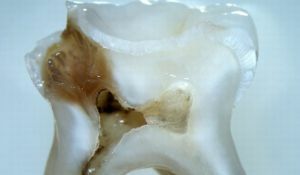
 Deep caries is an irreversible process of destruction of dental tissues, due to the activity of harmful microflora.
Deep caries is an irreversible process of destruction of dental tissues, due to the activity of harmful microflora.
In the process of development of this pathology, a thin layer of normal dentite is observed between the bottom of the carious cavity and the pulp.
If you do not receive timely treatment, this kind of education can cause the development of pulpitis, which eventually develops into periodontitis. When such a disease develops, the inflammatory process spreads beyond the tooth pulp with the simultaneous formation of a purulent sac near the apex of the dental root.
Contents
- About the disease seriously
- Causes and factors provoking the development of the disease
- Classification of the disease
- How to identify a violation
- Diagnostic approach
- Therapy: a review of effective techniques
- Possible complications and prevention
About the disease seriously
At its core, deep caries is considered the final stage of carious developmentprocess, which is characterized by the destruction of hard dental tissues together with deeper layers of dentite.
Clinically, this disease is determined by the nature of the destruction of the crown of the teeth, accompanied by the occurrence of pain in the process of thermal, chemical or mechanical exposure.
Diagnosis of deep caries is carried out on the basis of patient complaints, data obtained as a result of examination, thermal diagnostics.
As a technique for treating deep caries, the practice of applying special tabs, the installation of seals, as well as the preparation of a carious cavity. With this disorder, solid dental tissues are demineralized and destroyed. 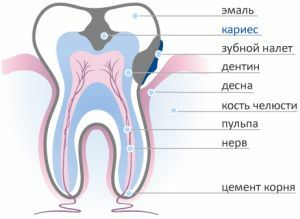
In dentistry three main stages of caries are distinguished:
- initial;
- surface;
- average;
- deep.
Causes and factors-provokers of the development of the disease
To date, scientists have been able to achieve significant results in studying the factors that cause such a disease as caries.
Carious processes are always spread due to the effect on the dental tissues of organic acids produced by individual cariogenic organisms that promote accelerated dissolution. To form such defects, simultaneous combined action of several factors is required.
For this reason, the carious process can not develop in everyone, regardless of the fact that the composition of the microflora of the oral cavity in humans is almost the same.
The following are the main factors contributing to the development of caries:
- Geographic .The development of the disease can be affected by the amount of precipitation, the mineral composition of the local soil, climatic conditions. For example, in the US, caries is spread by 99% of the population, and in Nigeria, only 2%.Fluorine contained in drinking water has a significant effect on the formation of the microflora composition in the oral cavity. The more this substance, the higher the resistance of dental tissues to the effects of harmful microflora. Excessive amounts of fluoride can cause the development of fluorosis, which contributes to external changes and the formation of defects in dental tissues.
- Sexual .The likelihood of caries in girls is much higher than that of men. This is due to the peculiarity of the female body. At a time when girls breastfeed babies, they lose a large amount of vitamins and trace elements. In addition, the regular diet of women includes too many sweets.
- Professional .People who take part in the production process of acids and alkalis, working with confectionery, have a better chance of developing carious processes in the oral cavity.
- Age of the .If one is guided by the data obtained from statistical studies, it can be argued that the activity of the development of carious processes begins to increase from the age of two, and by the age of 11 it may well reach 60%, and its decline has been observed since 40 years.
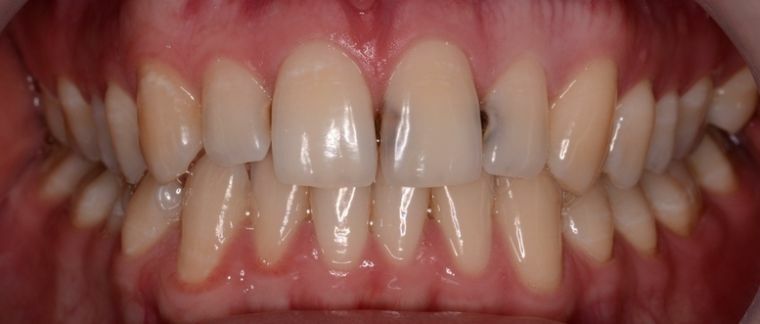
In the photo you can see what a deep caries looks like in the life of
Classification of the disease
Classification of caries according to Black began to be used in 1896 to establish standard medical procedures for the individual manifestation of the disease. Under each class is meant a separate method of filling and preparation.
So:
- to the first class is considered to include carious formations in pits, fissures and other natural depressions;
- second class refers to carious formations on contact surfaces;
- to the third class includes the formations on the contact surface of the front teeth and canines that do not violate the integrity of their cutting faces;
- the fourth class implies a much more serious formation on the fangs and incisors, the caries at the same time destroys the cutting edges of the teeth;
- caries in the fifth stage affects all teeth in areas close to the gums;
- for of the sixth is characterized by carious formations on the cutting surfaces of canines and anterior incisors and on the molars of molars.
How to identify a violation of
In the initial stages of the development of the disease, spots of dark or white coloring appear. The enamel is not destroyed and remains smooth.
The formed small spots are removed with the use of special dental devices, after which remineralization of dental tissues is carried out, so that carious formations do not arise in the future.
When the enamel starts to break down, painful sensations arise from a sudden change in temperature and when chewing spicy or sour food. With medium caries, the enamel layer is completely destroyed. At this stage, you must always contact the dentist.
Deep caries can affect internal dental tissues and spread very widely.
Diagnostic approach
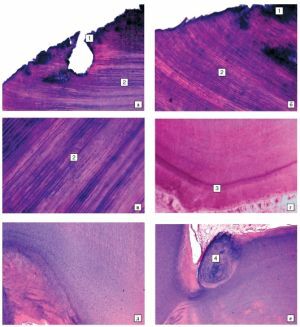
Diagnosis of deep caries using a special solution
The complexity or simplicity of determining the disease depends on the location of the foci of infection and the stage of their development. To detect carious formation at the earliest stages, special means are used.
More complex forms can be recognized already using a probe or a conventional dental mirror. Diagnosis can be carried out in a domestic setting.
Multiple formations in themselves are noticeable both visually and to the touch, causing painful sensations in contact with food, and in some cases, the teeth begin to ache even with the inhalation of air in frosty weather.
In this case, caries can develop unnoticeably to the stage at which it is already necessary to remove the tooth, and sometimes also to conduct depulpation.
Therapy: an overview of effective techniques
Modern diagnostic methods provide an opportunity to identify the disease and significantly reduce the duration of treatment. Modern technologies allow to make the process of treatment of even deep caries simple and practically painless.
Getting rid of such diseases is much more difficult. Professional treatment guarantees success even when deep caries develops.
The treatment procedure consists in the complete removal of tooth areas affected by caries. This can be achieved by using a drill and following the subsequent filling procedure.
In accordance with the defeat group, the procedure for removing carious formations may have such features:
- The first-stage formulations are treated by remineralization. This procedure is the saturation of the affected tooth enamel with fluoride and calcium.
- Surface form of is treated in a standard way using such technical means as a drill.
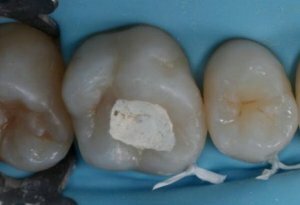
- Deep tooth decay can be cured in one or more sessions. Basically enough two visits to the dentist in order to completely get rid of this problem. During the first visit all tooth tissues affected by caries are removed, medicinal substances are laid out, and the treated place is hermetically sealed with a seal. To prevent the development of pulpitis, dentists install a special treatment pad. If the toothache has stopped, then instead of a temporary seal, a constant is established.
Treatment of deep caries under a microscope - all stages clearly:
Possible complications and prevention of
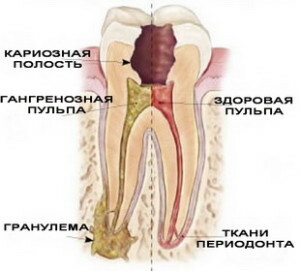 If the caries is not treated for too long, the dental nerve will eventually die off. In this case, decay begins to develop in the carious cavity.
If the caries is not treated for too long, the dental nerve will eventually die off. In this case, decay begins to develop in the carious cavity.
In such situations, the body struggles with complications independently through the formation of granuloma, which after a while becomes larger and grows to the standard size of a cyst. Running caries can cause pulpitis and periodontitis.
For the prevention of dysfunctions, dentists often recommend the use of special toothpastes, which promote the saturation of minerals with tooth enamel, inhibit the development of bacteria, and also remove soft plaque.
It should be noted that the use of fluoride-containing agents is recommended only in regions where less than 1.2 mg of this substance per liter of water is contained.
