymph nodes. Gums and other soft tissues of the oral cavity become inflamed and swell, rashes appear in the form of vesicles on the lips, tongue, cheeks.
What to do in viral pathology?
Obligatory medical examination is required. He will be able to determine the form of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment, in severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
Treatment is carried out in a complex way and pursues several purposes:
-
 antiviral effect;
antiviral effect; - anti-inflammatory effect;
- strengthening of the body's immune function;
- acceleration of healing.
For topical use, the patient is assigned Acyclovir, Zovirax, Holisal .As an immunomodulating agent is recommended Viferon .
When talking about whether herpetic stomatitis is contagious, it should be noted that this species is particularly contagious and transmitted by airborne and by contact. The incubation period for primary infection lasts 3-5 days, with a chronic form may not manifest for several years.
How long does the temperature last?
 High temperature in acute form can last up to 7 days, with an average temperature of up to 3 days. External manifestation of the disease occurs in 1-2 weeks, it is impossible to destroy the virus completely in the body.
High temperature in acute form can last up to 7 days, with an average temperature of up to 3 days. External manifestation of the disease occurs in 1-2 weeks, it is impossible to destroy the virus completely in the body.
All varieties of stomatitis most often affect young children. They are manifested in different ways, but require an indispensable examination of the doctor and appropriate treatment.
