A multi-chamber ovarian cyst is a cavity formation that has internal septa. Most often filled with a liquid of different viscosities - from watery to slimey. The multicameral ovarian cyst has its own characteristics of the clinical course, treatment and diagnostic tactics. Such neoplasms should be treated with caution, since inside the tumor on the septa can form foci of malignant growth. What are the multi-camera cysts and how to deal with them correctly?
Types of multi-chamber cysts and their features
A multi-camera can be any ovarian cyst. Partition walls can be formed initially or in the process of growth of the neoplasm. Most often you have to deal with the following multi-chamber cysts:
- Follicular, is functional and is formed on the site of a non-burst follicle. More often these cysts have a one-chamber structure. And only with long flow and large sizes they become multi-structural.
- Yellow body cyst , also functional, is formed on the site of the bursted follicle.
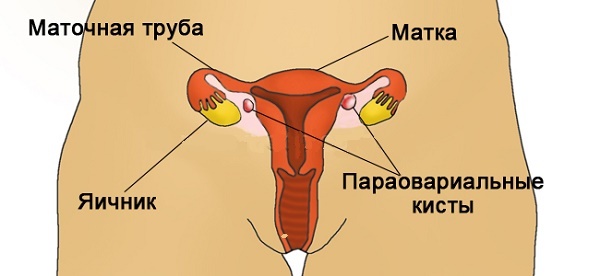
- Paraovariables - are located next to the ovary, grow not from its tissues. But it is often difficult to specify in diagnostics that this is just such a cyst, as in structure it is no different, but is close to all structures.
- Endometrioids are formed from an initially small foci of the endometrium on the ovary. Over time, the cyst grows, is filled with chocolate-colored contents and forms a multitude of chambers.
- Cystadenoma is also a fairly common ovarian tumor. There are three of its types: serous, mucinous and serous-papillary. The latter has internal proliferation, and therefore the risk of its malignant growth is highest among all others.
- The dermoid cyst can also be multicameral. This type of education is formed in the period of embryonic development, gradually the tumor increases and becomes noticeable in studies. Inside it in the cells you can find formations that resemble fatty tissue, nails, hair, etc.
Multicameral cysts differ in their flow patterns. The main ones are as follows:
- they are usually large enough, from 5 cm;
- such cysts are less susceptible to conservative treatment, since they have a multitude of cavities where the production of secret - internal contents is constantly going on;
- at first glance, not having any signs of malignant growth, they can hide the cancer inside on partitions;
- often give symptoms( abdominal pain, menstruation disorders and others) and complications( rupture, torsion of the legs, etc.)
 We recommend reading the article on inflammation of the ovarian cyst. From it you will learn about the causes, symptoms and signs of pathology, conducting diagnostics and methods of treatment.
We recommend reading the article on inflammation of the ovarian cyst. From it you will learn about the causes, symptoms and signs of pathology, conducting diagnostics and methods of treatment.
And here is more about the ovarian cyst in the menopause period.
Why there was a multi-chamber ovarian cyst
Unambiguous reasons for the development of multi-chamber cysts have not yet been established. In each specific case, the form and structure of education is formed under the influence of external and internal factors.
Predisposing moments for the formation of such cysts are as follows:
| Cause | Why the consequences arise |
| Inflammatory processes of the genitals | The role is played as an infection of the uterine cavity and the vagina, and the appendages. |
| Endocrine disorders | Ovary in its functioning is closely related to other organs of internal secretion, primarily with the thyroid gland. Therefore, changes in its work with time lead to the formation of cysts. |
| Disorders of the menstrual cycle that arise from the imbalance of sex hormones | This affects the functioning of the ovaries. |
| Pregnancy, especially if it is interrupted both at the request of a woman and spontaneously | At this time in the body there are serious restructuring, hormonal and structural, and sharp failures lead to violations of all these processes. |
| Intrauterine effect on the girl's body of unfavorable factors | This can be both medicines, and poor-quality food, the environment, etc. |
| The risk of occurrence of similar formations is also higher during the formation of menstruation in adolescents and during the onset of menopause | It is due to the fact that the body undergoes significant hormonal changes. |
Symptoms of education in the left and right ovaries
Symptoms of the disease do not differ from those that are present in ordinary, single-chambered, ovarian cysts. The following can be distinguished from the main ones:
- Periodic or persistent pain in the lower abdomen. They can be localized more to the right or to the left, to give in the sacrum and waist.
- Instead of pain, a woman can simply feel pressure on the bladder, rectum. This can form a false urge to defecate, as well as frequent urination.
- With a large tumor size, it can create additional pressure in the abdominal cavity, which will cause shortness of breath and shortness of breath. Also, the size of the abdominal circumference in a woman can increase.
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse, which was not before. Usually, this is an acute pain in case of abrupt movements or a change in the position of the body. In violent sexual intercourse, even a cyst can break, and this is an emergency that requires emergency medical care.
- Any physical activity can provoke pain.
- There is a violation of the menstrual cycle, most often these are delays of different duration, less often - periodic daub.

Also should be alerted if the following occurs:
- Increased temperature without obvious signs of ARVI or other ailments.
- Weakness, dizziness and even loss of consciousness may indicate a ruptured cyst and intra-abdominal bleeding.
- If a woman notes that in a short period of time she has signs of hyperandrogenemia - an increase in the number of hairs on the chin, nasolabial fold, along the white line of the abdomen, and so on.
- Sharp weight loss while maintaining normal diet and exercise.
- When determining a tumor in the abdomen below the navel.
Look at the video about the ovarian cyst:
Diagnosis of having a multi-chamber cyst
It is possible to suspect the presence of a multi-chamber cyst in a woman based on the complaints and the prescription of the disease. When gynecological examination, you can clearly identify the tumor in a small pelvis and give its approximate characteristics. Based on this, the gynecologist prescribes an additional examination, the approximate list is as follows:
- Ultrasound examination of pelvic organs. This is the most accessible and sufficiently informative method for detecting ovarian tumors, especially if technologies are used to study blood flow in the cyst - dopplerometry area. With ultrasound, you can clearly trace the structure, determine the number of cameras, the presence of sprouting on the partitions, the contents and much more.
- To determine the nature of the tumor process( benign or malignant), tests for oncomarkers should be submitted. The minimum list is CA-125, CA-15-3, HE-4, ROMA index. At normal values, the probability of a malignant tumor is minimal.
- If necessary, CT or MRI can be given, which gives an accurate picture of the structure of the neoplasm.
- In acute surgical pathology, puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix can be performed to clarify the presence of intra-abdominal bleeding.
- As a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure, laparoscopy can be performed.
Than a cyst of a large size
is considered to be moderate. Cysts up to 5 cm are considered average. Anything higher is considered to be large and causes many inconveniences to a woman, and can also lead to aggravation of chronic pathology and the development of other diseases. There are cysts 20 and more cm in diameter. The most common complications of such formations are:
- There is a compression of a number of located organs - the bladder, rectum, vessels, nerve endings. This leads to dysfunctions, congestion of venous blood, progression or development of small pelvis varicose and lower limbs.
- Elevated intra-abdominal pressure affects the diaphragm, which leads to shortness of breath, impaired cardiac activity. Against the background of chronic diseases( bronchial asthma, heart defects, etc.), all this will clearly be felt by a woman.
- The larger the cyst, the higher the risk of injury and rupture with a life-threatening condition.
- Risk of malignancy and development of ovarian cancer.
Features of the emergence of multi-chamber cysts in pregnant women
Multi-chamber cysts in pregnant women are formed by the same processes as in the usual states. In most cases, it is a malignant neoplasm that passes on its own up to 12 to 16 weeks.
But if previously the girl was not observed in a gynecologist, it is possible that the cyst on the ovary has an endometrioid or dermoid structure.

The whole problem of such formations is as follows:
- It is difficult to exclude 100% malignant growth, especially if the cyst does not last until 16 weeks.
- During the growth of the uterus, additional pressure will be applied to it, which can cause a rupture. The longer the gestation period, the more difficult it will be to establish an accurate diagnosis and carry out the treatment.
Treatment of multicameral ovarian cyst
The tactics of multicameral cyst treatment depend in many respects on the results of the examination( features on oncomarkers), as well as on the size and concomitant complications.
Is it possible to do without the operation
If the woman's condition is compensated( there is no rupture of the cyst, etc.), treatment begins with conservative measures. Their effectiveness is considered for two to three months. If the cyst is preserved after this period, the neoplasm is removed. Conservative therapy includes the following:
- antibacterial drugs;
- anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic;
- enzyme medications;
- hormonal preparations;
- vitamin complexes and some others.
Puncture treatment
For puncture it is necessary to strictly approach the indications. Cysts with suspicion of endometrioid or dermoid, with inflammation, etc. are not suitable.
Operation as one of the reliable methods of getting rid of the cyst
If the cyst does not disappear on its own after conservative treatment, it is recommended to remove it surgically.

These include the following:
- aesthetic cuts - just a few small punctures, which over time are barely noticeable;
- low traumatism;
- little blood loss;
- rapid recovery, already for 5 days a woman can return to the usual way of life with some restrictions.
What can I do if I'm pregnant
If a girl has a cyst before the pregnancy is planned, she should be removed and only then try to conceive the baby. If the same education is revealed during gestation, the tactic is as follows:
- . Up to 16 weeks, dynamic monitoring of ultrasound and well-being of a woman is carried out. All oncomarkers must be checked to exclude malignant growth.
- If the cyst is preserved after 16 weeks, surgical treatment is suggested, if its size is more than 3 cm.
- In case the tumor is up to 3 cm, the removal issue is decided on an individual basis.
- If the cyst is detected after 16 weeks for the first time, the tactics are individual. Up to 22 weeks, you can still remove it, after this time it is technically extremely difficult.
How to prevent the development of multi-chamber ovarian cyst
It is not always possible to influence the process of cyst formation, especially to prevent its multi-chambering. Of the general recommendations, the following can be singled out:
- All inflammatory diseases of the genital organs should be detected and treated promptly and all other gynecological pathologies should be treated.
- Only on indications to use hormonal preparations, and oral contraceptives carefully to select individually.
- Healthy lifestyle: proper nutrition, body mass correction, sufficient physical activity.
 We recommend reading an article on the treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery. From it you will learn about the types of pathology and the causes of its appearance, symptoms and possible consequences, as well as the methods of treatment.
We recommend reading an article on the treatment of ovarian cysts without surgery. From it you will learn about the types of pathology and the causes of its appearance, symptoms and possible consequences, as well as the methods of treatment.
And here is more about the ovarian hormonal cyst.
A multi-compartment ovarian cyst is a pathology that can mask the signs of malignant growth. Timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease will help to maintain the health of the woman, her reproductive function.

