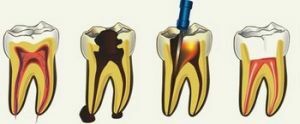
 Extirpation of pulp is a dental operation, during which there is a complete removal of connective tissue filling the cavity of the tooth.
Extirpation of pulp is a dental operation, during which there is a complete removal of connective tissue filling the cavity of the tooth.
Pulpotomy is performed at the level of the apical foramen. This is necessary to completely remove the affected pulp.
Contents
- Indications and contraindications for intervention
- Two methods of amputation
- Vital extirpation
- Devital method
- Possible complications
Indications and contraindications for
intervention Extirpation of pulp is performed in the following cases:
- irreversible variants of pulpitis development;
- parodontogenic pulpitis;
- fracture of the tooth crown, accompanied by the involvement of pulp in the process.
- no effect from conservative treatment of the inflammatory process.
Pulpectomy can also be performed with a completely healthy pulp. This is done in cases where it is necessary to prepare the teeth to install the prosthesis.
As with any surgical intervention, there are contraindications to pulp amputation, in particular: 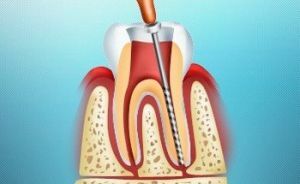
- complete obstruction of the root canal;
- absorbable root in the milk tooth;
- presence of unformed root in the tooth;
- severe physical illness;
- immunodeficiency states;
- anesthesia intolerance.
Two methods of amputation
In modern dental practice, two main techniques are used to perform pulp extirpation:
- Vital method .After local anesthesia, pulpectomy is performed. All the necessary manipulations fit into one visit.
- The devital way of the .It is held in two visits. On the first visit to the doctor, the devitalizing paste is laid, causing slaughter of the pulp. On the second visit, direct removal of necrotic tissues is carried out.
Let's consider each of the methods in more detail.
Vital Extirpation
The main advantage of this method is that all the necessary manipulations are carried out in one visit. Also, this method does not require the use of devitalizing agents that negatively affect the condition of periodontal disease.
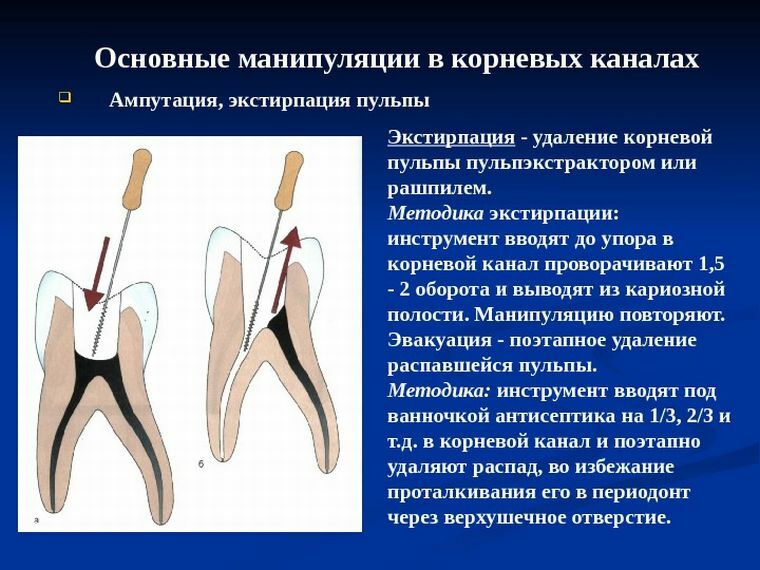
Vital amputation is performed as follows:
- disease detection;
- cleaning of the affected tooth;
- introduction of anesthesia;
- section of the arch of the tooth cavity;
- extirpation;
- measuring the length of the channel;
- giving the channel a regular shape with subsequent treatment with a disinfectant;
- installation of permanent seal.
This method is more popular, both among dentists and among patients. However, if the patient is hypersensitive to anesthetics, removal of pulp by this method is not permitted.
Devital method
It is considered a traditional method and is based on the complete removal of pulp after its killing. For this, specialists use devitalizing agents:
- arsenic paste;
- parapharmaldehyde paste.
If electrochemical necrosis can be used to kill the pulp in inaccessible areas during the treatment, it is impossible to completely pass the canal. When using this method, anesthesia is necessary, since with the saved pain sensitivity it will be impossible to act on the pulp with sufficient current strength.
From contraindications to the use of this method, the following should be highlighted:
- increased sensitivity to devitalizing agents;
- purulent forms of pulpitis;
- presence of unformed root in the tooth.
The treatment itself is conducted in two visits. So, on the first visit to the dentist, the following will be done: 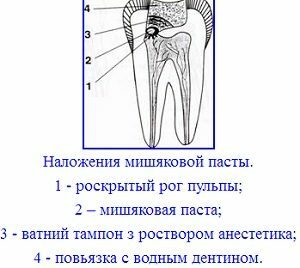
- diagnosis;
- cleaning of damaged tooth;
- cavity opening;
- paste application;
- installation of temporary seal.
A second visit can be scheduled in 2 days if an arsenic-based paste was used or a week later, if paraformaldehyde was used. During the second visit, the doctor must perform the following manipulations:
- removal of the temporary seal;
- providing sufficient access to the root canals;
- complete pulp removal;
- channel processing;
- canal filling;
- installation of permanent seal.
Possible complications of
After the surgery, a number of complications may occur, namely:
- Periodontal irritation of .It manifests itself as a pain syndrome and is a response to mechanical rupture of the pulp near the apical foramen. Passes after using anesthetic. In some cases, darsonvalization or fluxometry may be necessary.
- Traumatic periodontitis .Occurs as a result of ingress of the filling material beyond the root canal.
- Burn of mucous .Appears due to improper diathermocoagulation. The lesion focus must be treated with antiseptic agents, as well as anti-inflammatory therapy. Perforation of the root .In the event of a violation of the technique of performing dental intervention, it is possible that the root of the root is perforated by the instrumentation. This leads to a serious inflammation, up to the development of osteomyelitis.
If the postoperative recommendations are not followed, it is also possible to form complications. So, if after the first stage of devital pulpotomy, postpone the repeated visit, prolonged exposure to arsenic in the cavity of the tooth can lead to the development of periodontitis.
This is why, in order to avoid consequences, it is important not only to contact a qualified specialist, but also to follow all of its appointments. In this case, the risk of complications decreases at times.
