About 30% of women experience lifelong tumors of internal genital organs during their lifetime. Fear of a possible operation and a long course of therapy causes most patients to wonder, but can the myoma dissolve itself? Medical statistics keep records of such cases. However, not all so simple. To make an informed decision, to treat a tumor or not, women should be well aware of the mechanism of the occurrence of such a pathology.
Uterine fibroids: causes inbody
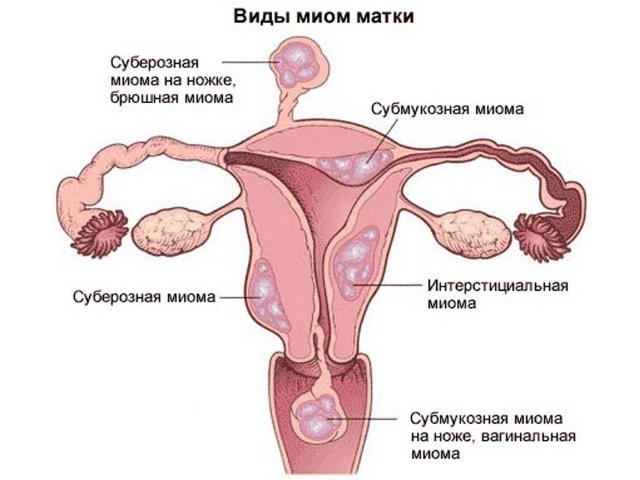
Benign tumor that affects the uterus of the patient, occurs due to certain hormonal fluctuations in the blood. It has long been proven that with the surge of female sex hormones, estrogens, there is an increased growth of the endometrium. This tissue layer is in large quantities in the uterine cavity.
It is the growth of the endometrium that experts call the myoma of the body of the uterus. This pathological process can localize in the walls of the reproductive organ, occupy a certain space in the cavity. It is not uncommon for cases when the neoplasm was on the outer wall of the uterus.

For standardization of data, gynecologists determine the value of a benign tumor in comparison with a pregnant uterus. The more weeks from the moment of conception, experts fix, the less chance that the uterine myoma will resolve itself.
As already mentioned, the main cause of neoplasm is a spike in estrogen in the woman's blood. This can occur during the development and ovulation of the egg in a woman, during pregnancy, childbirth. Even the process of puberty girls can lead to uncontrolled growth of this hormone. By the way, abortion is the start to a large release of estrogens, so frequent abortion operations can provoke a tumor process in the uterine cavity.
There is a medical theory that if the growth of a tumor depends on a high level of hormones, then with a drop in estrogens, the fibroid should decrease in size and virtually disappear. This beautiful assumption has not yet found practical confirmation. Myoma does not want to obey the rules and laws of biology. Therefore, the question of whether the uterine myoma can pass itself, remains open.
What specialists say about the facts of spontaneous resorption
The only period in the life of a woman, confirming the postulate that with decreasing estrogen levels, uterine neoplasms can regress, is the menopause period. At approach of this age period in the patient the quantity of sexual hormones in blood gradually decreases and in 2 - 3 years reaches minimal values.
This fact has a beneficial effect on muscle tumors in the body of a woman. Myoma body and uterine cavity begin to decrease in size, and often completely dissolve. Much depends on the size of the neoplasm. Myomas with diameters up to 20-30 mm are several times more likely to pass themselves than larger tumors.
The location of the degenerate endometrium also plays an important role. If the node is located in the uterine cavity and is sufficiently mobile, the chances of spontaneous disappearance are significant. But whether the hysteromyoma can disappear if it has grown into the depth of the muscular wall remains a highly controversial issue.

Of course, the more estrogen in a woman's body, the more it will retain the symptoms of youth and freshness. However, at the same time, a high percentage of these substances do not allow benign tumors to resolve.
In nature, everything is interconnected, and the patients with a minimal fat layer have the greatest chance of getting rid of the uterine tumor without treatment. At the same time the aging process in such women is more pronounced.
Situations are described where the process of pregnancy led to the disappearance of the uterine body by the myoma. In this case, everything also depends on the change in the level of estrogen and progesterone in the body of the future mother. As with menopause, self-destruction is most often susceptible to small tumors with high mobility.
However, it is not recommended to expectant mothers to hope for such a smile of nature. More often than not, the presence of myoma of the uterus will create additional difficulties in bearing the child and subsequent childbirth.
If a woman has a neoplasm of internal genitalia during a preventive examination, then one should not think about whether the uterine myoma can disappear or not. Any benign tumors, especially in women, require appropriate treatment. The reason is that the female hormonal background promotes the transition of a benign process to oncology 3 to 4 times stronger than that of men. Therefore, experiments with your health can lead to disastrous consequences.
Drug therapy for neoplasm in the uterine cavity
Even 20 years ago, when diagnosing a similar pathology, most specialists insisted on urgent surgery. Amputation of the uterus with or without appendages was considered the main measure to prevent the transition of a benign process to cancer.
Currently, approaches to the treatment of this pathology have radically changed. Only 10% of women who suffer from this disease show surgical treatment.
If the patient does not reach a large size of the uterine fibroids, gynecologists are successfully used to treat a combination of various hormonal proto-vaginal products. Most often, patients are recommended oral medication "Novinet" and "Ovidon."These drugs well suppress the main symptoms of a tumor of the uterine cavity, such as bleeding and pelvic pain during the period of ovulation and the last days of the menstrual cycle.
Positive results are confirmed with the use of gonadotropin hormone antagonists."Diferelin" and "Zoladex" can reduce the size of myoma almost twice. However, the effect of these substances is well pronounced only during the treatment. These drugs are often prescribed before the operation to remove the uterus.
Quite a controversial recommendation is to use for the treatment of uterine fibroids a drug such as Dufaston. Substances leading to an increase in progesterone in the patient's blood, thereby reducing the effect on her body of estrogens, which leads to a reduction in the size of a benign tumor.
In addition to drugs for the treatment of fibroids, FUS-ablation is currently being applied, that is, melting the affected uterine tissue with an ultrasound beam. This procedure is absolutely painless and is carried out in the conditions of a polyclinic or medical centers.
This technique allows you to remove even large myomoneous nodes, while the tissue structure of the uterus is completely preserved, which guarantees a successful motherhood in the future. To minimize the impact on the tissues of the affected uterus, this method of treatment is usually combined with MRI.The only negative criterion of FUS ablation is still the relatively high cost of the procedure.
 We recommend to read an article about the treatment of multinodular myoma of the uterus. From it you will learn about the diagnosis of the disease, the need for treatment, the effectiveness of drug therapy and surgical intervention.
We recommend to read an article about the treatment of multinodular myoma of the uterus. From it you will learn about the diagnosis of the disease, the need for treatment, the effectiveness of drug therapy and surgical intervention.
Operative way of treatment of benign tumors of the uterus
All modern gynecology subdivides the operative method of treating uterine fibroids in two ways. In most cases, specialists have to resort to hysterectomy or removal of the uterus body with or without appendages. A variant is possible when the cervix is excised together with the uterus.
The scope of surgical intervention usually depends on the severity of the patient's condition, tumor size, concomitant gynecological and somatic diseases. An important factor can be the results of cytological research, which are often performed right during the operation.
Myectomy
Recently, the method of myomectomy or the removal of some of the provoked nodes has become widespread. This method of treatment, of course, is more sparing, requiring a smaller volume of surgery and, accordingly, a more labile postoperative period.
Some drawbacks of such surgery include the possibility of acute bleeding during surgery, the formation of a massive adhesive process in 60-70% of cases after working in the abdominal cavity and repeated growth of uterine fibroids. In each specific case, the surgeon discusses the estimated amount of surgical treatment with the patient.
Removal of embolizate
In many clinics, the introduction of a special substance - embolizate - into the uterine vessels is quite widespread. Nutrition of the nodes of the uterus stops, necrosis or reverse development of the uterine nodes occurs. Quite often, the mobile tumor is independently released from the uterine cavity with menstruation.
If after diagnosing the problem is aggravated, but whether the myoma can disappear, then the patient should first of all get a qualified consultation from a specialist. The percentage of self-resorption of benign uterine tumors is so low that fear of treatment can prolong the disease and require much more effort from doctors and the patient than immediately after diagnosing a benign tumor.
The most dangerous property of uterine myomas is the possibility of malignancy of the process. In this case, a passive expectation can lead to disastrous consequences.