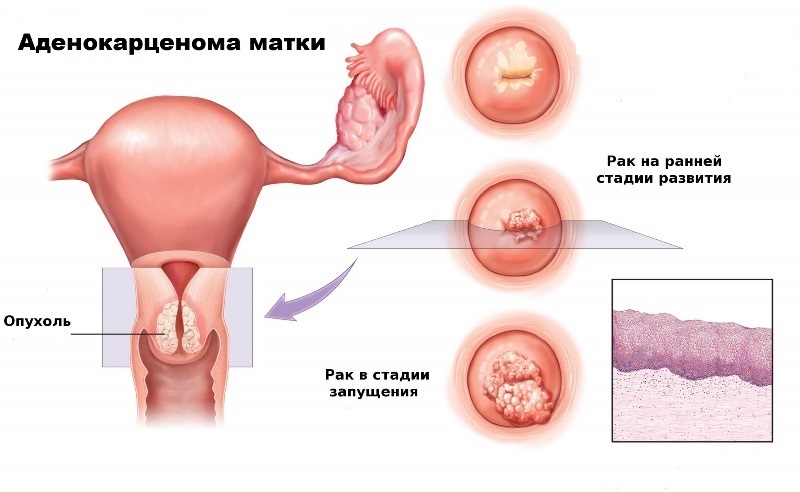
Adenocarcinoma is a malignant tumor that develops from the endometrium, less often from the cervical cells. Most often this is a highly differentiated formation, therefore, with timely detection has a favorable prognosis of treatment. The whole danger of the disease is that the symptoms can be masked under the pathology of the endometrium and therefore ignored by the woman. How and why develop the disease, how to suspect and choose the most optimal treatment?
reasons for the development of adenocarcinoma of the uterus and cervix
Reliable reason for the formation of the body, and adenocarcinoma of the cervix has not yet been detected. But there are a number of factors that significantly increase the likelihood of this disease. Most of these women are registered with a gynecologist and other specialists about any pathology. The main provocative moments include the following:
- Early menarche and late menopause. The more a woman's body is under the influence of high concentrations of estrogen, the higher the risk of getting sick. This is due to the fact that this sex hormone contributes to the excessive division of endometrial cells, which leads to various mutations and atypia.
- Excess body weight, especially during menopause. The fact is that in fatty tissue there is a metabolism of hormones, including estrogens. Normally, this is necessary for the formation of the menstrual cycle and puberty.

- Diseases of the endocrine organs, especially hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus and others. They all lead to some degree of imbalance of sex hormones.
- It is noted that in nulliparous and never lactating women, the risk of adenocarcinoma is higher.
- Polycystic ovary, hyperandrogenemia of any genesis and other similar ailments.
- Polyps, endometrial hyperplasia, especially if there are signs of adenomatous growth or atypia.
- Weighed down the heredity of the cancer of the body of the uterus and cervix.
- The effect of a chronic stress condition can not be ruled out.
- Exposure to radiation from both long-term doses and single-dose doses.
Thus, all of these factors can identify two tie points:
- violation of ovulation processes,
- hyperestrogenemia.
 We recommend to read an article about menstruation with cancer. From it you will learn about the impact of malignant cells on the woman's body, the effect of pathology on the duration of the cycle and the nature of menstruation.
We recommend to read an article about menstruation with cancer. From it you will learn about the impact of malignant cells on the woman's body, the effect of pathology on the duration of the cycle and the nature of menstruation.
And here it is more in detail about, whether the uterine myoma can grow into a cancer.
Classification of adenocarcinoma of the uterus body
The prognosis and tactics of treating women diagnosed with adenocarcinoma depend in many respects on how differentiated the tumor tissues are, where it is located.
Highly differentiated adenocarcinoma
This is the most benign form that has the features of diagnosis and flow. Even according to the results of the histological analysis, sometimes it is difficult to establish whether the adenocarcinoma is just an atypical endometrial hyperplasia. Fabrics are characterized by minimal signs of malignancy. Small areas are involved. Highly differentiated adenocarcinoma has the most favorable course, rarely gives metastases, general symptoms of intoxication, etc.
Moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma
This type of tumor process is characterized by a greater degree of cellular changes. Not only the surface layers are involved, but also deeper layers. This is accompanied by an increased likelihood of adenocarcinoma spreading through the lymphatic and blood vessels. But also with respect to other tumor processes, moderately differentiated tumors have a favorable prognosis of treatment.
Low-grade adenocarcinoma
This is the most dangerous form of adenocarcinoma. Tissues of this tumor have pronounced signs of malignant growth, often metastasize, not so easily treatable.
Endometrial adenocarcinoma
In 2/3 of cases, adenocarcinoma has to deal with this type of tumor process. It is possible to establish the diagnosis only histologically. It often occurs in older women. At the same time, the cells that synthesize mucus are involved in the pathological process. Therefore, often women notice the appearance of a large number of transparent vaginal discharge.
Cervical adenocarcinoma
The process in this case begins in the flat epithelium of the cervix, spreading further outward into the vagina or inside the cavity. Also there is a papillary type of adenocarcinoma, in which the sprouting has the appearance of Brussels sprouts.
Look at the video about the cancer of the uterus:
Stages of development of adenocarcinoma of the uterus
There are four stages of development of adenocarcinoma. Affiliation to one or the other is established, based on the size of the tumor, the involvement of the uterine muscles, the presence of metastases and some other symptoms. The main criteria are as follows:
- 1st stage. Characterized by the fact that cancer cells are located strictly in the uterine cavity. In addition to the endometrium, the muscular layer of the uterus-myometrium can be captured. But the lymph nodes and other organs are intact. The forecast of this stage is very favorable.
- 2nd stage. Set if the cervix is involved in the process. The tumor goes deeper into the myometrium, but does not germinate right through, leaving intact all the internal organs and lymph nodes.
- Stage 3. At this stage of the disease, the tumor progresses. It sprouts into the entire thickness of the endometrium, is implanted into neighboring organs - the rectum, bladder and others. Also, nearby lymph nodes may be involved.
- 4th stage. Established if distant metastases are found in the lungs, bones, etc.
Symptoms of adenocarcinoma
In most cases, the uterine adenocarcinoma appears already at the initial stage. Therefore, to identify at an early stage of pathology is not particularly difficult. But the following reasons lead to late treatment and neglected cancer:
- Adenocarcinoma is "masked" for various variants of endometrial pathology. In particular, for polyps, hyperplasia, adenomatosis, and the like. Poor diagnosis can lead to the tumor, especially the highly differentiated variants, will progress.
- Women do not always turn to the doctor in a timely manner, believing that abundant periods are the norm, especially during the period of menopause. And pulling pains are written off to problems with a loin, etc.

Complaints in which adenocarcinoma should be excluded primarily:
- Appearance of of profuse menstruation, with clots at any age.
- Periodic daub of varying intensity, up to breakthrough bleeding. Sometimes in menopause, women think that they have a new month, and do not consider this a problem. And also on absolutely insignificant bloody allocation simply do not pay attention.
- The appearance of a transparent, watery or mucus-like consistence of excreta from the genital tract is more common. Typically, you have to use daily pads, 2 - 3 or more per day. Often this is serous adenocarcinoma.
Also, if this tumor occurs, the following nonspecific symptoms may be of concern:
- Drawing pains in the lower abdomen, lower back, sacrum, including during sexual intercourse.
- Appearance of general weakness, lethargy, increased sweating, subfebrile temperature.
- Unexplained weight loss in a short period of time.
- Increased abdominal circumference if ascites is formed( fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity).
Diagnostic methods for adenocarcinoma
Diagnosis of adenocarcinoma when a tumor is suspected does not differ from the usual pathology of the endometrium. It includes the following:
- Inspection of the gynecological chair allows you to find an enlarged uterus, more normal lymphatic or some other pathological formation.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs helps to identify foci of abnormal growth. It can be a picture of a polyp, hyperplasia or another, at first sight benign pathology.
- If there is a focus in the cervix, swabs are important for oncocytology( PAP test).
- Separate diagnostic curettage or, better, hysteroscopy. In both cases, tissue is taken and then sent to the histology laboratory for clarification. But with hysteroscopy, biopsy is aimed, which increases the probability of correct diagnosis. With the usual curettage, the malignant polyp can be accidentally missed, since the whole procedure is done "blindly".
- If necessary, CT, MRI, lymphography, urography, colonoscopy and other methods are performed. As a rule, they are already necessary for ascertaining the degree of prevalence of the process.
Is it necessary to remove the adenocarcinoma of the uterus and cervix
? When removing the original tumor, the probability of full recovery is maximum. In this case, often a woman forgets about her tumor for 10 - 15 years and even for life.

So you can achieve the maximum effect of treatment.
In the fourth stage, removal is not always carried out. In the following cases it is not advisable to do it:
- When the general condition is serious, a woman, when she can not bear such an operation.
- When removal of the uterus will not bring any meaningful result due to the severity and vastness of metastases.
- If a woman refuses surgery.
Treatment of adenocarcinoma of the uterus and cervix
The tactics of managing women with an identified adnocarcinoma are different, depending on the stage, age and many other factors. The approximate plan is as follows:
- In the first stage, only removal of the uterus is sometimes sufficient. In some cases, laparoscopic surgery with preservation of the ovaries can be performed. This is especially important for girls who have not yet given birth. So they will have the opportunity to use the surrogate motherhood service.
- In the second and third stages only classical laparotomy operations are performed. The amount of intervention is often supplemented by the removal of the vagina, lymphatic vessels, nodes and even adjacent organs.
- The question of the removal of the uterus at the fourth stage of the disease is solved individually. Sometimes these are palliative measures, for example, to restore passage of intestinal contents or urine, if there is germination or metastasis in these departments.
The main treatment is supplemented if necessary by radiotherapy, chemotherapy. Radiation therapy implies the impact on both local and distant metastases. Special devices are used to supply radiation radiation as closely as possible to the tumor. Chemotherapy includes drugs( Doxirubicin, Cisplatin and many others) to fight cancer cells.
Prognosis for adenocarcinoma of the uterus and cervix
The prognosis of the disease depends on the degree of differentiation of the tumor, the stage, the age of the woman, the effect obtained from the treatment, and the like. To say it is not always possible.
The most favorable course in highly differentiated adenocarcinomas 1 - 2 stages. Radical treatment allows you to almost forget about the tumor for a long time( more than 5 years).
Least favorable prognosis for stages 3 through 4, as well as for tumors with low differentiation. In this case, the five-year survival rate is not more than 5-10%.
A slightly worse overall prognosis for cervical adenocarcinoma, but also depends on the stage and nature of the tumor.
Prevention of the appearance of adenocarcinoma of the uterus
It is not always possible to avoid the development of any malignant neoplasms. But you should try to minimize the risk factors, as well as regularly undergo examination by a gynecologist for early detection of the tumor process. The main recommendations are as follows:
- it is important to monitor body weight, especially in menopause;
- for the purpose of contraception is useful to use hormonal drugs;
- is also important to lead an active lifestyle, observe proper nutrition.
And here is more about the treatment of cervicitis.
Adenocarcinoma is the most common form of malignant uterine tumors. Timely detection and treatment of pathology gives high chances for the subsequent high probability of complete recovery. It is therefore important to contact specialists and undergo a survey even with seemingly minor complaints.

 We recommend reading the article about cervical leukoplakia. From it you will learn about the causes and symptoms of pathology, diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
We recommend reading the article about cervical leukoplakia. From it you will learn about the causes and symptoms of pathology, diagnosis and treatment of the disease.