 The causes of the appearance of the flux may be different: the presence of a decayed tooth decaying tooth, the development of infection in the gums or a severe bruise.
The causes of the appearance of the flux may be different: the presence of a decayed tooth decaying tooth, the development of infection in the gums or a severe bruise.
In any case, this disease is inflammatory, it is quite complicated and requires immediate complex treatment at the dentist. In the absence of the latter, the ailment threatens with dangerous complications. How to get rid of the periostitis of the jaw will be discussed below.
Contents
- Meet - inflammation, swelling and pain!
- The basic principles of therapy
- We go to the dental clinic
- Comprehensive shock for the disease
- Use of antibiotics
- Antihistamines
- Rinse mouth
- Treatment of concomitant pathology
- Physiotherapy
- Possible complications
Meet inflammation, swelling and pain!
Flux is an infectious, inflammatory disease of the maxillary periosteum. His scientific name periostitis. 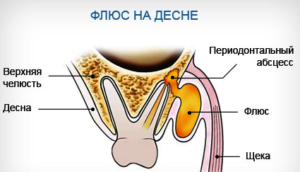 The disease manifests itself in the form of a small painful tubercle, a seal on the gum in the root area of a diseased tooth. Without proper treatment, the formation very quickly increases in size, swelling of the cheek and other soft tissues in the facial area.
The disease manifests itself in the form of a small painful tubercle, a seal on the gum in the root area of a diseased tooth. Without proper treatment, the formation very quickly increases in size, swelling of the cheek and other soft tissues in the facial area.
The person can significantly increase body temperature, puffiness spreads to the lips, nose and lower eyelid, a purulent pocket forms on the gum, there is a pronounced malaise and weakness. If the cause of the inflammatory process is the tooth of the lower jaw, then the tumor can spread to the chin, neck and affect the lymph nodes.
Basic principles of therapy
Purulent periostitis requires a comprehensive approach, the use of only one method will not give the necessary results and may lead to a relapse of the disease. Treatment usually includes:
- surgical operation - dissection of the formed inflammation and removal of purulent masses;
- therapeutic procedures: taking medications and rinsing.
 If the disease manifested itself at the initial stage, the dentist may well do without opening the gums. It is enough for him to drill a tooth and open the canal so that the pus formed can leave the infection area without hindrance. In some cases, you have to resort to removing the causative chewing element.
If the disease manifested itself at the initial stage, the dentist may well do without opening the gums. It is enough for him to drill a tooth and open the canal so that the pus formed can leave the infection area without hindrance. In some cases, you have to resort to removing the causative chewing element.
In this case, treatment is prescribed with medications, mainly antibacterial drugs. This stage of periostitis primarily requires reducing puffiness and preventing the further development of the disease with the formation of a purulent focus.
If the flux has a more complex shape, it becomes necessary to cut the gums( periosteum) in the area of inflammation. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. After surgery, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, antihistamines. In addition, to speed up healing, the dentist can recommend rinsings, therapeutic ointments and physiotherapy procedures.
 Surgical treatment may be required in case of ineffective drug exposure or neglected form of disorder. The main principles of treatment of the disease are as follows:
Surgical treatment may be required in case of ineffective drug exposure or neglected form of disorder. The main principles of treatment of the disease are as follows:
- ensuring the outflow of formed purulent masses from the focus of infection;
- elimination of microbial inflammation by taking antibacterial agents;
- local exposure to antiseptics;
- eliminates the re-occurrence of dental flux.
Objectively assess the severity of periostitis and prescribe appropriate treatment can only the dentist. Therefore, when the first signs of the disease appear, consult a specialist as soon as possible.
We go to the dental clinic
Treatment of periostitis in a dentist with the use of surgery may be required when the disease has become quite extensive. In this case, taking antibiotics will not bring the required results and will only take away precious time, thereby aggravating the situation.
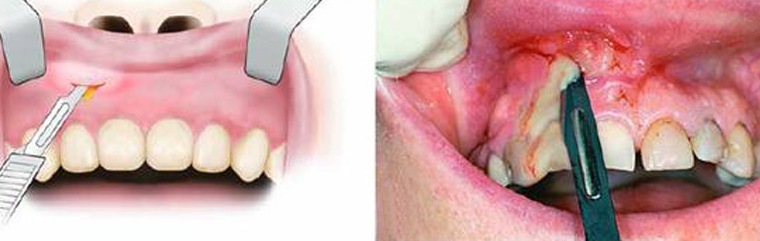
Surgical treatment includes the following procedures:
- examination and X-ray examination to find out the cause of periostitis and choose the way to solve the problem;
- local anesthesia of the necessary area of the periosteum;
- dissection of the tooth cavity and tooth canals in order to allow pus to leave the inflamed near-root area;
-
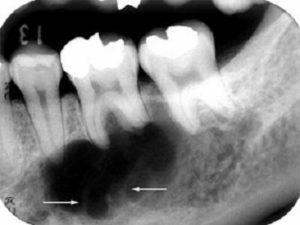
In the picture, radiography with periostitis
if the X-ray shows the impossibility of retaining the tooth, then it is to be removed, the formed well is thoroughly cleaned of purulent masses and washed, it is placed in drainage for the outflow of newly formed pus;
- in some cases, it may be necessary to open the gums at the site of flux formation by cutting and removing pus, followed by installing a drainage device;
- after the surgical intervention very often the patient is prescribed treatment with antibiotics and antihistamines, if the disease has reached a difficult, complex shape, then physiotherapy can be prescribed by laser or ultrasound.
Comprehensive stroke for the disease
Treatment of periostitis of the jaw with the use of medications is actual both at the initial stage of the disease as an independent therapy, and after surgical intervention.
Use of antibiotics
Antibiotics with tooth flux are prescribed in case of infection, complications and the elimination of formed pus. In addition, the need for antibacterial agents is determined depending on the stage of the flux.
Most often appointed:
-
 If treatment is started in a timely manner at the initial stage of development, the patient is prescribed a tablet with a wide range of action to exclude the possibility of further spread of the infection.
If treatment is started in a timely manner at the initial stage of development, the patient is prescribed a tablet with a wide range of action to exclude the possibility of further spread of the infection. - If the disease is at an advanced stage, the patient will need stronger drugs.
- Antibacterial drugs are prescribed after surgery. In this case, antibiotics will not allow bacteria to multiply in the resulting wound and cause inflammation.
At the reference to the stomatologist at first the analysis is carried out and the originator of disease is found out. Most often in this role are the bacteria of staphylococcus or streptococcus. Depending on the result of the study, the patient is assigned the appropriate drug.
In the pharmacy you can buy drugs that are most often prescribed by dentists:
- Amoxicillin and Amoxiclav;
-
 Doxycycline;
Doxycycline; - Linkomycin;
- Trichopol;
- ;
- Ampioks;
- Azithromycin.
The required dosage of the drug in each case should be determined by a specialist.
In the treatment of periostitis, rinsings, antihistamines and physiotherapy are used to reduce edema.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines in the treatment of periostitis are prescribed along with antibacterial agents. They increase the resistance and resistance of the body in relation to infection. Also, antihistamines relieve intoxication caused by the formation and spread of purulent masses.
Usually assigned:
-
 Erius;
Erius; - Diazolin;
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Peritol;
- Fenkarol.
These drugs not only increase the resistance of the body, but also exclude the development of allergies, which can appear against the background of taking antibiotics.
Mouth rinses
For this problem, rinsing of the mouth is recommended:
-
 at the very beginning of the disease;
at the very beginning of the disease; - on the fading stage;
- during antibiotic treatment;
- for the relief of pain syndrome;
- if there is no possibility to visit the dentist urgently;
- for chronic flux course.
With periostitis, rinsing with medicinal herbs is used: chamomile, sage, calendula, horticulture.
For medicinal purposes, decoctions and tinctures are used. Plants can be brewed either individually or as a collection. The procedure is carried out every 2 - 2.5 hours.
A good analgesic and antibacterial effect gives a rinse with a solution of soda and salt. Very well removes the inflammation of the broth, prepared from the bark of oak. Tincture of propolis( natural antibiotic) relieves pain and has a healing effect. From drugstore medicines it is recommended to use Chlorhexidine.
Treatment of concomitant pathology
 In the treatment of flux, accompanying diseases of the oral cavity such as caries, pulpitis, periodontitis can not be ignored. Possible foci of inflammation and caries-affected teeth must necessarily be healed in order to avoid the recurrence of the disease.
In the treatment of flux, accompanying diseases of the oral cavity such as caries, pulpitis, periodontitis can not be ignored. Possible foci of inflammation and caries-affected teeth must necessarily be healed in order to avoid the recurrence of the disease.
Pain syndrome with periostitis and fever are removed with anesthetic and antipyretic agents.
Physiotherapy
In the acute course of the disease, the patient, along with other therapeutic measures, is prescribed a course of physiotherapy. This is necessary for the early healing and strengthening of the purposeful action of drugs.
 The following physiotherapeutic procedures are applied:
The following physiotherapeutic procedures are applied:
- zone effect of electric current on the inflamed area;
- UV irradiation;
- infrared irradiation;
- microwave sessions;
- electric field of UHF.
Possible complications of
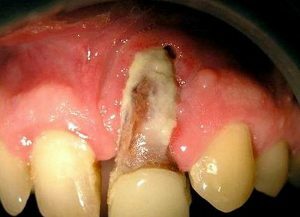 It is very dangerous to consider the flux of the upper jaw, since in an unfavorable course of the disease purulent masses can spread to the face area and then to the brain. Pus has the ability to pass extremely quickly to soft and hard tissues, so without proper treatment, impairment very quickly can lead to abscesses of soft facial tissues and osteomyelitis.
It is very dangerous to consider the flux of the upper jaw, since in an unfavorable course of the disease purulent masses can spread to the face area and then to the brain. Pus has the ability to pass extremely quickly to soft and hard tissues, so without proper treatment, impairment very quickly can lead to abscesses of soft facial tissues and osteomyelitis.
But the most dangerous consequence is sepsis - the infection of blood, which can lead to death.
Periostitis develops very very quickly. Therefore, in order to avoid deplorable consequences, in no case should one engage in self-medication. At the first symptoms of the disease you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
For the causes of flux development, treatment and possible complications, see this video:
