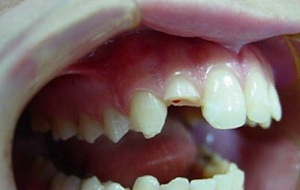
 The presence of an inflammatory process in the periodontium( connective tissue between the alveolar plate and the root of the tooth) is called periodontitis. The disease is characterized by rupture of ligaments, which fix the tooth in the alveolus, as well as the destruction of bone tissue. It appears in the form of cysts and granulomas of large and small sizes.
The presence of an inflammatory process in the periodontium( connective tissue between the alveolar plate and the root of the tooth) is called periodontitis. The disease is characterized by rupture of ligaments, which fix the tooth in the alveolus, as well as the destruction of bone tissue. It appears in the form of cysts and granulomas of large and small sizes.
Traumatic periodontitis occurs with mechanical damage, for example, when it strikes or falls. In this case, the acute course of the disease is characteristic.
Traumatic periodontitis may be caused by incorrect manipulation by medical( incorrectly staged seal) or addictions( raskusyvanie solid objects, etc.) especially if there are no standing next teeth. Such injuries are minor, but permanent, which leads to a chronic course of the disease.
Content
- Acute and chronic
- Clinical picture
- The diagnosis
- Medical Assistance
- forecast and consequences
- Preventive measures
Acute and chronic
presence of interstitial fluid in the periodontal ligament facilitates load teeth when chewing. Fractures and cracks in the tooth roots are excellent vehicles for the development of pathogenic environment( streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci).
In the periodontium itself there is a huge number of receptors that react to pressure. In the case of an inflammatory process( development of periodontitis), there are pronounced painful sensations, there is swelling. If there are obstacles to outflow of the interstitial fluid, the disease is characterized by an acute course( serous or purulent).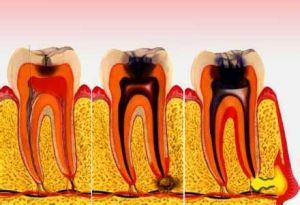
If possible outflow of fluid through the root canal, pain weakening, but it creates the conditions for the transformation of the disease in the chronic form. For this form of periodontitis, periods of exacerbation and rest are characteristic. The slightest hypothermia or even a stressful situation may trigger a sharp worsening of the disease as traumatic overload periodontal already occurred once or permanently injured tissue. The inflammatory process in this case develops lightning fast. It is believed that this form of the disease is more severe.
Clinical picture
Traumatic periodontitis is not always possible to promptly detect, as the main symptom is pain, but due to impact or other damage to the affected area in any case will be ill, may form a hematoma. That is why the disease quickly takes an acute form.
 A few days after the injury, the patient may begin to worry about discharge, even purulent, in which case there is an increase in body temperature. A damaged tooth can become mobile and change its color( with extensive damage to blood vessels).Possible collateral swelling of the gum and an increase in regional lymph nodes that are painful on palpation. A clinical blood test will show an increase in the number of leukocytes and increased sedimentation of erythrocytes( ESR).
A few days after the injury, the patient may begin to worry about discharge, even purulent, in which case there is an increase in body temperature. A damaged tooth can become mobile and change its color( with extensive damage to blood vessels).Possible collateral swelling of the gum and an increase in regional lymph nodes that are painful on palpation. A clinical blood test will show an increase in the number of leukocytes and increased sedimentation of erythrocytes( ESR).
The symptoms of chronic disease are minor. The patient may complain of mild pain while chewing or direct pressure on the problem tooth. Such a process can go unnoticed for a long time.
Diagnosis of
Initially, a physician collects an anamnesis of the patient, then conducts a physiological examination. Based on the results of the examination, an x-ray examination can be prescribed. In the absence of crowns on the teeth, it is possible to designate an electrodontiagnosis( EOD), which will help determine the pulp condition, and also reveal the presence of periapical changes.
Acute traumatic periodontitis is difficult to confuse with other diseases due to its etiology. But the chronic course is often differentiated from pulpitis, but with a detailed examination periodontitis has a characteristic difference:
- pain clearly localized, constant, spontaneous;
- changes in mucosa;
- painless probing;
- no reaction at temperature;
- discoloration of tooth, crown;
- general malaise.
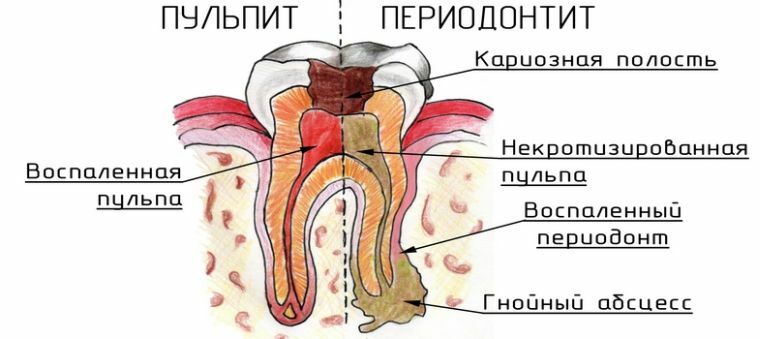
Than pulpitis is different from periodontitis
Medical care
Traumatic periodontitis is treated in several stages. In its acute course, it is necessary initially to provide free waste of fluid released from the tissues during the inflammatory process( exudate).If the liquid is contaminated with pus, the patient is given broad-spectrum antibiotics. Physiotherapy is prescribed, as well as rinsing of the mouth with antiseptic solutions.
If the disease has acquired a chronic form due to small regular injuries, the primary task is to remove the pulp and damaged dentite. Further, the channel is thoroughly sanitized with ultrasound. After eliminating the inflammatory process in the periodontium, the canal is sealed.
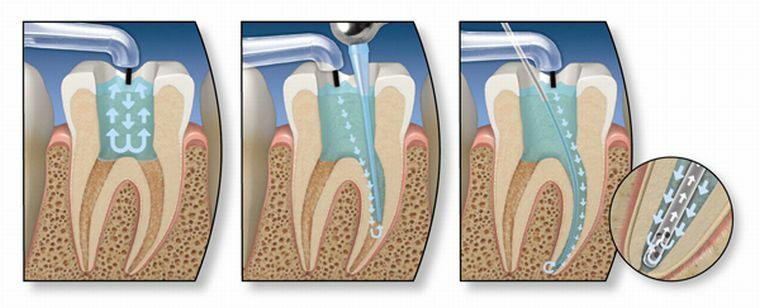
If the disease is caused by a poorly delivered seal, its complete replacement is necessary with further manipulations to eliminate painful symptoms.
In severe cases, doctors can resort to apical excision of the root of the tooth, fixing the remainder in the alveolus.
Prognosis and consequences of
When the inflammatory process is stopped in most cases, a full recovery occurs. If negative habits have led to traumatic periodontitis, it is necessary to refuse them. There are cases when the treatment has not yielded positive results( often this happens with neglected processes), in this case the patient is removed a tooth and decides the question of further prosthetics.
In addition, scientists have found a link between periodontal diseases and cardiovascular diseases and tumors in postmenopausal women. Therefore, in the presence of problems in the oral cavity, you must immediately contact a specialist.
Preventive measures
Prevention of traumatic periodontitis is difficult, as it is impossible to predict a serious injury or injury. But it is possible to avoid minor domestic damage. It is necessary to use dental floss carefully, not to bite tough food( bones, nuts, etc.), to choose the experts in the field of dentistry, to avoid inadequately placed seals and crowns.
If the patient is aware of the chronic course of periodontitis, but for some reason it is currently impossible to protect the tissues from permanent damage( eg, playing with wind instruments), then a number of simple recommendations should be followed:
- Oral hygiene .It is necessary to clean the teeth at least two times a day. Change the toothbrush once every three months. Bristles of the brush
 should be atraumatic in order to avoid the risk of infection.
should be atraumatic in order to avoid the risk of infection. - Professional cleaning, removal of tartar .It is recommended to conduct professional cleaning at the dentist with parallel preventive examination at least once a year.
- Prosthetics .In case of incompleteness of the dentition, it is recommended to install a prosthesis. This will help reduce the high load on the remaining teeth, prevent deformation of the bite, which will reduce the likelihood of exacerbation of the disease.
Well, it is not superfluous to recall the need to visit the dentist at least twice a year.
