Myoma of the uterus is the most common gynecological disease, and its most common form is fibromyoma. It is diagnosed in our country in 40% of women aged 30 to 55 years. Fibromyoma of the uterus, the symptoms and symptoms of which are quite typical, nevertheless often has erased manifestations in women of different age categories. Therefore, it requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and comprehensive treatment.
Causes of fibromyoma and its development
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that have a mixed muscle and connective tissue origin.

The maximum incidence of a tumor at the age of 35 to 55 years is due to the fact that a woman has accumulated a number of negative factors by the age of 35 that contribute to the development of fibroids. These include:
- strong emotional experiences, stress;
- abortion in history;
- hormonal contraception for a long period, uncontrolled or inadequate;
- nulliparous to 35 years of age;
- concomitant diseases of pelvic inflammatory organs( ovaries, uterus, appendages and so on).
Another important role in the development of the tumor is played by additional external factors:
- obesity;
- endometriosis;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- pathological menopause;
- metabolic disorders;
- various neuro-endocrine disorders.
Fibromioma of the uterus is characterized by uneven growth, occurring jumps, jerks. This means that it can be for many years in the so-called "sleeping" state, do not grow and show no signs of progression. And then the period of sharp development begins, connected mainly with any provoking external factors.
This can be the age of a woman, some nervous or endocrine fluctuations in the body, lifestyle changes, inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs and so on. The growth of the tumor is very diverse and occurs in different directions( both inside the uterine cavity, and outwards).Moreover, the plurality of foci, their location and size may also be different.
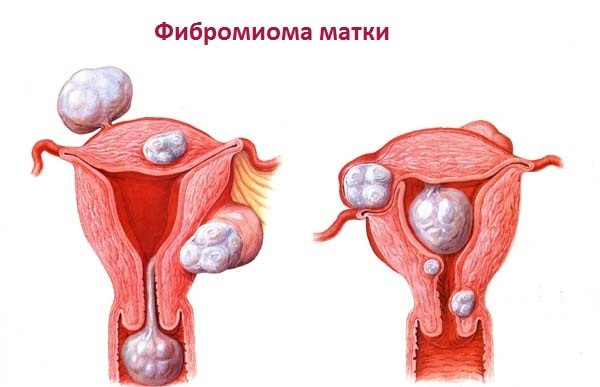
Symptomatics and Diagnosis of Fibromioma
Fibromyoma of the uterus, the symptoms of which are often a long period do not make themselves felt, requires an integrated approach. To detect in this case, it is possible only on ultrasound, or with the help of other instrumental methods of investigation.
How to recognize the signs of uterine fibroids? One of the early and characteristic signs of a tumor is dysmenorrhea or algodismenorea. That is, painful and atypical monthly, up to vydeleny different nature. It can be and heavy bleeding, and unstable daub.
It should also be taken into account that the fibromyoma clinic can be erased and lubricated due to frequent combination with other gynecological diseases, in particular inflammatory pathologies of the ovaries, appendages and other small pelvic organs. All these diseases have a similar clinic and can also cause uterine bleeding. Therefore, in such cases, it is mandatory to pass additional studies to establish a differential diagnosis.
For an adequate diagnosis, the first thing to do is to go to the gynecologist once a year( especially after 35 years).The most informative are such examinations as examination on the gynecological chair, ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages, computed tomography of the pelvic organs, cytological and histological examination of the material taken by biopsy.
Methods for the treatment of fibroids
Uterine fibroids, whose treatment can only be complex, includes two methods - operative and conservative. Indications for surgical treatment of fibroids:
- heavy bleeding, which leads to rheological disorders of the blood;The
- node is localized in the submucosa;
- is a growing fibromyoma in postmenopausal women;
- is located near the cervix;
- abrupt growth of fibroids or tumor progression on histological examination;
- localization near the fallopian tubes( leads to infertility);
- presence of concomitant pathologies;
- uterine fibroids, the size for the operation of which is analogous to the 14th week of pregnancy;
- effect on the surrounding organs( compression of ureters, intestines and so on).
The choice of a specific surgical method depends on the patient's age and potential childbearing function. In the case of a woman less than 40 years old, or if she has not yet given birth, a conservative operation of local removal of fibroids by the laparoscopic method is indicated. The only exception is the very multiple dissemination of the uterus by the foci.

Fibromyoma of the uterus, the operation to which it is contraindicated, is treated by a medicamentous method. It is especially relevant if it is a young woman who did not give birth, and the myomatous nodes are small and do not show a tendency to growth( diagnosed at an early stage).
Adequately conducted conservative therapy at an early stage in the development of fibromioma allows a high degree of probability to prevent further tumor progression, node growth and the appearance of new ones, and, as a consequence, preserve the reproductive function of the woman.
The main drugs of choice are agents that inhibit the synthesis of gonadotropic hormones in the pituitary gland. Fibromioma of the uterus, the size of which is less than the 14th week of pregnancy, responds well to such substances. Accepting them, the patient is put into a state of artificial menopause, and the level of estrogen and progesterone in the blood drops dramatically.
However, if the tumor is primarily based on connective tissue, its susceptibility to treatment with such drugs will be minimal. This is due to the fact that there are practically no hormoneally active receptors in such fibromas.
Auxiliary therapy for
fibroids. Additional therapy consists mainly in alleviating the negative symptoms of the disease and strengthening the general properties of the body:
- anti-inflammatory drugs( especially in the case of concomitant pelvic inflammatory disease);
- correction of hemorrhagic anemia with iron-containing preparations;
- neuroprotectors and sedatives for normalizing the emotional background;
- vitamin therapy and lifestyle correction.
Prevention of fibroids is in the right way of life and following a set of recommendations. Mainly it is adequate hormonal contraception and control of the hormonal background in general, normal sexual activity and the realization of the childbearing function. An important role is also played by periodic examinations at the gynecologist.

 We recommend reading the article about the difference between fibromyoma and myoma. From it you will learn about the features and manifestations of the disease, the existing types of myomas, the establishment of major differences, the difference in the prescribed treatment.
We recommend reading the article about the difference between fibromyoma and myoma. From it you will learn about the features and manifestations of the disease, the existing types of myomas, the establishment of major differences, the difference in the prescribed treatment.