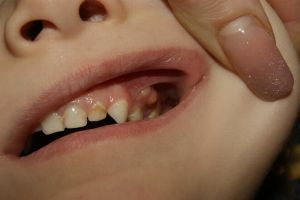
 Fistula is the formation of a non-gum color in the form of a tubercle that connects the root of the tooth or the lower jaw with the oral cavity.
Fistula is the formation of a non-gum color in the form of a tubercle that connects the root of the tooth or the lower jaw with the oral cavity.
This formation is inflammatory and is represented by a small hole, which contains a purulent secret.
A special concern for this kind of disease is in the parents, because in most cases the fistula on the gums is formed in children aged 4-8 years who have weakened and less resistant to inflammation immunity.
Not always a fistula can be a threat to the health of the child, as it can be manifested in the change of milk teeth to permanent.
However, the cause of the appearance of the fistula should be clarified, since in some cases its appearance may be caused by dental problems or respiratory diseases. Diseases of this nature can cause complications.
Efficiency in treatment will allow to completely get rid of the fistulous canal and there will be no need to perform a cosmetic surgery for its infection in the soft tissues of the face or near the surface of the cheek.
In any case, consultation with a specialist does not hurt, because the formation of an inflammatory nature has the property to expand.
Moreover, there is an increase in bacterial flora, the secretion of pus becomes abundant with pain, which brings discomfort in the process of eating.
Contents
- What can provoke the formation of a fistula
- How does he manifest himself?
- Approach to diagnosis
- Professional approach to therapy
- What does traditional medicine offer
- Possible complications of
- About prevention of
What can provoke the formation of a fistula
The main reasons for the appearance of a fistula in a child are:
- caries of infant teeth, which can be complicated by periodontitis;
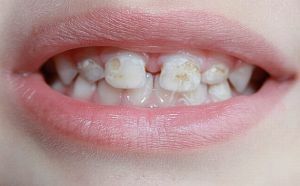
- appearance of pustular lesions of different nature on the gum;
- retinized milk tooth;
- maxillary sinusitis of an inflammatory nature;
- complications caused by improper dental medication;
- infectious lesion of bone tissue;
- infection of the site of mechanical injury of gingival tissues;
- any inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
The provoking factors are as follows:
- getting injuries with wound infection;
- weakened immunity during the formation of molars;
- overeating sweet;
- non-compliance with simple hygiene rules;
- improper oral care;
- dishonest and poor-quality canal sealing;
- overwork, hypothermia and infectious diseases.
How does he manifest himself?
The characteristic symptom of the appearance of the fistula is:
- The painful sensations of the on contact not only with the neoplasm, but also with the aching tooth that can be the cause of its
 appearance.
appearance. - As a result of reddening, swelling of the gums with the release of pus, , tooth mobility and bad breath from the mouth of can be observed. Most often, this situation is observed with inflammatory processes of granulating periodontitis of the baby teeth.
- Immunity status may be the cause of of osteomyelitis in infants .With progressive forms of the fistula, the child's temperature rises, lymph nodes increase, the face becomes asymmetric, as not only the upper lip swells, but also the neck.
- The inflammation and buildup of pus helps block the nasal passage, which creates difficulty in breathing .
- Affected areas become pink, and when touched, they feel pain. After some time swelling passes to the orbit and eyelids of .
The fistula symptomatology, caused by the chronic form of monotonous sinusitis, is diverse depending on the age category of the child:
- For example, in infants, newborns and young children has inflammation of the upper jaw and symptomatology is in some cases similar to osteomyelitis.
- In older children, , inflammation of not only the maxillary parts of the nasopharynx, but also other sinuses is added.
- The general picture of the disease : fever, headaches, shortness of breath with swelling of the soft facial tissues, severe pain along the trigeminal nerve. When palpation of canine fossa and teeth, painful sensations are observed. In the area of the upper lip and nasal openings, reddening of mucous membranes and external skin is noted.
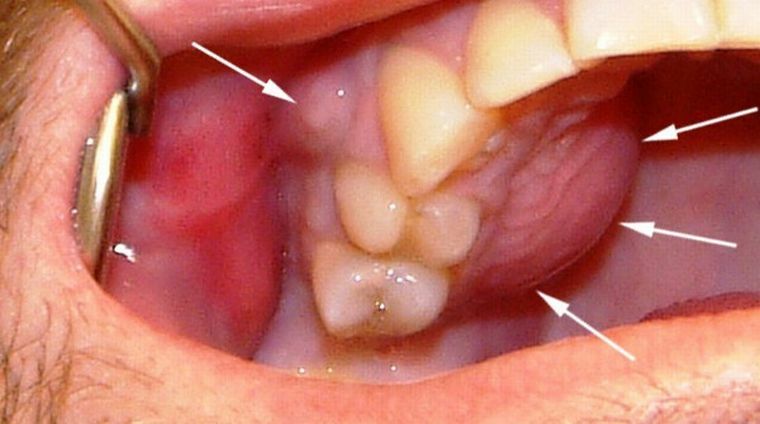
In the photo, the arrows show where the child has a fistula on the gums of the
 Thus, the secretion of pus and an unpleasant odor should be the reason for an urgent visit to the dentist.
Thus, the secretion of pus and an unpleasant odor should be the reason for an urgent visit to the dentist.
If you notice any symptoms of your baby, then immediately consult a doctor, as the children's body is too vulnerable and sensitive to inflammatory processes.
Approach to diagnostics
Fistula is an entity that is easy to notice with the naked eye. This tubercle has a different color from the gums and is most often located in the root regions of the teeth on the gum or under the tongue.
In most cases, the symptoms of the disease for a long time does not make itself felt, and then the toothache is sharply increased and painful sensations arise when the affected area is touched.
To detect and determine the true cause of the fistula, it is possible only during a routine dental checkup.
An x-ray of the jaw, which can be prescribed by a doctor, will help to draw a conclusion about the extent of the oral cavity and the pathology of the disease. Therefore, after a thorough and thorough examination, effective treatment will be prescribed.
Professional approach to therapy
Diagnosis and treatment of infant fistula should be handled by a dentist.
In the presence of a fistula near the molar tooth, the treatment of the disease is carried out in a therapeutic way: the old filling is removed and  completely cleans the tooth canal, which is covered with a temporary filling and anti-inflammatory drugs are placed there. When the inflammation is removed, a permanent seal is placed.
completely cleans the tooth canal, which is covered with a temporary filling and anti-inflammatory drugs are placed there. When the inflammation is removed, a permanent seal is placed.
When a milk tooth is affected surgically, it is removed. This is necessary to prevent the proliferation of granulated tissues and the subsequent occurrence of a purulent process already on the permanent molar tooth, which can subsequently collapse.
The extensive spread of infection to soft gum tissue requires the removal of these affected tissues. Modern medicine does not require anesthesia in this case, since removal of lesions by the laser procedure is not painful.
In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infection of the whole body of a child.
Treatment of the fistula involves the use of drug treatment, the purpose of which is to relieve inflammation. This is helped by a complex of antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agents in the form of gels, ointments or solutions. In parallel, oral administration of antihistamines is necessary.
What folk medicine offers
 Traditional medicine can be used as an auxiliary therapy to relieve inflammation and pain in the fistula.
Traditional medicine can be used as an auxiliary therapy to relieve inflammation and pain in the fistula.
In this case, rinse, compresses or ointments are particularly effective, which contribute to the healing of fistulous wounds.
Such popular folk medicine is very popular:
- infusion of chamomile, sage or marigold flowers , which should be rinsed every three hours;
- a piece of propolis the size of a pea must be chewed on a healthy side 2 times a day for 10 minutes for 5 days;
- infusion of oak bark or mountaineer snake, which can be used in combination with chamomile and calendula.
For the removal of pain, it is recommended to exclude irritating factors:
- to abandon solid and coarse food in favor of soft, which is further crushed;
- avoid sweet, sour, spicy and spicy foods;
- If it is not possible to brush your teeth, rinse your mouth.
Possible complications of
In most cases, fistulas are accompanied by a chronic form of periodontitis, which occurs without any special symptoms, therefore at an early stage it is difficult to detect this disease.
And if you miss the moment of treatment, then fistula and periodontitis can provoke infection of the bacterial flora throughout the body.
In chronic osteomyelitis, the disease affects the jaw bone, and its progressive form can go not only to the neck and cheeks, but also cause an abscess in the nasal cavity, on the eyelids and near the inner corners of the eyes.
In the absence of proper treatment, complications are unavoidable, as the disease can spread to other sites.
In addition, exiting pus and re-infection can affect the development of molars and tissues around it. Therefore, regular visits to the dentist will help to identify the disease and begin an intense struggle with it.
On the prevention of
To prevent the disease, the following preventive measures should be taken:
- oral hygiene;
- preventive examinations at the dentist;
- timely treatment of dental diseases;
- adherence to the diet and proper nutrition.
Fistula is a disease that is the result of more than one cause. Having certain risk factors and pathology, the disease should be diagnosed by a dentist. After that, appropriate surgical treatment is prescribed.
At home, fistulas can not be cured, on the contrary it threatens with a number of complications. Along with professional treatment and treatment with folk medicine, prevention of the disease should be carried out.
