 The human body is arranged in such a way that periodically this or that organ becomes ill, partially or completely losing its functionality.
The human body is arranged in such a way that periodically this or that organ becomes ill, partially or completely losing its functionality.
Very often, the reason for concern is the teeth affected by periodontitis.
Contents of
- What is it?
- Causes of development of the disorder
- Classification of the disease
- Classification by origin
- Classification by ICD
- Classification by Lukomsky
- Symptoms of the disease
- The main stages of treatment
- Possible complications
- What if the tooth hurts after periodontal therapy?
What is it?
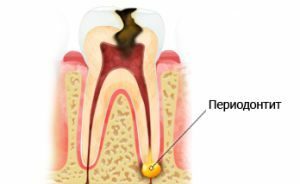
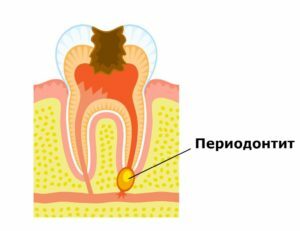 Periodontitis is the inflammatory process that develops in the tissues around the tooth root - periodontium, responsible for the stable position of the tooth in the row.
Periodontitis is the inflammatory process that develops in the tissues around the tooth root - periodontium, responsible for the stable position of the tooth in the row.
At the time of the onset of the disease, microbes in most cases reach the tissues through the root canal in pulpitis, provoking inflammation.
A periodontium enriched with a variety of receptors responds with severe pain to the increased pressure caused by the development of the disease. Then, fluid swelling and disease progression are observed.
Causes of development of a disorder
Provoking the occurrence of the disease may groups of general and local factors. The first set consists of diseases of the cardiovascular, endocrine and nervous systems. This series can be continued, calling more than three dozen pathologies, including diabetes.
Among the local factors:
-
 addiction to bad habits( alcohol, smoking);
addiction to bad habits( alcohol, smoking); - lack of vitamins and trace elements;
- inappropriate oral hygiene;
- complicated forms of dental and gum disease;
- mechanical trauma of facial skull tissues;
- carrying out poor-quality dental treatment.
Classification of the disease
The assignment of a definite form of periodontitis to a particular group is necessary, because, depending on the characteristics of the development of the process, preference is given to a particular treatment tactic.
Classification by origin
The following types of periodontitis are distinguished by the origin of the disease:
-
 Infectious , the cause of which is pulpitis or developing caries, which contributes to the penetration of pathogens into the periodontium.
Infectious , the cause of which is pulpitis or developing caries, which contributes to the penetration of pathogens into the periodontium. - Traumatic , caused by excessive stress on the surrounding tooth root tissue. Such a mechanical effect can be of a short-term nature( bruise, trauma) or be chronic( wearing orthopedic structures, malocclusion, etc.).
- Medicated , resulting from the effects on the periodontium of medications.
Classification by ICD
Classification of periodontitis, proposed by the international organization WHO, is comprehensive: it does not disregard not only the form of the disease, but also common complications. Periodontitis in ICD-10 refers to section K04.
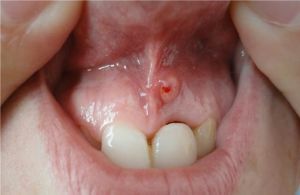
On a photo the periodontitis with fistulous
So, on МКБ allocate such kinds of a periodontitis:
- K04.4 Acute apical is a traditional variant, characterized by a clear cause of development and obvious symptomatology; in other words, apical periodontitis. The paramount task of the medical staff is to eliminate the source of infection and remove the primary clinical manifestations.
- K04.5 Chronic apical , often requiring surgical intervention( resection, truncation of the upper part of the dental root).
- K04.6 Periapical abscess with fistula, various forms of which give rise to the need for the help of an ENT doctor, since in the presence of a fistulous course in the maxillary sinus, the development of maxillary sinus is inevitable.
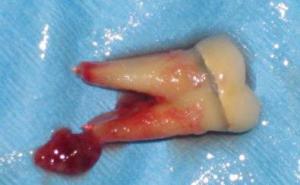
Cyst on the root of the tooth
If it's a case of a neglected case, the fistula may not dissolve on its own, then surgery is needed.
- K04.7 Periapical abscess without fistula .
- K04.8 Root cyst , the treatment of which involves a long-term therapeutic course or surgical intervention.
Classification according to Lukomsky
According to it, periodontitis can manifest itself in acute and chronic forms. The first one undergoes two stages of development:
-
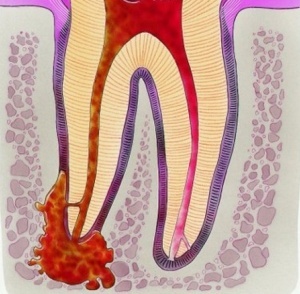
Acute purulent process
Serous inflammatory process , accompanied by localized expansion of capillaries, the grouping of blood cells that are responsible for the body's immune system. Intracellular fluid accumulates, edematous periodontitis, pain syndrome.
- Purulent inflammatory process of , causing proliferation and further fusion of purulent foci. Tissues strain under pressure, which causes acute pain, which ceases only in case of outflow of pus.
The chronic form of the disease can flow out of the acute or develop initially. The development of periodontitis in this case passes through three stages:
- Fibrous stage is the most gentle, manifested in periodontal consolidation phase. The X-ray image will show only the widening of the periodontal gap mainly in the terminal region of the root.
- Granulomatous is an intermediate inflammatory phase. There is a formation of connective tissue capsule, which is designed to delimit the focus of inflammation. In the cavity creates pressure, leading to a gradual degradation of bone tissue.
- The chronic is the most progressive, during which there is a rapid destruction of the structure of the bone in the area of inflammation, besides this, connective tissue grows very quickly. An x-ray study will show foci of enlightenment with an indistinct pattern of bone tissue.
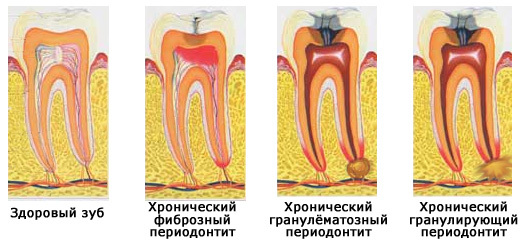
This classification also identifies the chronic form of periodontitis in the stage of exacerbation. The clinical picture of the disease is similar to the acute form of the disease, however, on the X-ray, the symptoms are chronic.
Symptoms of the disease
Diagnosis of diseases is especially simple on the basis of signs characteristic of all forms of the disease.
Among them:
-
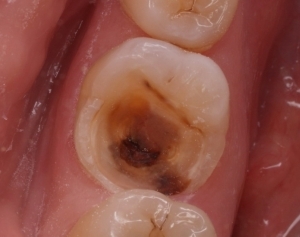
On the photo the destroyed tooth crown
the external area of the tooth is subject to appreciable destruction;
- the reaction of the affected tooth to cold or hot is absent;The
- sensing procedure does not deliver painful sensations, even when the root canal is exposed;
- tooth color change;
- presence of pain when pressing on a tooth or tapping on it.
The acute or exacerbated form of periodontitis is accompanied by the following set of symptoms:
- very strong, unbearable pain, passing on to neighboring teeth, giving through the trigeminal nerve into the ear or the temple area;
-
 sensation of an enlarged toothache: when the jaw is closed, the contact point is only visible in the affected area;
sensation of an enlarged toothache: when the jaw is closed, the contact point is only visible in the affected area; - redness and swelling of the mucosa and gums in the projection area;
- painful sensations when touching the affected area;
- enlargement of lymph nodes;
- mobility of the affected tooth( disappears as the severity of the inflammatory process decreases).
Patient with chronic periodontitis in rare cases observes a pronounced clinic of the disease, all signs of the disease are revealed during X-ray examination.
The main stages of treatment of
The modern method of root treatment of the tooth with periodontitis involves the following stages:
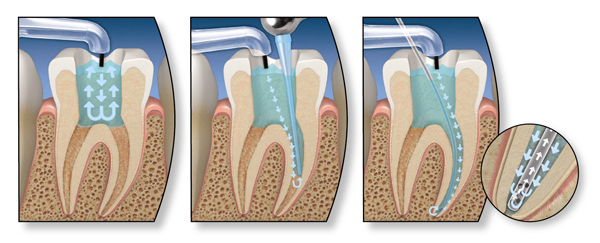
- Mechanical preparation of .At the current stage, the dental canals expand, and their purification is carried out. The affected dentin layer is eliminated, and the entire contents of the channels are deleted. In the treatment of acute disease, the procedure is accompanied by the outflow of a special fluid( exudate) from the area of inflammation. After the event, the pain is weakened, the inflammatory process calms down and does not affect nearby tissues. In the process of mechanical preparation, a specialist uses a drill, in some cases also a dental microscope.
- Treatment with antiseptic means .Disinfection of channels is carried out. Sometimes the introduction of drugs. It is very important to prevent the penetration of potent formulations into the upper part of the dental root. This is followed by intra-channel ultrasound physiotherapy.
- Sealing of the channels is the most important event, the task of which is a thorough blockage of the channel throughout its length. Depending on the structure of a particular channel, a certain filling material is selected and, accordingly, the filling technique.
- As an adjunct, physiotherapy, rinsing of or of antibiotics can be prescribed by a specialist.
More on how to treat periodontitis:
It should immediately be noted that the treatment of periodontitis with "grandmother's" recipes is not able to save the patient from an ailment. Perhaps only a temporary decrease in the intensity of pain, for example, with the help of hypertonic rinses.
To this end, it is necessary to dissolve 1 tsp.soda and the same amount of salt in a glass of boiled water, then add a few drops of iodine to the solution. Rinse should be done every 1-2 hours.
Possible complications of
In the absence of timely treatment of any form of periodontitis, complications may develop. They are common or local.
 The first set represents the various symptoms of an organism's intoxication caused by the active vital activity of pathogens. The substances released by them, appearing in the bloodstream of the patient, stimulate the body to various manifestations.
The first set represents the various symptoms of an organism's intoxication caused by the active vital activity of pathogens. The substances released by them, appearing in the bloodstream of the patient, stimulate the body to various manifestations.
Among such may be headaches, fever, general malaise, etc.
If the microbes get into the blood, infection in the organs can not be ruled out, and such a serious complication in medical practice is called sepsis or blood infection.
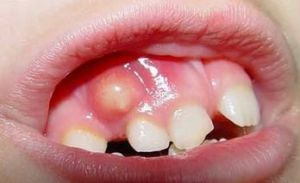
Flux in a child
To a group of local complications in acute periodontitis is a flux that can grow into an abscess and a phlegmon of the maxillofacial zone.
It is possible to diagnose and acute osteomyelitis, in which the bone jaw tissue is actively destroyed.
Chronic chronic periodontitis often causes the formation of cysts, which in the process of growth affect the neighboring tooth roots. Sometimes they sprout into the maxillary sinus. If the cyst is suppurated, a chronic fistula is formed.
What if my tooth hurts after periodontal therapy?
Often patients complain of the pain that accompanies them for some time after filling the affected tooth. This can be acute or periodic pain, in some cases just hypersensitivity to contact with the tooth surface.
What if you are faced with such a problem, and do not have the opportunity to seek medical help? In such a situation, the patient will benefit from traditional medicine. Here are some effective methods in combating toothache:
- As often as possible, rinse the mouth of with soda-salt solution .Dissolve 1 tbsp.l.ingredients in a glass of heated water.
-
 If you are worried about the pain of a pulsating nature, use a piece of propolis .Preheat it in your hands to a soft consistency and put on the surface of the gum of the affected tooth, you should get a small applique. You can use just a few pieces of propolis.
If you are worried about the pain of a pulsating nature, use a piece of propolis .Preheat it in your hands to a soft consistency and put on the surface of the gum of the affected tooth, you should get a small applique. You can use just a few pieces of propolis. - In case of pain and inflammation of the mucosa it will be useful to rinse the oral cavity with infusion from of celandine .Pour 1 tbsp.l.raw with boiling water in the amount of one glass and leave the product stand for 20 minutes. After cooling, use it for the intended purpose.
If the procedures performed at home did not relieve you of the problem, and the tooth continues to hurt, you should definitely seek dental care. The specialist will conduct a survey and take appropriate measures.
More about periodontitis and possible complications the dentist will tell:
Ignoring the signs of such a serious disease as periodontitis will inevitably lead to the development of complications, followed by the only way to solve the problem - removal of a sick tooth.
Only the patient is able to react to the situation in a timely manner, thus preserving the health of his teeth.
