
Uveitis is a whole group of eye diseases associated with inflammation in the choroid of the eye( another name is the uveal tract).
The vascular or uveal membrane is represented by the three components of : the iris( in Latin, iris), the ciliary body or the ciliary body( in Latin corpus ciliare) and the choroidal choroidal vessel itself( in Latin chorioidea).
Depending on the site of inflammation, the following forms of uveitis are distinguished: cyclite, iritis, iridocyclitis, chorioretinitis, choroiditis, etc. The main danger of this group of diseases are possible consequences in the form of blindness or blindness.
- 1. Types of the disease
- 2. Causes of the disease
- 3. Symptoms of the disease
- 4. Diagnosis of the disease
- 5. Treatment of the disease
- 6. Treatment of the disease with folk methods
- 7. Prevention of the disease
The appearance of this disease is facilitated by,that the vascular network of the eye is very common, and the blood flow in the uveal ways is slowed down, which can lead to a delay in the microorganisms in the choroid.
Under certain conditions these microorganisms can lead to inflammation. The appearance and development of inflammation is also influenced by other features of the choroid, in particular, the different blood supply and innervation of its different structures: the
- front section( iris and ciliary body) is supplied with blood by the anterior ciliary and posterior long arteries, and innervated by ciliary fibers of the first branchtrigeminal nerve;The
- posterior section( choroid) is supplied with blood by the posterior short ciliary arteries and is characterized by a lack of sensory innervation.
These features define a separate lesion of the anterior and posterior parts of the uveal tract. May be either one department or another.
Types of the disease
- By anatomical principle, uveitis is divided into anterior, intermediate( or middle, peripheral), posterior and generalized forms.
- Anterior uveitis: iritis, anterior cyclite, iridocyclitis. Inflammation occurs in the iris and vitreous body. This localization of inflammation is more common than others.
- Median uveitis: posterior cyclite, pars-planitis. Ciliary body, retina, choroid and vitreous are affected.
- Hind uveitis: choroiditis, chorioretinitis, retinitis, neuroveitis. Choroid, retina and optic nerve are affected.
- Generalized uveitis - panoveitis. This type of disease develops if all parts of the vascular membrane suffer.
- serous,
- purulent,
- fibrinous-plastic,
- hemorrhagic,
- mixed uveitis.
Causes of the disease
Uveitis can occur due to infections, allergic reactions, metabolic disorders, hypothermia, decreased immunity, injuries, common body diseases.
The most common( almost half of cases) are infectious uveitis. Infection can cause mycobacterium tuberculosis, toxoplasma, streptococci, treponema, herpes virus, fungi. Infection in the choroid can come from any focus in viral diseases, tuberculosis, syphilis, dental caries, tonsillitis, etc.
Allergic uveitis occurs in the background of food and drug allergies.
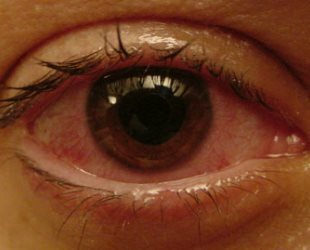
Uveitis can occur in the presence of the following diseases of the body: rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, psoriasis, ulcerative colitis, multiple sclerosis, glomerulonephritis, etc.
There may be uveitis of traumatic nature due to eye burns, penetrating damage to the eye, foreign body entering it.
Uveitis can develop on the background of hormonal dysfunction and metabolic disorders( with menopause, diabetes, etc.), blood diseases, eye diseases( scleritis, blepharitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, retinal detachment, etc.).
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of each form of uveitis differ.

We continue to disassemble eye diseases - symptoms and treatment of glaucoma! Review of effective methods of diagnosis and treatment.
Read on( article) on how to properly treat a lazy eye in adults.
Anterior uveitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- redness of the eye,
- photophobia,
- visual acuity reduction,
- chronic lacrimation,
- pupil narrowing,
- soreness,
- increase in intraocular pressure.
In the chronic course of anterior uveitis, symptoms occur rarely or mildly: only minor redness and floating dots in front of the eyes.
Peripheral uveitis occurs with the following symptoms:
- is often affected by both eyes symmetrically,
- "flies" before the eyes,
- deterioration of visual acuity.
The posterior uveitis is characterized by late appearance of symptoms. They are characterized by:
- blurred vision,
- object distortion,
- floating points before the eyes,
- visual acuity reduction.
Diagnosis of the disease

Timely diagnosis of uveitis is very important, becauseIn the absence of treatment, dangerous eye pathologies can develop which can lead to complete blindness.
Ophthalmic examination for suspected uveitis may include:
- regular external examination,
- visual acuity check,
- visual field determination,
- tonometry( intraocular pressure measurement method),
- pupillary reaction test,
- biomicroscopy( examination with a special slit lamp),
- gonioscopy( to study the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye),
- ophthalmoscopy( eye fundus examination),
- eye ultrasound,
- angiography of retinal vessels,
- tomography of varioustruktur eye( including the structure of the optic nerve),
- rheoophthalmography( measurement of blood flow in vessels of the eye).
If the causes of uveitis are other diseases of the body, it is necessary to conduct in parallel a laboratory and functional diagnosis and treatment of these diseases.
Treatment of
disease Ophthalmologist appoints treatment for uveitis depending on the type and cause of the disease. Therapy in this case is aimed at preventing complications that can lead to loss of vision.
For the treatment of uveitis use:
- mydriatica( atropine, cyclopentol, etc.) eliminate the spasm of the ciliary muscle, prevent the appearance or rupture of already existing seizures.
- application of steroids locally( ointments, injections) and systemically. To do this, use betamethasone, dexamethasone, prednisolone. If steroids do not help, prescribe immunosuppressive drugs.
- eye drops to reduce high intraocular pressure,
- antihistamines for allergies,
- antiviral and antimicrobial agents in the presence of infections.
With the timely treatment of light forms of uveitis pass through 3-6 weeks.

In severe cases, with significant destruction of the vitreous body, surgical treatment of uveitis is required. With iridocyclochorioiditis( or panoveitis), they can perform vitreoectomy( surgical removal of the vitreous body), and if the eye can not be rescued, the eyeball is eviscerated( all the internal structures of the eyeball are removed).
Treatment of the disease folk methods
In the treatment of uveitis, you can use some methods of traditional medicine, after discussing the possibility of such treatment with a doctor:
- Helps with uveitis a decoction of chamomile, dog rose, marigold or sage. To make it, you need 3 tablespoons of herbs and a glass of boiling water. The mixture should be infused for about an hour. Then you should strain it, and rinse with this decoction of the eye.
- Aloe can also help. You can use aloe juice for instillation into the eye, diluting it in cold boiling water in a proportion of 1 to 10. You can make an infusion of dry leaves of aloe.
- You can use the crushed althea root. To do this, you need 3-4 tablespoons of althea root to pour a glass of water at room temperature. It is necessary to insist it for 8 hours, and then use it for lotions.

Read more - reasons why eyes can be itchy. An overview of the disease for which the main symptom is the itch of the eye.
In the news about how to treat the twitching eye.
Treatment of barley on the eye with folk remedies!http: //moezrenie.com/bolezni/ zabolevaniya-vek / yachmen-na-glazu.html
Prevention of diseases
For the prevention of diseases, one should observe eye hygiene, avoid hypothermia, eye injuries, fatigue, develop allergies, and timely treat various diseases of the body. In the event of any disease of the eye, it should immediately begin treatment, so as not to provoke the appearance of more serious diseases.
