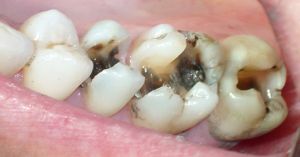
 Caries is the most common dental disease. During the development of the disease, any part of the tooth may be affected.
Caries is the most common dental disease. During the development of the disease, any part of the tooth may be affected.
The deepest, most complex and aggressive form of the disease is the caries of the tooth cement( its root).Such a progression of the disease can lead to complete destruction of the tooth and its loss.
Contents
- About the localization of carious areas
- Basal VS cement - what's the difference?
- Causes of appearance and risk factors
- Features of the clinical picture
- Diagnostic criteria and methods
- Treatment or removal?
- Conservative therapy - it's not too late
- Operational approach
- How to restore the root?
About the localization of carious areas
Determining the stage of the disease depends largely on the location of its localization. In dentistry, the classification is widely used, according to which caries happens:
- cervical( basal);
- of dental crown( enamel and dentine);
- of the dental root( cement).
Most often, cement destruction is diagnosed in people over 60 years of age. This category of patients accounts for 60 to 90% of all cases detected.
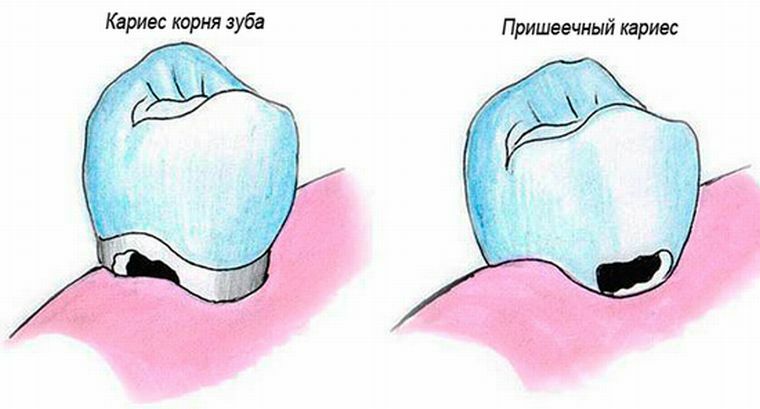
Basal VS cement - what's the difference?
With caries cement, the site of destruction is located at a sufficient depth under the gum and is rarely detected by the naked eye. With this form of disease, the integrity of the root tissue is disturbed, which during visual inspection is impossible to see.
In the case of a cervical location of the carious area, the enamel surface area near the gingival margin suffers. Basal caries is almost always formed on the lingual, buccal, contact surfaces of the teeth along the bare roots. At the reception, the dentist will immediately identify such violations when examining the patient.
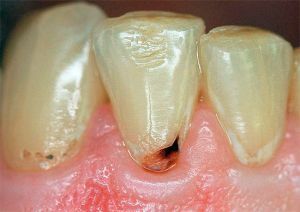
Causes of appearance and risk factors
As a rule, the destructive process in the root area develops due to existing diseases. It can be a dystrophy of tissues, atrophy, complication after wrong treatment, hereditary predisposition. Also, the risk group includes people over 60.
Initially, the open root part of the cervical area is affected, and then moves deeper into the cement area, which leads to disastrous consequences.
The main reasons that trigger the development of the disease:
- The formation of the gingival pocket. The gums do not adhere to the cervical part of the tooth, because of which the leftover food can get into the cavity formed, forming a bacterial plaque.
- This stage of the disease is often a consequence of radical caries, in the absence of treatment which, the destruction will go deeper inside.
- Late initiation of treatment with the development of a carious area in the crown area.
- Wrong set crown. In the event that a gap is formed through which pathogens can penetrate. This site will become the main place of accumulation of bacterial plaque.
- The expiration date of the installed crown. In such a situation, a carious cavity of a small size is first formed under the crown. At any time, infection of the inner part of the tooth can occur, which will certainly lead to inflammation of the pulp. And the result of this process is the destruction of caries of dentin and cement.
Features of clinical picture
When the lesion cavity reaches a serious size, it becomes noticeable in the gum area. During this period, the following symptoms appear:
- Reaction to temperature exposure to the affected area when eating.
- Reaction to chemical irritants, manifested as a sharp short-term pain. Basically this happens when eating sweet food or drinks.
- Formation of a gingival pocket where food particles enter. It manifests itself with severe pain until the remnants of food are eliminated.
- Inflammatory process with high sensitivity of periodontal tissues.
- A feeling of discomfort during the chewing process. A damaged root can deform, shift, which causes severe soreness.
Diagnostic criteria and methods
For the timely detection of caries in the root of the tooth requires a comprehensive diagnosis. Basic methods:
- Initial inspection of .The dentist listens carefully to the patient's complaints and conducts a visual examination. In the course of this
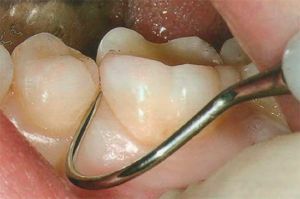 , a preliminary evaluation of the condition of the teeth, gums, and mucosa takes place.
, a preliminary evaluation of the condition of the teeth, gums, and mucosa takes place. - Sounding .For the survey, a special instrument is used - a probe, with which you can penetrate the gums. The presence of a rough or smooth structure at the root surface makes it clear whether the tissue is healthy or subject to changes.
- Radiography .With the help of this method, it is possible to diagnose even the smallest defects, to reveal the extent of the lesion and to draw up a treatment plan.
- Visiography .Using this method of research, the dentist receives a detailed picture on the monitor screen, where all the existing problems with dental health are clearly visible.
- Thermodiagnostics .A stream of water washes the tooth, while its temperature changes. Short-term pain speaks of superficial abnormalities. A severe manifestation of pain indicates a serious problem when a destructive process has already reached the pulp.
- Electroodontometry .For this method of research, an electric current is used with varying strength. By acting on the pulp, the stage of destruction of
is determined. Treatment or removal?
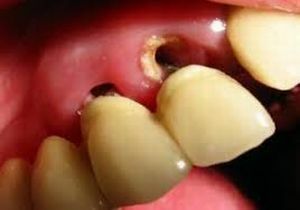
In the photo, denudation of the roots of the tooth is a typical symptom of the caries of cement
There is no single correct approach to the treatment of root caries. In each case, everything will depend on the size of the lesion, the depth and localization of the carious area. Particular attention should be paid to the overall clinical picture. The doctor should study the state of the oral cavity and how the injured root and tooth behave as a whole.
In any case, at any stage of the disease, professional cleaning is carried out initially.
Until the root surface is cleared of bacterial plaque and stones, there can not be any treatment or speech. Before opening access to bare roots, it is necessary to completely eliminate the possibility of re-infection.
There are two methods of treatment: operative and conservative, but the second method in case of root caries is almost not applied. In the most severe cases, tooth extraction is required, in order to avoid infecting the rest of the dentition.
Conservative therapy - it is not too late
The first manifestations of carious lesions are the detection of unnatural stains on the surface of the enamel of black or white. Treatment in this case is possible using the following techniques:
- It is proposed to perform professional cleaning of the tooth surface of from bacterial deposits.
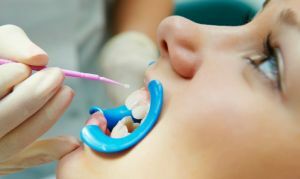
- Patients undergo deep fluoridation .In this way, it is possible to increase the number of microcrystals of calcium and fluorine at the enamel surface several times, which ensures the preservation of teeth for a long period. For surface defects, special preparations with fluorine content are used. They are available in the form of gel, lacquer, paste. In some cases, complex drugs are used, which include additional nutrients: magnesium, calcium, phosphorus.
- In addition, a special remineralization procedure is assigned.
Operational Approach
Operative treatment of caries of cement consists in removal of the amazed dental tissues with carrying out of the subsequent sealing. For areas located under the gums, some difficulties are characteristic. There is a high probability of damaging the periodontium.
The following precautions are used for the protection of the gums:
- is carried out as a diathermocoagulation .With the help of a special tip, excessive areas of periodontal tissue are removed under the influence of hot temperature.
- Retraction .The overhanging gingival margins are removed. To do this, use a thin thread that has been previously impregnated with a hemostatic solution.
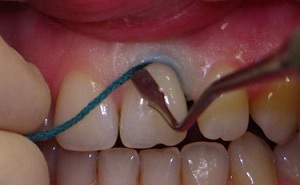 Each of these two procedures causes painful sensations. Therefore, anesthesia will be required.
Each of these two procedures causes painful sensations. Therefore, anesthesia will be required.
The cured process of the disease often looks better than its open form. But with hidden flow, a more serious approach to therapy and methods for correcting damaged parts is required. Already at the first admission the dentist performs an excision of the inflamed gum.
The main treatment for root caries is the following:
- injection of an anesthetic;
- removal of damaged dental tissue;
- check by the caries indicator for the presence of the remaining infected tissue;
- cavity formation;
- isolation of the formed cavity from saliva;
- selection of suitable material for sealing;
- restoration of the affected surface.
Deep defects are eliminated by artificial crown or insertion. The best and most convenient are the ceramic structures, but they are very expensive. Composite, in turn, is considered a quality material and inexpensive. With its help, you can carry out a qualitative restoration, easily modeling the future crown.
The procedure for the removal of hard tissues is accompanied by constant cooling of the tooth with water. When the affected tissue is removed, the resulting cavity is treated with an antiseptic. So the possibility of subsequent infection is excluded. Then comes the sealing phase.
How to restore the root?
Special materials are used to restore the shape of the roots. Most often use the following: 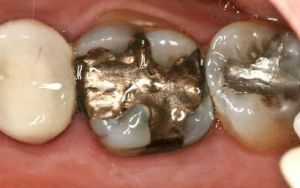
- Amalgams .Seals from it will last long and securely. They mix with mercury. In modern dentistry, this material is used very rarely due to hazardous components.
- Compomers .The seals are durable, ensuring a secure fit to the dental tissue. It consists of glass ionomers and a composite.
- Glass-ionomer cements .The best material for sealing in hard-to-reach places. In the composition there are special fluorides, due to which the cured tooth will acquire a good mineral structure.
The biggest danger of destruction in the cement field lies in the complexity of its diagnosis. Until a certain moment, the disease can not give itself out as any symptoms, and the pain appears even with large carious areas.
In the absence of treatment of caries under the gum, the next stage will be inflammation of the tissues around the tooth. As a result, the level of the gum will decrease, the root will be exposed. And this can lead to pulpitis and the development of periodontitis.
