Imbalance of hormones in the female body can lead to various consequences: cycle disorders, fertility problems, and the like. Often as a result of such processes, as well as under the influence of other factors, follicular and cysts of the yellow body can be formed. For the development of a pathological condition, sometimes only a few weeks is enough, signs can be low-symptomatic or even absent. What is a hormonal ovarian cyst, is it necessary to treat it and how to do it correctly? Does it affect the possibility of conception?
Development of pathological education
Almost every cycle on one of the ovaries begins the growth of the dominant follicle. For its maturation is responsible follicle-stimulating hormone - FSH, which is produced in the pituitary gland of the brain. It is also affected by estrogens and some other biologically active substances. Usually the follicle with the egg reaches a size of 14 - 18 mm, after which the ovary capsule breaks in this place - ovulation. The process is not normally accompanied by pain or any other sensations. For a combination of reasons, in some cases, there may not be a rupture and release of the egg, this is called the follicle persistence. Such violations lead to a malfunction of the menstrual cycle. As a rule, this is a delay. This month, conception can not happen.
Further persistent follicle can go in two ways. In the first case, it significantly decreases in size to a few millimeters. If these disorders are repeated, polycystic ovaries are formed. In another case, the follicle begins to grow at the expense of the liquid formed inside it - it is soaked from the blood vessels located in its walls. A cyst is formed, which sometimes can reach in the sizes 10 - 15 and more centimeters.
If ovulation occurs, a yellow body forms at the site of the rupture. So it's called because of its color. The yellow body is formed by the action of the luteinizing hormone( LH) of the pituitary gland. It itself secrete progesterone - a pregnancy hormone, the lack of production of which can lead to miscarriage. Under the influence of many factors in the tissues of the yellow body begins to accumulate lymph and other liquid components. This leads to the formation of a luteal cyst. It can appear both outside pregnancy at the site of the ruptured follicle, and even after conception.
Reasons for the appearance of
To hormonal formations can be attributed two of their species - the follicular cyst and appeared on the place of the yellow body. The latter often occurs during pregnancy. Symptoms, tactics of treatment are the same, it is not always possible to establish exactly what was formed - the follicular or yellow body.
An exception is the detection of such tumors in early pregnancy. In 90% of cases, it is about the cysts of the corpus luteum, they can be detected already from 4 to 5 weeks, and independently regress to 16 - 18.
Similar formations can occur at any age, but more often they appear in womenreproductive period. Many factors influence this process.
Age fluctuations
Characteristic is the formation of hormonal cysts during the period of menstrual function in adolescent girls and for women on the eve of menopause. Practical for every 5 to 7 years before menopause, notes a failure in the cycle, an increase in the volume of menstrual blood - in most cases this is due to a violation of the function of the ovaries and the formation of such formations in them.
Hormonal imbalance of
Of course, in the first place in the formation play the role of sex hormones in the ovarian cyst. Especially in cases of artificial stimulation of the body, for example, during the preparation for IVF.All the methods used very rigidly "press" on the reproductive system of women. Artificial methods on the ovaries stimulate the growth of several dominant follicles simultaneously. After 2 to 3 attempts of IVF, not only does the risk of cysts on the ovaries increase, but also malignant tumors in the organ.
Similarly, all drugs used to increase the likelihood of pregnancy, for example, with polycystosis, also work. Of course, their influence is softer, but still can lead to further functional failures.

The hormonal background of a woman drastically changes after abortions, miscarriages. Not only the mammary glands are responsible for these processes( mastopathy occurs), but also the ovaries( formation of functional cysts).
Inflammatory processes of
Any infectious processes in the pelvic cavity, in the uterus or ovaries entail a disruption of the hormonal background, which eventually transforms into luteal and follicular cysts.
Their formation occurs in most cases at the end of an acute period of a month or two after treatment. If the infection is subclinical( with a minimum of symptoms), a woman may not be aware of the changes that occur in her body.
Hyperestrogenia of any genesis
An increase in the amount of estrogens in the blood also contributes to the formation of cysts and all the consequences that result from this. It must also be taken into account that fatty tissue is the source of these hormones. Accordingly, all women with overweight have risk factors for the development of such a pathology.
Stresses
Psycho-emotional experiences always entail a disruption of the relationship between all structures and bodies. Genital organs receive "commands" from the pituitary and hypothalamus, which are located in the brain. It is here that LH and FSH are formed, as well as other important biologically active substances.
Endocrine Diseases
The sexual system is in close association with other organs. Especially with those that perform endocrine function. First of all, these are the thyroid gland and adrenal glands. Chronic thyroiditis, hypothyroidism and other diseases can lead to the formation of functional cysts on the ovaries.
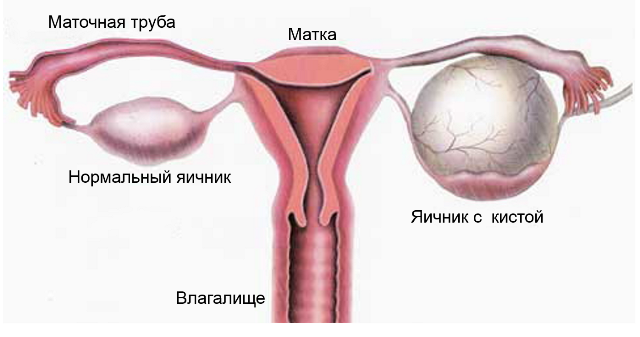
Symptoms of the presence of the
cyst In some cases, both luteal and follicular cysts are asymptomatic and are an accidental finding during surgery or ultrasound of the pelvis. There may also be various symptoms associated with the development of this condition.
Treatment of ovarian cysts with hormonal drugs in most cases helps to cope with all signs of ailment. And this is:
- Periodic or constant pulling pains in the lower abdomen, right or left. They can irradiate in the lower back, into the perineum and rectum. In most cases, pain intensifies after physical exertion, sexual intercourse, sharp turns or inclinations.
- The character of menstruation changes: regularity is broken, more often it is a delay of 14 or more days( even up to several months).Menses become more abundant, often with clots( some compare them with chunks of the liver).Critical days are more painful than usual.
- Decreases sex drive. Cysts often cause the impossibility of pregnancy for some time.
- When constructing a basal temperature chart or when performing ovulation tests, it is impossible to determine the time of release of the egg precisely - this process does not occur during the formation of cysts. The temperature measured in the rectum, as a rule, does not rise above 36.9 degrees during the whole cycle.
Signs of rupture of the ovary
Follicular and luteal cysts do not become malignant. The most formidable complication of such formations is their rupture. At the same time, intra-abdominal bleeding develops, without urgent surgical intervention a woman may die.

Often when a girl breaks, they indicate a sharp ache in her stomach that soon passed. Localization can be on the right, left or at the bottom of the stomach in the center. Then there are minor pulling pains in the same place, the intensity of which increases, and taking analgesics does not stop seizures. Over time, there is a feeling of pressure on the rectum, bloating. At this time the pain no longer has a clear localization, it is scattered all over the stomach.
As the blood loss increases, the pressure decreases and the pulse becomes faster, the skin becomes paler, darkens in the eyes, dizziness, drowsiness and weakness can occur until the fainting condition. With these symptoms, an emergency operation is shown, otherwise the consequences can be the most deplorable.
Do I need to be treated?
Follicular and luteal cysts should be treated when detected, starting with vitamin and hormone preparations, sometimes, with small sizes and no complaints, you can observe the education within 2 - 3 months. In the absence of dynamics during this period of time, treatment is prescribed. If the cysts are preserved after this, the operative removal of the neoplasm with subsequent histological analysis is indicated. The method and method of treatment can be established only by the doctor individually in each situation.
It is also important in the presence of any cysts on the ovaries definition of oncomarkers, in particular, it is CA-125, HE-4 and ROMA index. The increase in any of the indicators increases the risk of development of the oncological process in education. Such cysts are subject to immediate surgical removal, even if initially it was assumed that they are functional.
Treatment of ovarian cysts with hormonal drugs is the most commonly used and effective way. In most cases, this therapy is combined with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, as well as various kinds of resorbants. Hormonal pills for ovarian cysts are usual oral contraceptives, which are selected individually, taking into account the constitution and health status of a woman.
Surgical treatment involves the removal of a cyst, it is safer and less traumatic to do so using a laparoscopic technique. After such treatment, oral contraceptives for a period of three to six months or more are also prescribed. This is a kind of prevention of relapse.
 We recommend that you read an article on the paraovarian ovarian cyst. From it you will learn about the pathology and the causes of its development, symptoms of neoplasm, types of parovarial cysts, diagnosis and treatment.
We recommend that you read an article on the paraovarian ovarian cyst. From it you will learn about the pathology and the causes of its development, symptoms of neoplasm, types of parovarial cysts, diagnosis and treatment.
Can I get pregnant with a hormonal cyst?
The follicular cyst leads to a disruption in the cycle. When it is formed, ovulation is not present, and therefore conception can not occur. But in the process of treating such formations, the menstrual function can be restored. And even with such a cyst, the growth and maturation of other full-blown follicles occurs. And, of course, pregnancy can occur.
The same applies to luteal cysts. The only feature - often the formation of these formations occurs after conception has occurred.
Functional( hormonal) ovarian cysts can form in almost every modern woman. Often they proceed asymptomatically, being a finding at a planned ultrasound of the small pelvis. In most cases, after conservative therapy, neoplasms disappear. Hormonal treatment of the ovarian cyst is almost always carried out, in the same way, prevention of their appearance is carried out. If there are even insignificant complaints from the genitals, the specialist should be examined as soon as possible. Only he can guess the cause of the pathology and prescribe an effective treatment.
