 Diverticular disease of the colon - a pathological process, which is characterized by changes in the walls of some parts of the large intestine.
Diverticular disease of the colon - a pathological process, which is characterized by changes in the walls of some parts of the large intestine.
According to statistics, diverticulosis of the colon is more common in people in developed countries. In countries with a low standard of living, this phenomenon is rather rare.
Contents
- What is the concept of diverticulosis
- The main causes of the pathology
- Classification of the disease
- Symptoms characteristic of the violation
- Diagnosis of the pathology
- Treatment methods
- Traditional therapies
- Experience of the centuries
- Correction of the ration
- Complications and danger
- Preventive measures
What does the term "diverticulosis »
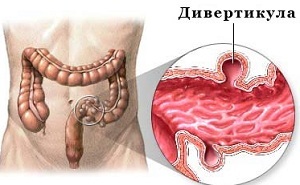
Diverticulum is a protrusion of the intestinal wall, resembling a pouch in appearance, which can arise in different departments.
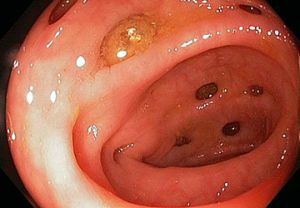
Diverticula
Look So often diverticula are observed in the descending colon, but more often they develop in the intestine of the sigmoid. Diverticula appear much less frequently in other parts of the large intestine.
Other parts of the large intestine( transverse and ascending colon, caecum) also get the risk of developing a disorder, but here it occurs much less often.
The reasons for the development of pathology can be a variety of factors( local or systemic), so the disease is classified as a polyethological class.
The formation of diverticula occurs in places that are less able to resist. Most often, the localization of the disorder occurs on the left side of the colon.
The main causes of the pathology of
The main contributing factor in the development of the disorder is malnutrition, this may be an insufficient amount in the diet:
- fluid;
- fruit;
- vegetables
- vegetable fiber.
Excess of easily assimilable products:
- products from wheat flour of the highest grade;
- eggs;
- fatty fish and meat.
With this type of nutrition, the fecal masses become denser, which invariably leads to constipation, stretching and traumatizing the walls of the intestine.
The latter become loose and form protrusions in the form of pockets turned inside out. People, after 50 years old and those who suffer from constipation for a long time, stand on the top step in the risk group of the disorder.
Overweight and sedentary lifestyle also play an important role in the development of the disease. Residents of Western countries suffer from diverticulosis much more often than the population of Asian countries. Moreover, the latter often affects the right side of the large intestine.
Most likely, this is due to the fact that the diet of Asians is rich in plant food( fiber), which favorably affects the work of the intestines, as it provides the formation of soft feces.
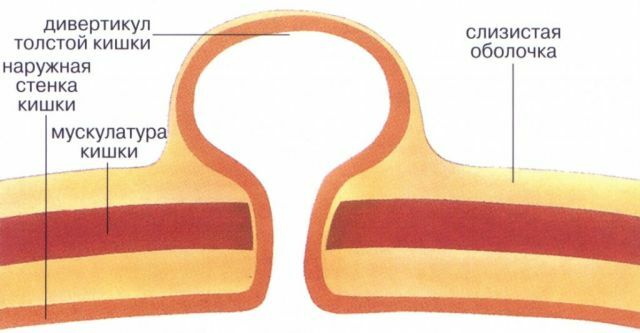
Classification of the disease
There is a clinical classification of the diverticular disease in the Russian Federation, thanks to which the doctor can assess the patient's condition, select an appropriate therapy and predict the disease prognosis.
Diverticulosis happens:
- Asymptomatic .In the first group of patients there are no intestinal symptoms of the disease. The pathology is diagnosed at them casually, at research of an intestine on other diseases.
- With clinical signs often manifests spasm of intestinal musculature, a violation of the balance of intestinal flora and digestive process. This form of the disease requires complex therapy, and in complicated cases - surgical intervention.
Diverticular disease can be complicated by such disorders:
- parietal infiltrate;
- diverticulitis;
- intestinal fistula;
- diverticulum perforation;
- Intestinal bleeding.
Symptoms typical of
violation Many people with a disease do not even know about it - it's an asymptomatic form of disorder. The rest of the patients are concerned about the following symptoms of the diverticulosis of the large intestine: 
- blunt or cramping pain in the abdominal area, which, after going to the toilet, decreases( the localization of pain directly depends on the location of the diverticulum);
- after emptying a feeling of relief does not come( the patient seems to have a full bowel);
- disorders of the stool - persistent constipation, alternating with diarrhea;
- bloating, flatulence.
Diagnosis of pathology
To diagnose a disease, the doctor directs the patient to the following research methods:
- Irrigoscopy is an X-ray of the large intestine using a barium contrast enema. Using this method, you can not only determine the presence of diverticula, but also their location, size and quantity.
- Fibrocoloncopy - this method is less effective than the previous one, so it is resorted to much more rarely.
- US - with the help of ultrasound the doctor can determine the complications of diverticulosis.
- Computed tomography using contrast agent , administered intravenously, like ultrasound, helps to identify complications.
- Obstructive radiography of the abdominal region - thanks to it, one can detect the perforation of the diverticulum.
- Laboratory studies of - in the bloodstream in this pathology, characteristic inflammatory changes are observed: an increase in C-reactive protein, platelets, and leukocytes;acceleration of ESR;blood loss is accompanied by anemia.
Methods of treatment
The purpose of the therapeutic course of treatment for rectal diverticulosis depends entirely on the degree of severity of the pathology. Treatment of an asymptomatic form of the disease is limited to compliance with the appropriate diet, and more complex requires medical or surgical intervention.
. Traditional methods of therapy.
. Non-surgical methods of treatment are based on the appointment to the patient: 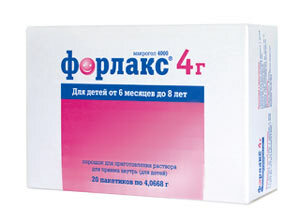
- laxatives ( Forlax, Mukofalk, Lactulose);
- with spasmodic pain shows spasmolytic ( Buscopan, Drotaverin, Mebeverin);
- with flatulence and swelling should take defoamers ( Plantex, Disflatil, Espumizan);
- antibacterial medicines ( Piperacillin, Co-trimoxazole, Rifaximin, Metronidazole, Ciprofloxacin);
- NSAIDs ( Salofalk, Mesakol, Sulfasalazine).
The operation is indicated in the following cases:
- intestinal perforation;
- narrowing - intestinal obstruction;
- profuse bleeding;
- abscess;
- intestinal fistulae.
Surgical intervention may be required in the absence of a positive result against the background of adequate conservative treatment, and with frequent bleeding, and with repeated diverticulitis.
The aim of the operation is to remove the affected area of the large intestine. The remaining parts are stitched either immediately or during a second operation( depending on the situation).
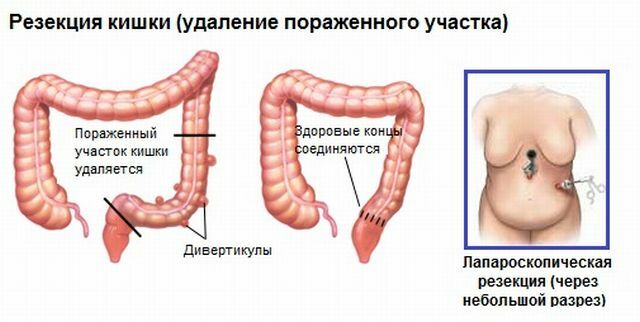
The experience of the centuries
Diverticulosis of the large intestine can be treated with folk remedies, which are very numerous and can not be described all within the framework of one article.
Here are the two most popular recipes.
- Herbal infusion of .With the help of a blender, it is necessary to crush dill, wild rose berries, motherwort, chamomile flowers, nettle. All components must be taken in equal proportions. One tablespoon of the obtained raw material should be poured into 200 ml of boiling water. Stir the mixture for 2-3 hours. Take the broth should be on an empty stomach in the morning and evening before dinner, 150 ml. The therapeutic course is 1.5 months. It is very important that at this time the patient's diet is saturated with fiber.
- Cleansing of the intestine by the Kuznetsov method .With this method, the patient can improve his state of health and prevent the development of complications. In equal proportions you need to take green apples and wheat germ. Skip all through the meat grinder.
For 250-300 gr.gruel take over breakfast. Course - 30 days. Take a break for 1 month and repeat the treatment.
Correction of the
diet In the asymptomatic course of diverticulosis, it is often enough to adjust your diet. To prevent dangerous complications, it is necessary to fill the lack of fiber and fluid in the body.
What you need is:
- fruits and vegetables, legumes, cereals, brown rice;
- sour-milk products( kefir, yoghurt, yogurt);
- first courses;
- juices from fresh vegetables and fruits;
- drink a lot of plain water.
That it is not necessary to eat absolutely or only in the limited quantities:
- crackers, popcorn, chips( to exclude completely);
- seeds and nuts;
- radish, persimmon, pineapple;
- fresh milk and eggs( limited).
Complications and danger
 Many complications of this disease require immediate medical intervention, often an operation is prescribed.
Many complications of this disease require immediate medical intervention, often an operation is prescribed.
Symptoms such as nausea with vomiting, fever, blood during defecation, changes in the nature of pain, impurities in the urine, and palpation of the formation in the abdomen can signal the development of complications.
The main complications of diverticulosis include:
- intestinal bleeding;
- inflammation of diverticula;
- perforation of the diverticulum;
- abscess in the cavity of the diverticulum;
- intestinal obstruction.
Preventative measures
Prevention of the disease is reduced to avoid constipation and maintain proper intestinal motility. A large role in this is played by rational nutrition and regular therapeutic exercises aimed at maintaining the abdominal muscles.
Daily consumption of clean water should not be less than 2 liters. A full rest, alternating with moderate physical exertion, also has a beneficial effect on the body and the intestine in particular.
The appearance of the disease threatens the patient with serious complications, therefore it is necessary to undergo a full diagnostic of the intestine once in two years. Indeed, with a timely diagnosed pathology, the prognosis is always favorable. And ignoring the problem is fraught with dangerous and unpleasant consequences.
