Problems with one of the layers of the uterus - endometrium - can be of a different nature. Some of them are associated with excessive activity of its components, when stromal and glandular cells pathologically increase their number. The causes of endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus are not detected by 100%.But long-term observations allow specialists to identify several circumstances that contribute to the provocation of the disease.
Balance of hormones
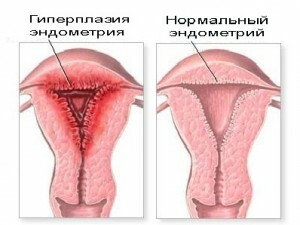 The work and condition of the reproductive organs are dependent on the composition of hormones. All disorders are associated with disorders in this area. Not an exception and hyperplastic development of the endometrium, a push for which may be an increased concentration of estrogens.
The work and condition of the reproductive organs are dependent on the composition of hormones. All disorders are associated with disorders in this area. Not an exception and hyperplastic development of the endometrium, a push for which may be an increased concentration of estrogens.
The uterus is the target organ for these substances for any number of them. In healthy women of reproductive age, estrogens participate in the preparation of the functional layer of the mucosa to the ovulation stage, thickening it.
With hyperplasia, the process has a protracted character, since the birth of fresh cells of the uterine membrane takes place uncontrolled and beyond measure.Age-related changes
Endometrial hyperplasia of a cause may conceal in a new life stage that no woman passes after the end of the reproductive period. It's about menopause, in which the balance of hormones changes significantly. Normally this happens with a decrease in the level of estrogens. But almost to zero their number does not immediately pass.
This stage is preceded by a premenopause, in which the concentration of substances is spasmodic. At the peak of values, estrogens may exceed the norm. Sometimes this is enough to launch a pathological process.

The listed disturbs the reducing capacity of the organ shell, weakening it and reducing the resistance to the effect of estrogens.
Other diseases
 Causes of any type of endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus can be in the condition of other reproductive organs and areas other than the reproductive system.
Causes of any type of endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus can be in the condition of other reproductive organs and areas other than the reproductive system.
The same value can have:
- Diabetes mellitus. It is characterized by an imbalance of many substances, including hormones;
- Diseases of the liver. This body not only participates in the assimilation of the components necessary for the body and the excretion of excess, but also the production of hormones;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland. She also produces hormones. Failure to produce "native" substances for her often leads to a violation of the volume of estrogens;
- Obesity. This disease, which many do not consider, proceeds with the formation of tissues capable of producing estrogens. Perhaps, it is their influence, rather than those substances that are produced by the ovaries, that will provoke an abnormal thickening of the mucous uterus.
Stresses
Usually, the diagnosis of "endometrial hyperplasia" psychosomatics, as a branch of medical science, does not include its own. But it would be wrong to deny that the state of the nervous system strongly affects the work of the reproductive organs. After all, there is a connecting chain between them - the pituitary gland, the hypothalamus and the ovaries. Their functions, that is, the production of FSH, LH, sex hormones, depend on the normal functioning of the central nervous system.
Psychological stress, causing a failure in this part, can cause a delay. While a woman, going through for some reason, waiting for a period, the mucous of her womb, obeying the estrogen, thickens.
Stress also provokes obesity caused by excessive appetite, thyroid pathologies. And this is a complex of factors favorable for the development of the disease. And although at the heart of everything is hormonal disorder, the beginning is the psychological causes.
 We recommend to read an article about glandular cystic hyperplasia of the endometrium. You will learn about the causes of the development of the disease and its types, methods of treatment and elimination of hyperplasia.
We recommend to read an article about glandular cystic hyperplasia of the endometrium. You will learn about the causes of the development of the disease and its types, methods of treatment and elimination of hyperplasia.
Consequences of hyperplasia
 Having learned about the diagnosis of "endometrial hyperplasia", is it dangerous - the first problem facing its owner. Theoretically, presenting how the uterine mucosa develops, someone may not be aware of the severity of the disease. After all, the endometrium on certain days of the cycle thickens and is normal. And then, after completing its term, its replaceable part exfoliates and comes out in the form of menstrual flow.
Having learned about the diagnosis of "endometrial hyperplasia", is it dangerous - the first problem facing its owner. Theoretically, presenting how the uterine mucosa develops, someone may not be aware of the severity of the disease. After all, the endometrium on certain days of the cycle thickens and is normal. And then, after completing its term, its replaceable part exfoliates and comes out in the form of menstrual flow.
But the fact is that after the monthly mucous remains altered. And the new stage of cell division retains the former unhealthy character. What is dangerous is endometrial hyperplasia, in the first place can be estimated by the process of menstruation. It passes:
- With abundant secretions;
- With significant blood loss;
- Longer than a week;
- With a delay of 1-3 months;
- In frequent cases without ovulation.
Menses may alternate with uterine bleeding. All this, at least, threatens with anemia. And since the endometrium not only changes the thickness, but also the properties, in the case of pregnancy, it is more difficult for a fetal egg to gain a foothold. This already means a high risk of miscarriage.
The reasons for the detection of endometrial hyperplasia of the uterus can also be hereditary. But there is a chance to confront your own unwanted genes if you avoid the causes of the disease that provoke the disease: an incorrect lifestyle, inflammations, infections, casual connections, abortions, spontaneous medication. It is also possible to get sick at the initial stage, if you immediately consult a doctor when changing the features of menstruation.
