What are the first signs of HIV in children and adults? What are the stages of HIV?What if you have HIV?How does HIV manifest itself in a general blood test?
Contents of
- First early signs of HIV infection in women, men and children:
- stages First early signs of HIV infection in women, men: symptoms, photos
- First early signs of HIV infection in children
- After the first signs of HIV after infection in women,men and children?
- External initial signs of the disease of HIV-infected people in men, women, children: on the body, face, skin, tongue, lips, mouth
- Symptoms of HIV - temperature, herpes, rash: how to determine?
- Signs of HIV in a general blood test: how to determine?
- Signs of HIV in a month, six months, a year after infection in women, men and children: photo, description
- What is the difference between HIV and AIDS?
- Signs of the HIV disease: what to do?
- HIV Signs: Video
- Symptoms of HIV: Video
- What to do if HIV was detected: Video
The human immunodeficiency virus( HIV) has always been considered one of the most complex and incurable diseases in human history. To date, the situation is that living with HIV can be long and unhindered, but only in the case of timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease. That is why it is very important to know the main symptoms of HIV and in time to seek help from doctors.
The earliest signs of HIV infection in women, men and children:
 stages HIV stages
stages HIV stages The classification of stages of HIV infection has repeatedly changed throughout the study of this disease and the search for an antidote to it.
To date, there are 5 stages of the HIV infection process:
- The incubation stage is a period of the disease, the onset of which is associated with the moment of human infection with the virus, and the end with the time of its development by the immune system of antibodies. The duration of this period directly depends on the immunity of the patient - as a rule, it is from 2 weeks to 3 months.
- The stage of primary manifestations is the period of introduction, development and spread of HIV throughout the patient's body. This stage can last from 2 weeks to a month and a half - most often its duration is equal to a couple of weeks.
- Latent( subclinical) stage - the period of asymptomatic struggle of immunity with the virus. This stage is the longest - it can last from 2 to 10-20 years.
- The stage of secondary diseases( pre-AIDS) - a period when the immune system is already significantly eroded and destroyed - it lacks the strength to cope with those infections to which until now a person had immunity.
- The terminal stage( AIDS) is the last, final stage, characterized by irreversible processes in the human body. The outcome of this period is death.
First signs of HIV infection in women, men: symptoms, photos
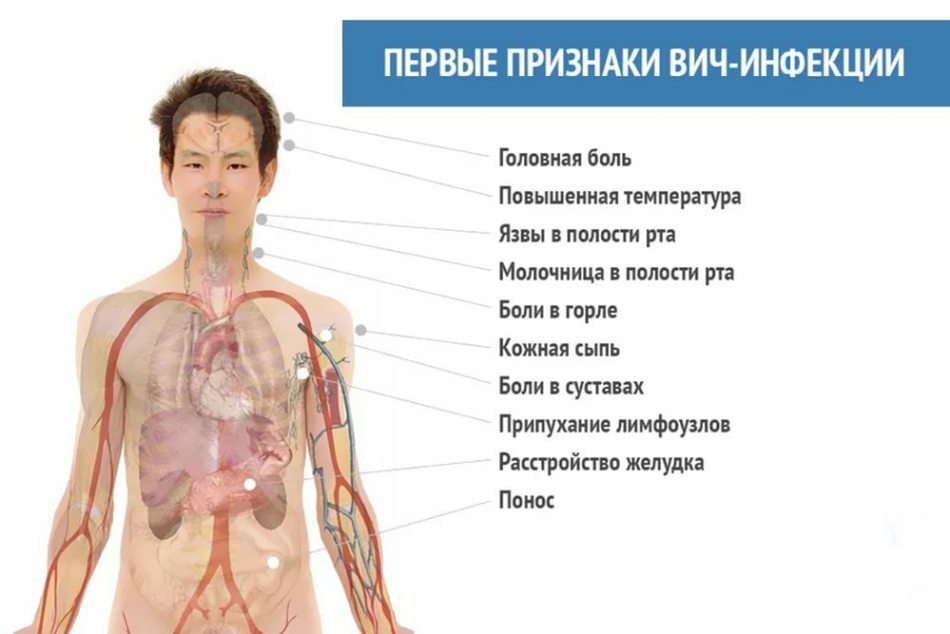 First signs of HIV
First signs of HIV The incubation stage of HIV is different in that it does not have any manifestations. In this period, any symptomatology will be absent, until the moment of the onset of the second stage - the primary manifestations.
The second stage of HIV is characterized by the development by the human immune system of antibodies to HIV and its fight against the virus. It is in this period that it is extremely important to record all possible manifestations of the infection and correctly identify it.
In turn, the second stage of HIV is divided into three more types:
- Asymptomatic
- Acute HIV infection without secondary diseases
- Acute HIV infection with secondary diseases
As it becomes clear from the name of the first stage variety, it is difficult to identify, since it passes absolutelyis asymptomatic. Identify HIV in this phase is possible only by the presence of antibodies to the virus in the blood.
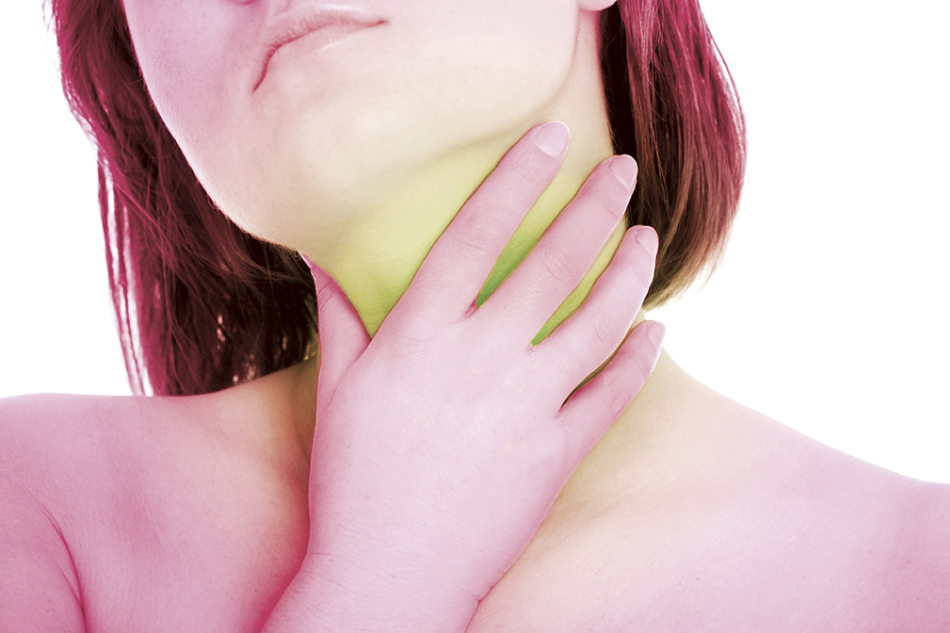 Early signs of acute stage of HIV without secondary diseases
Early signs of acute stage of HIV without secondary diseases Acute HIV infection without secondary diseases, as a rule, is symptomatic, similar to usual infectious diseases:
- lymphadenopathy
- breakdown
- fatigue
- chills
- sore throat
- headaches
- profuse sweating during sleep
- aches and muscle pain
- rash
- rash on the mucous
- diarrhea
- nausea
- vomiting
- enlarged liver and spleen
- pharyngitis
- subfebrile temperature
- weight loss
- thrush
Most patients experienced several of these symptoms during the acute stage of HIV.
Very often such a symptomatology is attributed to a disease such as mononucleosis( rubella).The reason for this are mononuclear cells, which can be detected in the patient's blood.
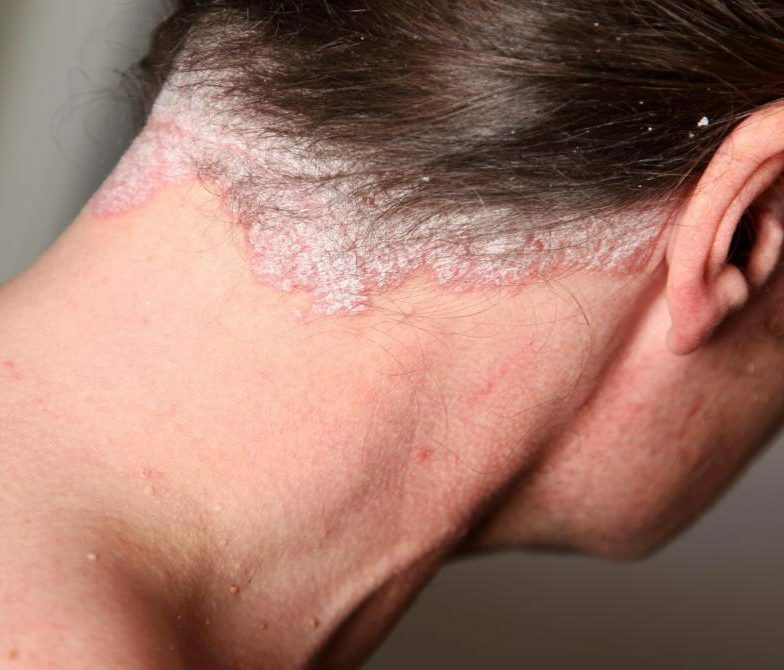 Signs of acute stage of HIV with secondary diseases
Signs of acute stage of HIV with secondary diseases Acute HIV infection with secondary diseases is often manifested by a number of the following diseases and conditions:
- angina
- pneumonia
- herpes
- fungal diseases
- psoriasis
- seborrheic dermatitis
Similar diseases at this stage of HIV are not particularly dangerous forpatient, as they are still well treatable.
The latent stage is characterized by a gradual suppression of immunity. In this period, patients have virtually no pathologies and manifestations. Identify HIV at this stage is possible only by detecting antibodies to the virus in the blood.
 Signs of HIV at the secondary disease stage
Signs of HIV at the secondary disease stage The stage of secondary diseases occurs when the body is almost completely depleted and the immune system is significantly destroyed. At this stage of HIV infection may develop a variety of opportunistic diseases:
- fungal diseases
- viral diseases
- disease bacterial
- zoster
- pharyngitis
- sinusitis
- prolonged diarrhea
- prolonged fever
- tuberculosis
- hairy leukoplakia
- Kaposi's sarcoma
- CNS
- oncological
diseaseThe terminal stage is characterized by aggravation of all existing diseases and impotence of therapy. Having reached this stage, a person can not count on recovery and life expectancy.
First Early Signs of HIV Infection in Children
 First signs of HIV in children
First signs of HIV in children In children who are infected in utero, HIV infection often develops much faster than in infants infected after a year. Symptomatology in such small patients manifests itself in the first 12 months of their life.
In many children, the signs of the disease can not be felt until 6-7, and sometimes 10-12 years.
The signs of HIV infection include:
- delay in physical development
- delay in psychomotor development
- lymphadenopathy
- enlargement of liver and spleen( myalgia)
- frequent
- problems with digestive tract
- skin rash
- disorders of the CNS
- cardiovascular failure
- encephalopathy
- anemia
How many first signs of HIV occur after infection in women, men and children?
 When do the first symptoms of HIV begin to appear?
When do the first symptoms of HIV begin to appear? Very often the onset of the disease in people of any sex and age is absolutely asymptomatic, and sometimes its symptoms can easily be confused with other, less dangerous infectious diseases.
In other cases, the first signs of HIV infection can be manifested as early as 2-6 months after infection. Such symptoms will indicate the onset of the acute phase of the disease.
External initial signs of the disease of HIV-infected people in men, women, children: on the body, face, skin, tongue, lips, mouth
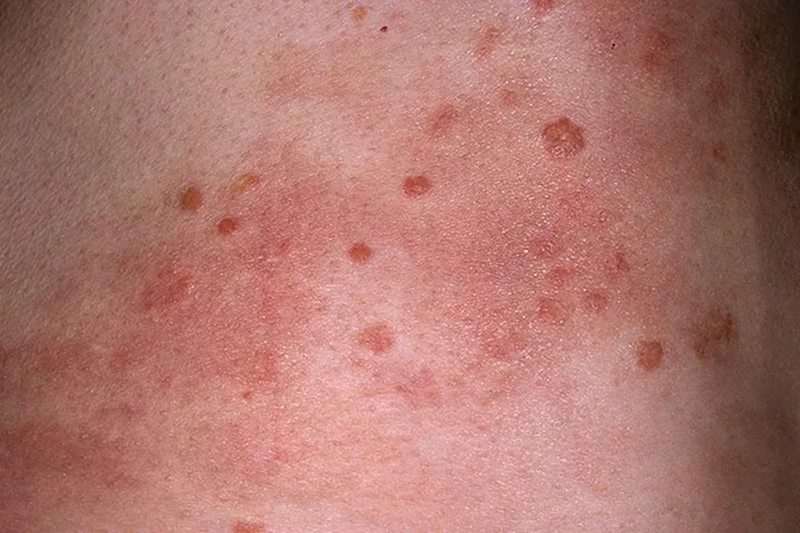 External manifestations of HIV
External manifestations of HIV The most common sign of the presence in the body of HIV infection in a patient of any gender and age is enlarged lymph nodes. At what, as a rule, not one group of lymph nodes increases, but several at once - on the neck, in the groin, under the armpits, on the elbows. When palpation, such nodes do not hurt and have a normal color. Lymph nodes can grow from 2 to 6 cm.
With regard to rashes and tumors that very often appear in HIV infection, they can be of the following nature:
- rash of pink shade
- burgundy-colored
- Candida
- papilloma
- herpes
- mucosal inflammation
- ulcers and erosion in the mouth
- inflammation in the vagina
- urticaria
- spotted papular rash
- seborrheic dermatitis
- rash with vascular changes
- pyoderma
- lichen
- psoriasis
- rubrophytic
- molluscum contagiosum
- sataya
- leukoplakia Kaposi's sarcoma
HIV Symptoms - fever, cold sores, rash how to identify?
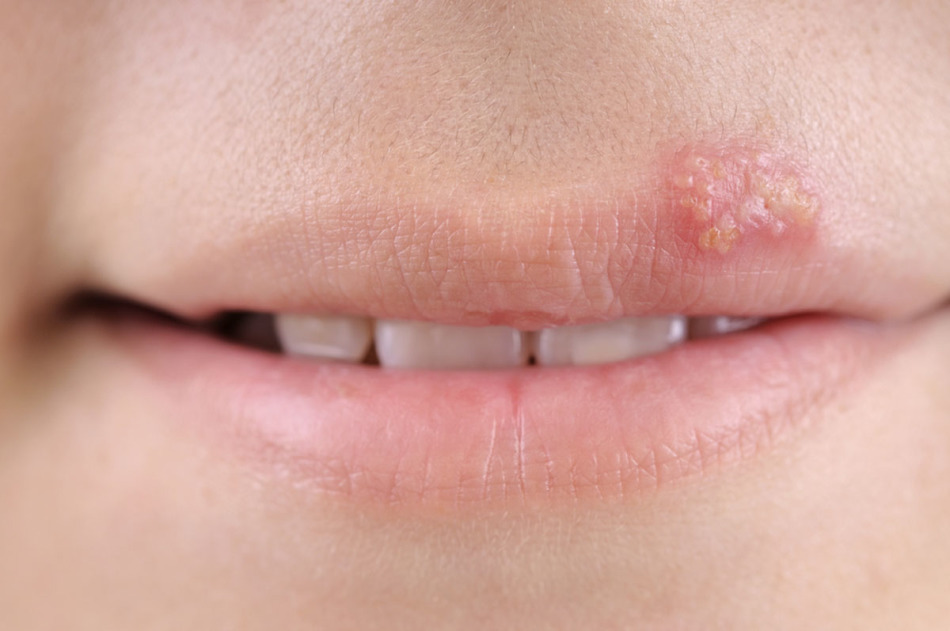 Herpes with HIV
Herpes with HIV Herpes virus is infected with 90% of the world's population. About 95% of infected people do not suspect about the presence of this virus in their bodies, and only 5% of infected patients face obvious symptoms - vesicular formations on the skin of the face, genitals, mucous membranes.
If the patient still has HIV infection, the herpes virus can manifest itself as follows:
- Recur very often( several times in 3 months).
- Herpes begins to penetrate deeper into the layers of the skin.
- Places of formation of a bubble rash are degenerated into ulcers, erosions, necrotic areas.
- Herpes begins to affect more and more areas with each subsequent relapse.
- Eruptions are formed on the surface of internal organs.
- Along with herpes, lymphadenopathy is observed.
- Eruptions are accompanied by severe pain.
- Anti-herpes therapy becomes powerless.
- Type 8 herpes can be regenerated into Kaposi's sarcoma - a malignant tumor that affects the epithelium, vessels, lymph nodes, and then all human organs and systems.
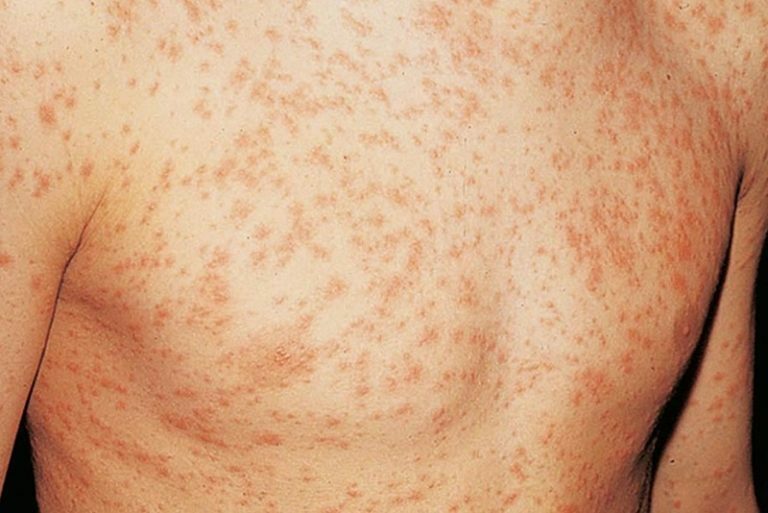 Eruptions in HIV
Eruptions in HIV Eruptions, as signs of HIV infection in humans, can be of different types and nature:
- Mycotic skin lesions are rashes and lesions on the skin that are the result of an organism's fungal lesions.
- Pyoderma - purulent skin lesions, caused by the penetration of pyogenic cocci into it.
- Spotted rash is a formation characterized by impaired vascular integrity( telangiectasia, haemorrhagic or erythematous spots).
- Seborrheic dermatitis is a rash, characterized by significant surface peeling.
- Eruptions caused by viruses.
- Malignant formations( Kaposi's sarcoma, hairy leukoplakia).
- Papular rash.
 HIV temperature
HIV temperature With regard to the temperature for HIV infection, it can be completely different:
- In some patients with HIV, the temperature remains within normal limits, up to the time of the appearance of some primary or secondary disease.
- Most patients with HIV in the acute phase have a fever of up to 38, and sometimes up to 39 degrees.
- Caution should also temperature of 37 degrees, which does not fall more than one month.
- In some HIV patients, a very low temperature( from 35 to 36 degrees C) can be observed - this may be the consequence of depletion of the body in fighting infection.
Signs of HIV in a general blood test: how to determine?
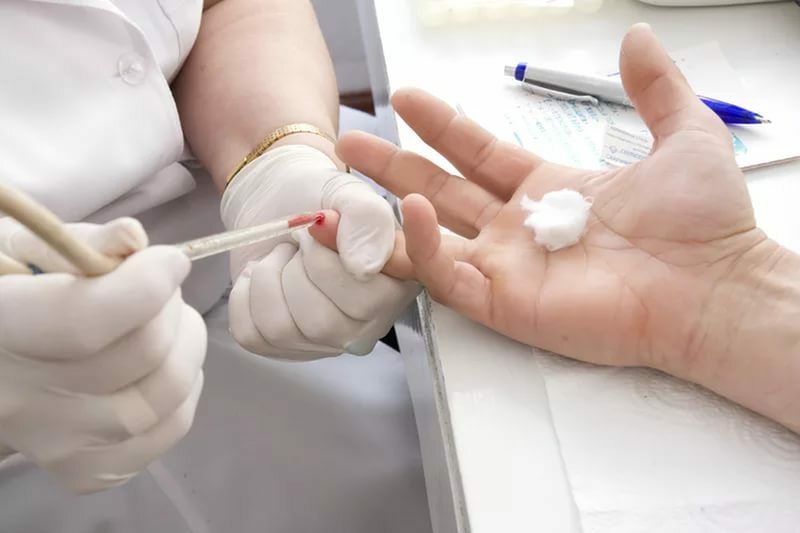 How to recognize HIV in a general blood test?
How to recognize HIV in a general blood test? A general blood test does not identify the human immunodeficiency virus itself, but it can detect a number of changes in its body.
If a person has HIV infection, a general blood test can record the following conditions:
- Lymphocytosis - an increased concentration of lymphocytes in the blood, due to the arms of immunity against HIV;is characteristic of the early stage of the disease.
- Lymphopenia - a decrease in the level of T-lymphocytes in the blood due to the weakening of the immune system in the process of fighting the virus;comes at the end of the acute phase.
- Thrombocytopenia is a decrease in the level of platelets responsible for blood clotting.
- Neutropenia is a decrease in the concentration of neutrophils( granular leukocytes) responsible for the initial stage of the fight against pathogenic agents in the blood.
- Anemia - a decrease in the level of hemoglobin.
- High ESR( sedimentation rate of erythrocytes).
- Increased mononuclear content( atypical cellular forms).
Signs of HIV in a month, six months, a year after infection in women, men and children: photo, description
 How does HIV manifest in different time intervals?
How does HIV manifest in different time intervals? Most likely, a month after the infection with HIV infection, a person will not notice any changes in his body. At this time, HIV will experience its first stage( incubation), at the stage of which the body is not yet beginning to fight the virus.
After 2-5 months after infection, the first symptoms of HIV can appear, the duration of which will not be more than 2 months.
At this time a person can observe:
- enlargement of lymph nodes
- frequent ASVI
- inflammation of palatine tonsils
- prolonged rise in body temperature to 37.1-38 degrees
- fast fatigue
- impotence and apathy
- weight loss
- insomnia
- profuse sweating during sleep
- headache
A couple of months after the onset of the acute phase of HIV, the latent phase begins - the longest stage of HIV( from 2 to 20 years).During this period, it is very difficult to diagnose the disease, since it does not betray itself.
What is the difference between HIV and AIDS?
 What is the difference between HIV and AIDS?
What is the difference between HIV and AIDS?- Many people confuse these two concepts and believe that it is about the same disease.
- In fact, there is a huge gap between HIV and AIDS that lasts for decades.
- HIV is the human immunodeficiency virus.
- AIDS is a syndrome of acquired human immunodeficiency.
- AIDS is a consequence of neglected HIV infection - this is its last stage, the most complex and lethal.
- With time diagnosed and healed by HIV infection a person can live for decades.
- With AIDS, the patient shines only a few years, and then provided there are no serious concomitant diseases.
- In the stage of HIV infection, immunity only begins to fight the virus.
- At the AIDS stage, the immune system is already in a destroyed state.
- With HIV, the body needs only support in the form of immunostimulants and virus blockers.
- In AIDS, immunity requires maximum protection and prevention, as well as the treatment of all complications and secondary diseases.
- All diseases at the stage of HIV are well amenable to standard therapy.
- With AIDS, therapy is virtually powerless.
Signs of the HIV disease: what to do?
 What should I do if I have been diagnosed with HIV?
What should I do if I have been diagnosed with HIV?- People, dumbfounded by an unexpected diagnosis of having HIV infection, can be advised not to panic.
- Modern drugs allow you to fully control and contain the virus in the human body.
- After receiving a positive result of the HIV test, a person needs to contact a specialized AIDS center.
- Most likely, within the walls of this facility, the patient will undergo a series of additional tests, one of which will be a repeated HIV test.
- Additional tests are used to identify other hidden complex infections and viruses that can harm the patient.
- In case of detection of concomitant diseases, most likely, it will be decided to immediately cure them, and then to take on the virus itself.
- For a long period of time, foreign immunologists practiced as late as possible on HIV therapy.
- This was due to the need to take quite toxic drugs by patients at the same time every day.
- Over time, foreign doctors decided to abandon this practice.
- Today, in order to avoid the development of other complex co-morbidities, antiretroviral therapy is prescribed from the first days of disease detection.
- In our country, unfortunately, the delay in the appointment of ARVT is explained by other, mercantile reasons.
- The fact is that the treatment of patients with HIV and AIDS in Russia is carried out at the expense of the state treasury.
- Thus, officials and their doctors are trying to save on HIV medications.
- The later ARVT is appointed, the less money the country will spend.
 HIV Therapy
HIV Therapy The protocol identifies the categories of people who fall under the urgent ARVT:
- Older people( after 50 years).
- Patients who wish to begin treatment immediately.
- Patients with complicated concomitant diseases( hepatitis B and C, kidney problems, mental development, diseases of the cardiovascular system).
- Women and couples planning a pregnancy - the virus can be transmitted from the mother to the fetus through the placenta, breast milk, while overcoming the birth canal.
Dear readers, if you were suddenly diagnosed with such a frightening diagnosis as HIV, do not despair. Timely diagnosis and treatment of HIV will allow you to live for many years with a sleeping virus that is not capable of harming you or your loved ones.
