Benign neoplasms of the body of the uterus, defined as a myoma, are frequent pathologies. Many have a general idea about them, not suspecting the existence of various types of tumors. And only after discovering their own diagnosis, which sounds unusually, women think that there is fibroids and fibroids, what is the difference between the concepts.
About the myoma
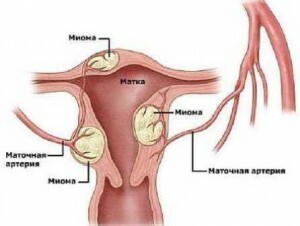 It is not hard to guess by the name of a benign tumor that it is related to myometrium. This deep layer of the uterus consists of smooth muscles. Under the influence of sex hormones, which lose balance, myometrium cells begin to share in a special way, leading to the formation of nodules. While the factors provoking the inaccuracy of their development exist, the process can continue, bringing the tumor to enormous proportions.
It is not hard to guess by the name of a benign tumor that it is related to myometrium. This deep layer of the uterus consists of smooth muscles. Under the influence of sex hormones, which lose balance, myometrium cells begin to share in a special way, leading to the formation of nodules. While the factors provoking the inaccuracy of their development exist, the process can continue, bringing the tumor to enormous proportions.
Myoma nodules are a collection of fibers of round or oval shape. Formations are single and multiple, can grow in the direction of the small pelvis or rushing into the body.
Other types of myomas in composition
But the main female organ consists not only of smooth muscles. It also has connective tissue. And although many specialists for patients simplify the notion of fibromyoma, uterine fibroids, there are differences between them.
They concern first of all the composition of the tissues from which the tumor is formed.
In fibroids, the largest volume belongs to the stromal cells. Smooth muscle fibers exist in the tumor in the minority. Despite this, the middle layer of the uterus becomes the base for fibroids.

Common in these neoplasms is that any of them has many blood vessels that feed tissues and support the characteristic symptomatology of the disease. But still in fibromioma there are more of them. A tumor, consisting only of smooth muscle cells, feels softer to the touch.
How to detect differences
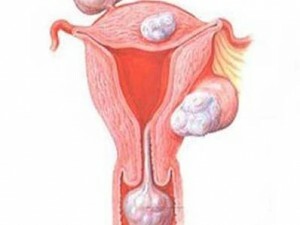 Even having received general information about what fibromyoma and myoma are, what is the difference between them, you can find it only after you have completed the examination. Symptoms both tumors give similar:
Even having received general information about what fibromyoma and myoma are, what is the difference between them, you can find it only after you have completed the examination. Symptoms both tumors give similar:
- Abundant discharge on menstruation days;
- Abdominal pain at rest, during intercourse;
- Bleeding any day of the cycle;
- Infertility depending on where they are located.
With a certain localization, both types of tumors press on neighboring organs, preventing their work. But the myoma does this less intensively because of the inherent elasticity of the tissues. A harder fibromioma, even with a smaller size, affects the intestine or bladder more vigorously.
But this is all a subjective sensation. You can clearly see the difference only by examining the structure with the help of ultrasound. The connective tissue present in the fibromioma, otherwise reflects ultrasound than the smooth muscle, is projected more clearly. So you can determine not only its availability, but also the volume.

Differences in the treatment of
What distinguishes myoma from fibroids of the uterus is the nuances of treatment, although the features of therapy for both tumors can not be called radically different. They can be determined by the fact that:
-
 Smooth muscles are more susceptible to hormones. Substances can cause both rapid growth of fibroids, and a decrease. Therefore, with a refined diagnosis and a small amount of neoplasm, it makes sense to begin treatment with hormone therapy to reduce the size of the tumor. This same feature leads the myoma to regression and disappearance during the menopause;
Smooth muscles are more susceptible to hormones. Substances can cause both rapid growth of fibroids, and a decrease. Therefore, with a refined diagnosis and a small amount of neoplasm, it makes sense to begin treatment with hormone therapy to reduce the size of the tumor. This same feature leads the myoma to regression and disappearance during the menopause; - Connective tissue behaves more calmly with respect to hormones. Therefore, with a small size of fibroids or fibromas, the physician will prefer a simple observation rather than anti-estrogen or angiogenetic therapy. But also expect that with the approach of menopause the tumor will decrease or disappear, in this case much less than the grounds. Hormone therapy can be prescribed only to stabilize the general background, reduce the opportunity for the development of a new tumor after surgery.
Otherwise, the choice of treatment is determined not so much by the structural composition of the neoplasm as by its location, size, and symptomatology. Large fibroids and fibroids are equally designed for surgical removal.
The most suitable method for this is chosen on the basis of more important considerations than the structural composition of the tumor. It is taken into account only in terms of the probability of bleeding during surgery, affecting its methodology, but not the very need for carrying out.
 We recommend reading the article on monthly for uterine myoma. You will learn about the disease and the causes of development, the impact on the menstrual cycle and the nature of the discharge, treatment of the consequences.
We recommend reading the article on monthly for uterine myoma. You will learn about the disease and the causes of development, the impact on the menstrual cycle and the nature of the discharge, treatment of the consequences.
Many people are concerned about the problem of degeneration of different types of myomas into cancer tumors. This occurs only in 1,5-2% of cases, it does not depend on the structure of the neoplasm.
With all this in mind, a woman with a similar diagnosis should not focus on how fibroids and fibroids are similar, what is the difference between them. It is better to leave these reflections to the doctor for an indirect prognosis about the speed and features of the development of the tumor. Today's medicine is able to rid of any type of this tumor.
