Hemophilus infection, penetrating the child's body, has a destructive effect and affects the nervous system and the respiratory system of a person. But from this terrible misfortune can be reliably protected any child.
Contents of
- What is a Haemophilus influenzae?
- Hemophilus bacillus treatment
- Hemophilus bacterium in child
- Hemophilus pneumonia
- Hemophilic meningitis
- Video: Meningitis vaccine - Dr. Komarovsky
- Do hemophilia vaccinations need?
- Video: Hemophilus bacillus
Hemophilus infection is a terrible disease that poses a serious threat to the health and life of children under the age of 5 and adults with weakened immunity.
The main danger of this infection is the stability of the bacillus strains to the majority of antibiotics used and the high probability of developing severe complications of the disease.
What is a Haemophilus influenzae?
Hemophilic rod ( Influenza rod, Haemophilus influenzae) is a predominantly childish disease, which in most cases causes the development of severe pneumonia, meningitis, and provokes nervous system damage.
There are six types of strains: a, b, c, d, e, f. The greatest danger for children is the b -infection. It is she who provokes the development of severe illnesses in children.
IMPORTANT: The greatest activity of the hemophilic rod is observed in February - April. The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets, through household items, toys, personal belongings of the patient. The first manifestations of the disease resemble the symptoms of acute respiratory disease, but very quickly the picture changes, and the patient's well-being deteriorates sharply.
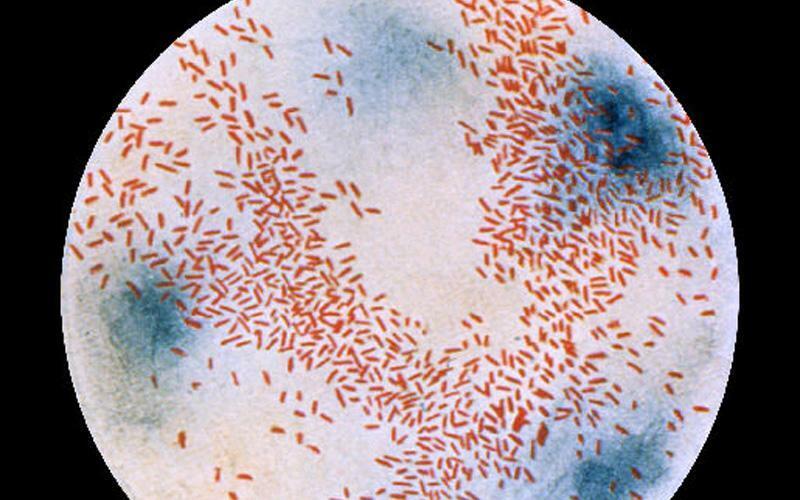 Hemophilia rod under the microscope
Hemophilia rod under the microscope Hemophilus rod treatment
Treatment is performed only under strict medical supervision. Constant mutations of the pathogen caused the acquisition of resistance to some antibiotics. Currently, cefolasporin, ampicillin, levometsetin, cefaclor, and erotomecin are used for treatment.
The duration of administration of antibiotics depends on the severity of the disease and the location of the infection and is from 7 to 14 days.
IMPORTANT: In cases of infection with a haemophilic rod, self-medication or untimely recourse to medical care can lead to severe deterioration of the condition, poisoning of the body and death of the patient.
In severe lesions with a haemophilus rod, respiratory organs require tracheal intubation. If it is not performed on time, the air passages in the airways can be blocked, which will lead to a quick death of the patient.
 Self-medication for hemophilic infection is strictly prohibited
Self-medication for hemophilic infection is strictly prohibited Hemophilus bacterium in the child
More than half of the healthy children are carriers of the hemophilic rod. At the same time, it does no harm and does not pose a threat to their health. However, at any time the infection can become more active and affect the most vulnerable organ of the child.
IMPORTANT: Children from six months to a year are more likely to be affected by hemophilic infection. During this period, the children's organism is most vulnerable, because it rebuilds its defense system to independent independent work.
50% of cases of children's meningitis happen precisely because of infection with a hemophilic rod. Purulent otitis, pneumonia, bronchitis and acute respiratory infections - all these diseases can also provoke Haemophilus influenza in children.
 Hemophilus influenzae can provoke the development of otitis in a child
Hemophilus influenzae can provoke the development of otitis in a child Hemophilus pneumonia
Hemophilic pneumonia causes the most dangerous strains in which an antigen is present b.
In children 8 to 14 months the disease is very severe, accompanied by severe weakness, in adults it has a focal character with fever, coughing and separation of large amounts of sputum, but the general condition of patients is somewhat easier.
In both cases there is a high probability of complications of the disease in the form of meningitis, arthritis, pleurisy.
IMPORTANT: It is possible to establish the exact origin of pneumonia only from the results of blood, sputum and urine tests.
For the treatment of pneumonia caused by a hemophilic rod, use antibacterial drugs: amoxicillin, clavulanate( augmentin), aztreonam.
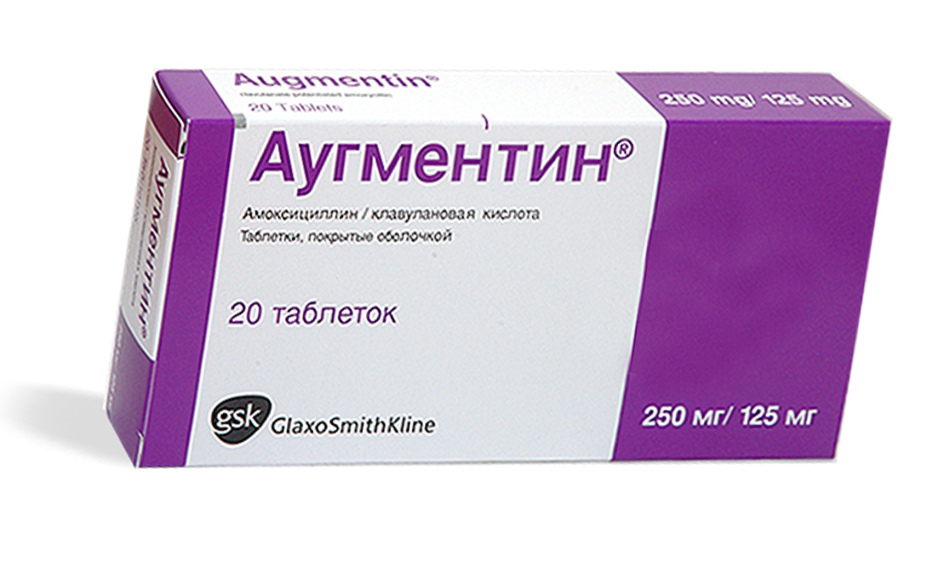 For the treatment of hemophilic pneumonia, augmentin
For the treatment of hemophilic pneumonia, augmentin is used. At risk for the incidence of hemophilic pneumonia are:
- living in unsatisfactory sanitary conditions
- non-hygienic
- patients with lymphogranulosis
- children attending pre-school institutions
IMPORTANT: Persons on this list are recommended to be vaccinated againsthaemophilus infection.
 Children under 5 years of age at kindergarten are at risk
Children under 5 years of age at kindergarten are at risk Hemophilic meningitis
Hemophilia influenza can cause meningitis. The disease is transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets. Under the impact of hemophilic meningitis, children more often than others are between the ages of six months and 1.6 years. The peak incidence falls on early spring and late autumn.
The onset of the disease is characterized by a sharp rise in body temperature to 39.5 - 40.5 ° C.Antipyretics are not very effective. The patient feels weak, tired, and feels a headache. Also possible:
- vomiting
- convulsions
- disorders of consciousness
- pallor of the skin
All these symptoms become more pronounced from 2 to 4 days after the onset of the disease. When medical care is provided to the patient on time, the improvement begins after 2 days. But for a full recovery it will take 4 to 8 weeks.
 Symptom of hemophilic meningitis is a very high temperature, not amenable to correction
Symptom of hemophilic meningitis is a very high temperature, not amenable to correction IMPORTANT: Sometimes meningitis develops against a background of purulent otitis, conjunctivitis, acute respiratory viral infection, complicated by a bacterial infection. And in some cases, pneumonia, otitis media, purulent inflammation of the subcutaneous layer, osteomyelitis, arthritis attach to hemophilic meningitis.
Modern treatment of hemophilic meningitis in children older than 1.5 months.consists in the intravenous administration of cephalosporins. Gentamicin and Ampicillin are used for younger children.
Video: Meningitis vaccine - Dr. Komarovsky
Is Hemophilia Vaccination Needed?
A child can be reliably protected from a hemophilic infection( HIB) by safe vaccination. The proven effectiveness of the modern vaccine is 99.5%.It contains tetanus anotoxin, which forms a strong immune response in the child's body.
IMPORTANT: Vaccinations are administered to babies from 2 months to 5 years. Older children do not need additional protection, since their immune system is already ready for an independent fight against hemophilic infection.
If the hemophilic rod is already present in the body at the time of vaccination, vaccination will reduce the likelihood of complications and secondary infection.
 Vaccination is a reliable way to protect a child from hemophilic infection
Vaccination is a reliable way to protect a child from hemophilic infection Vaccination is performed according to one of the following schemes:
- up to 6 months.- 3 inoculations every 2 months.+ Revaccination after 12 months.after the last inoculation
- from 6 to 12 months.- 2 inoculations after 1 month.+ Revaccination after 18 months.after the last inoculation
- from 12 months.up to 5 years - 1 injection of
IMPORTANT: Hib vaccine does not contain live microbes, therefore the occurrence of disease as a result of vaccination is impossible.
If vaccination against haemophilus infection is not foreseen by the national vaccination calendar, all children can be vaccinated at the request of the parents, and in particular:
- often sick
- visiting gardens
- children on artificial feeding
- premature babies
The vaccine is well tolerated by children. Only in 1% of cases there is a slight increase in body temperature during the post-vaccination period, and in 5% - slight reddening of the injection site.
If we talk about the prevention of hemophilia without vaccination, it is reduced to the conduct of a healthy lifestyle, hardening, proper nutrition and strengthening of immunity.
