 It would seem that devitalization( killing with the subsequent removal from the bowels of the tooth of its living core-pulp) must inevitably lead to the death of the tooth with its inevitable destruction. For the death of the pulp leads to death and the smallest vessels that make up the contents of the dental cavity, and equally small nerves that allow one to react to changes in conditions( in the oral cavity and in the body in general).
It would seem that devitalization( killing with the subsequent removal from the bowels of the tooth of its living core-pulp) must inevitably lead to the death of the tooth with its inevitable destruction. For the death of the pulp leads to death and the smallest vessels that make up the contents of the dental cavity, and equally small nerves that allow one to react to changes in conditions( in the oral cavity and in the body in general).
But if everything is just happening in the wild nature, then in the modern world, where the teeth are increasingly becoming a design object, the use of the latest dental techniques allows not only to completely preserve the tooth intact, but also to give it any desired shape.
And although, strictly speaking, there is no life in the tooth without pulp, its physical existence continues. But only under condition of constant tracking and repair in case of occurrence even the most insignificant changes in it. For this is a tooth, its status equating to a monument of architecture, only without a sign: it is protected by the state.
So, minus the methods of removing the pulp in that the tooth, left without attention, will collapse, leaving a gap in the jaw, and plus - the tooth remains in the ranks of their own kind, remaining for chewing, and for completeness of life sensations.
Contents
- When
- can not be avoided without pulp killing
- Devitalizing methods and applied and paste
- Use of chemicals
- Electroncrosis and its features
When
can be dispensed with without pulp killing
The indications for the devitalization of the tooth are cases,when the removal of the pulp is inevitable, because the preservation of its living becomes impossible because of the inflammatory process that has begun in it. 
This is the case of acute pulpitis caused by:
- by infection either through the decayed bottom of the carious cavity, either through the apical mouth, or through a system of microcracks in acute and chronic periodontitis;
- by opening the pulp chamber with mechanical damage to the tooth or due to inadequate dental intervention.
Also, the operation may be necessary if it is necessary to prepare the tooth for prosthetics, when the risk of developing inflammation under an artificial construction should be completely ruled out.
Devitalizing methods and applied and pastes
The arsenal of means for tooth devitalization includes:
- depulpating pastes: containing arsenic, arsenic, formaldehyde-based compounds;
- use of electrochemical necrosis( electrocoagulation) method of pulp.
Despite the obvious toxic effect of arsenic, the need for ultra-accurate dosing and strict aging of the pulp cavity containing drugs, its use for devitalizing pulp is justified by a multitude of arguments.
For nothing else kills the pulp as reliably, quickly, painlessly as arsenic acid compounds.
Use of chemicals
Technically, the operation consists in applying a pulp paste containing arsenic collected at the tip of the probe to the exposed horn.
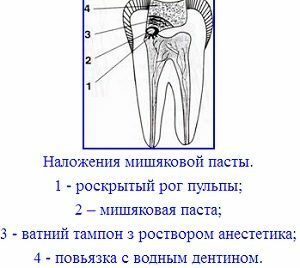
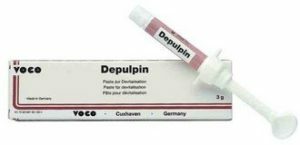 The applied paste is coated( without applying pressure) with a cotton swab impregnated with an anesthetic solution and wrung out. The dental cavity is closed( again, without pressure) with a loose bandage of water dentine, which has a temporary purpose, but which ensures the absolute tightness of the pulpal cavity.
The applied paste is coated( without applying pressure) with a cotton swab impregnated with an anesthetic solution and wrung out. The dental cavity is closed( again, without pressure) with a loose bandage of water dentine, which has a temporary purpose, but which ensures the absolute tightness of the pulpal cavity.
Given the volume of the pulp chamber( depending on the number of dental roots), the composition is removed from the cavity after 24 or 36 hours, with the development of the same chemical periodontitis, pulpectomy is performed immediately.
The probability of occurrence of short-term( within 1-2 hours) reactive pains of the patient is warned in advance, offering to soften their use of bromide preparations or Amidopyrin.
Another consequence of the use of arsenic pastes is the development of persistent toxic periodontitis, which happens when arsenic is exposed to long and excessive. Therefore, in order to avoid damage to the periodontal with the emergence of foci of necrosis when using arsenic, in calculating the dose and exposure time, factors such as the mass of the tooth and the age of the patient should be evaluated.
 Scientific works, however, proved that the use of adequate doses of arsenious acid( due to its diffusion into the periapical space) causes not only the destruction of the pulp, but also the stimulation of its stump and even leads to the regeneration of periodontal tissues.
Scientific works, however, proved that the use of adequate doses of arsenious acid( due to its diffusion into the periapical space) causes not only the destruction of the pulp, but also the stimulation of its stump and even leads to the regeneration of periodontal tissues.
Due to the peculiarities of the structure of children's teeth( with roots resorbed and undeveloped), as well as the child's inability to adequately assess the emerging sensations, the use of acids in pediatric dentistry is contraindicated, phenol-containing drugs are used to provide painlessness for pulpectomy.
Non-arsenic paste, which is used for the devitalization of pulp:
- Formaldehyde( Formalin);
- Phenol;
- is a combination of their derivatives.
In formaldehyde pastes, Formalin powder( Paraformaldehyde, Paraform, Trioxymethylene) is kneaded either on creosote, or on glycerin, or on petroleum jelly.
Their effect is weaker and less reliable than arsenic-containing pastes, and in case of insufficient exposure time, instead of pulp necrosis, it is possible to achieve only its mummification( sclerosing).However, the purpose of manipulation can be precisely this effect: with the amputation method, in the case of treatment of children, the sclerized pulp left in the microtubules is aseptic and the inflammatory process no longer causes.
 Of the three pastes: Formalin, Asphalin and Triopases with a formalin content of 2.54, 8.38 and 12.3%, respectively, the application of the latter caused the greatest optimism in summing up the results, because in the amputation method, the pulp stump prevents diffusion of the split formaldehyde into the periapical space, the application of Asfalina's paste to reactive periodontitis leads most often.
Of the three pastes: Formalin, Asphalin and Triopases with a formalin content of 2.54, 8.38 and 12.3%, respectively, the application of the latter caused the greatest optimism in summing up the results, because in the amputation method, the pulp stump prevents diffusion of the split formaldehyde into the periapical space, the application of Asfalina's paste to reactive periodontitis leads most often.
When using a paste containing Paraformaldehyde, Lidocaine and Phenol, its effect lasts from 6 to 8 days, but has a softer effect, without irritation of the periodontal structures.
There are no special features when applying paraformaldehyde paste, they are the same as for arsenic.
Various companies produce pastes with or without arsenic, allowing not only to achieve the desired effect, but also  to plan a patient's visit to the dentist.
to plan a patient's visit to the dentist.
Thus, the use of the dental paste "Devit-A", which has a pronounced anesthetic effect, allows you to stop acute pain in the treatment of acute pulpitis, "Devit-P" - cause mummification of the pulp of milk teeth and avoid its extirpation, and "Devit-C"Use the methods of the mortal excirpation or amputation in the treatment of residual root pulpitis in the teeth both permanent and temporary.
Electroecrotization and its features
Necrotizing paste is not used in case of intolerance of its ingredients, in such situations the electrochemical necrosis method of pulp is applicable.
The essence of the operation is the opening of the pulp chamber with the introduction into its cavity for a certain period of the composition, causing either necrosis or mummification of the pulp with subsequent extraction( complete removal) or with amputation( extraction by partial, due to the impossibility of extraction).
Two approaches are used in the manufacture of the operation:
- one-stage ( without previous chemical pulp killing) with anesthesia;
- devitalization of in several stages of using arsenious acid or other toxic chemical compounds.
 The step immediately following the perforation of the pulp chamber is the application of the chosen for manipulation means to the naked horn of the pulp, the dose and duration of which in the tooth cavity depends on many factors( the composition of the drug used and others).
The step immediately following the perforation of the pulp chamber is the application of the chosen for manipulation means to the naked horn of the pulp, the dose and duration of which in the tooth cavity depends on many factors( the composition of the drug used and others).
This can be either arsenic-free or non-arsenic paste, or preparations containing formaldehyde.
Thus, in the arsenal of the modern dentist, there are all possible means to perform procedures for killing and removing the root in accordance with the treatment plan that does not infringe upon the interests of the patient or his psyche.
