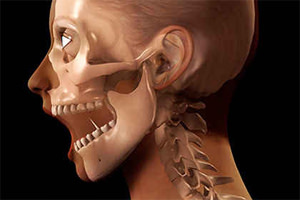
 Dislocation of the jaw is a lesion in which the temporomandibular joint is permanently displaced by the type of slipping, with the head of the articular process of the lower jaw extending beyond its physiological position with complete loss of functional mobility. Such a trauma requires specialized assistance, which consists in correct correction.
Dislocation of the jaw is a lesion in which the temporomandibular joint is permanently displaced by the type of slipping, with the head of the articular process of the lower jaw extending beyond its physiological position with complete loss of functional mobility. Such a trauma requires specialized assistance, which consists in correct correction.
Subluxation or partial dislocation of the jaw is the same process, but in this case the head retains a partial contact with the articular surface and the ability to return to normal position without the need for correction.
Contents
- Ascension factors
-
- Lindemann


is a common jaundice, therefore,it is worth getting enough sleep
The displacement of the temporomandibular joint components occurs in the overwhelming majority of the female sex.
This is due to the anatomical structure of the joint fossa, which has a lesser depth, as well as a less developed ligamentous joint apparatus than in men, resulting in a free exit of the mandibular appendage head from the articular bed under the influence of external and internal factors.
Such a trauma is not uncommon during the wide withdrawal of the lower jaw down due to yawning, singing, vomiting, attempts to bite off a solid and solid object. In dental practice, this is possible with a rotator expander or during intubation before surgery. Dislocation and subluxation can form as a result of traumatization of the joint.
Also pathological displacement of the temporomandibular joint is possible as a result of diseases such as gout and rheumatism, during which inflammation occurs followed by a degenerative change in the joint surfaces and a loss of elasticity of the ligaments.
During epileptic seizures, it is possible to exit the articular process due to uncontrolled convulsive contractions.
In elderly people, this phenomenon is possible due to the loss of stability of the ligamentous apparatus, which ensures the fixation of the joint.
Classification of injury
All dislocations and subluxations of the jaw are classified according to the time of occurrence and the factors that caused them. In the interim, injuries are divided into congenital and acquired. The latter are divided into traumatic and habitual:
- Traumatic occur due to mechanical influence on the joint. Depending on the deviation of the process of the mandible in relation to the bone structures, there is anterior, lateral and posterior dislocation / subluxation.
- The habitual is a repeated repetition of the jaw dislocation, as a result of chronic changes in the temporomandibular joint structures. Also there is a back, front and side.
Symmetry of joint lesions has unilateral and bilateral injuries. Dislocations / subluxations are considered acute, if no more than 10 days have passed since the 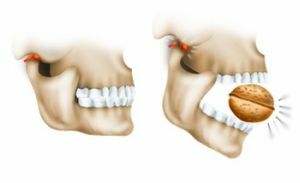 .If during this period there has not been a correction, then the process becomes chronic.
.If during this period there has not been a correction, then the process becomes chronic.
In the case when there is a change in the integrity of the skin over the joint, a rupture of the soft tissues, vessels and ligamentous apparatus, this dislocation is regarded as complicated, and, conversely, with the preservation of all structures, simple.
As a rule, most often in practice, bilateral bilateral dislocations occur.
Features of the clinical picture
Depending on the type of dislocation of the jaw, clinical symptoms will have their own characteristics, which also positively affects the diagnosis of the disease.
- The anterior dislocation of both joints is .The victim is maximally lowered down the jaw with strained muscles. The chin occupies a position with a shift down and back. The movement of the joint is made only in the direction of increasing the angle of opening. In connection with this situation speech is broken, salivation increases with difficulty swallowing. Similar changes are accompanied by pain syndrome. Perhaps the manifestation of edema in the area of the altered joint.
- The anterior dislocation of one joint is .Symptomatically, the pathology will be similar to the previous one, but the clinical difference between these cases is the visual displacement of the facial structures to the intact joint. This makes it possible to distinguish this pathology from a fracture of one of the processes of the lower jaw, as a result of which the face shifts toward the lesion.
- Posterior dislocation of both joints .The patient's mouth is in a closed position, with the impossibility of opening it. The location of the lower teeth is far behind the front teeth. There is pain in the joints and their swelling. Violation of the speech apparatus with copious salivation. Characteristic forced vertical position, when trying to lie noted choking.
- The posterior dislocation of one joint is .The symptomatology is the same as with bilateral bias, except for the presence of pain only from the side of the lesion, and there is also a displacement of the facial structures to a healthy side.
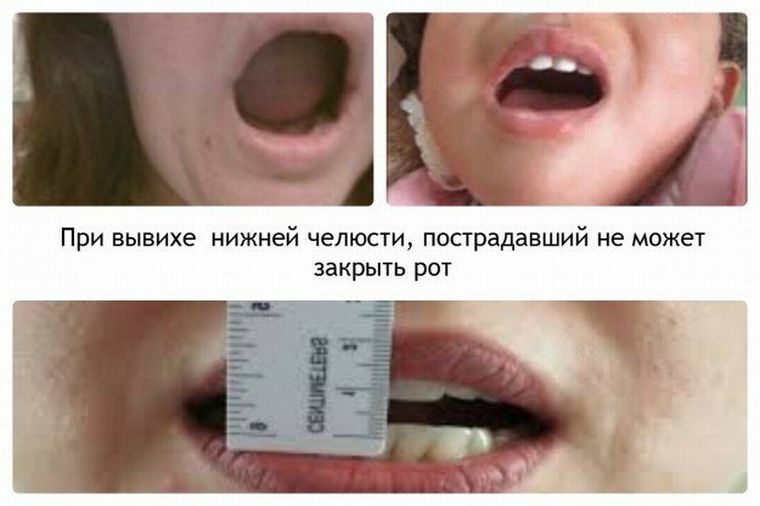
With all forms of subluxation, the position of the patient's mouth is closed, occasionally a limited opening of the jaw is possible. There is also pain symptomatology, which leads to the accumulation of a large amount of saliva. A distinctive feature of the subluxation is the detection, in palpation, of the process of the mandible on the anterior surface of the temporal bone.
Diagnosis of
The diagnosis starts with a general examination, in which it is possible to determine in advance which form of injury the 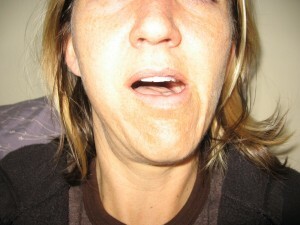 patient has.
patient has.
Anamnesis can also indicate the cause of the injury, giving the opportunity to differentiate traumatic dislocation / subluxation from the habitual.
After this, the palpation is determined the location of the bone structures of the joint with subsequent instrumental diagnostic methods, including X-ray and CT examination. The analysis of the obtained data allows to confirm the presence of pathology, as well as to determine the type and severity of the dislocation.
Methods of repositioning
Treatment of a dislocation involves directing the lower jaw to an anatomically correct position. There are several methods to do this, but they all provide for local anesthesia to relieve the pain syndrome.
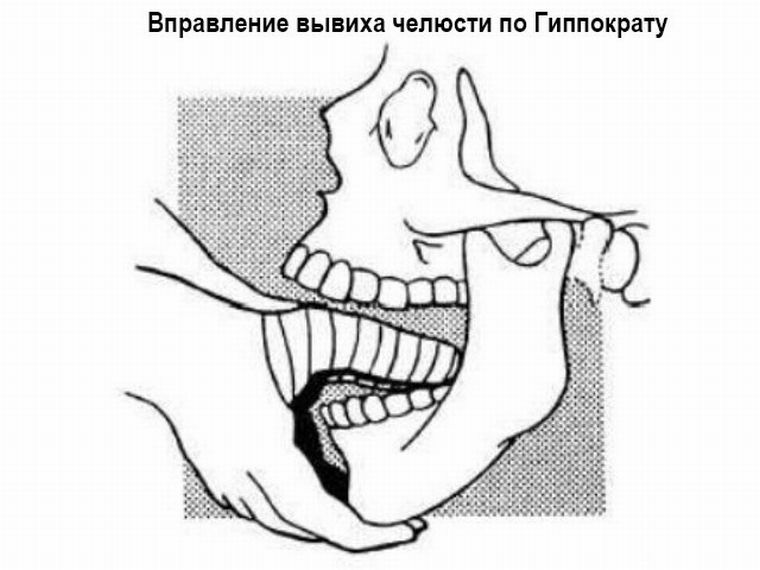
Method of Hippocrates
To avoid injury, the attending physician wraps his thumbs with a thick towel, thereby protecting them from biting the patient.
The victim himself sits on a chair. After that, the doctor applies thumbs to the far molars of the lower jaw, and the remaining fingers keep it from below. Slow pressing of the thumbs, the traumatologist presses down, while the other presses to the chin, lifting it up. This manipulation helps to relax the muscles of the facial part of the head.
Next, the joint must be moved back and up. At this point, the joint part of the jaw sinks into the articulation gap, producing a specific sound. Upon completion of manipulation, the jaw closes reflexively.
Method Popesku
This technique is used for severe pathological dislocations. The patient lies on his back. Between the distant molars of both jaws, a special gauze roll is applied, after which the traumatologist presses the chin up and back, returning the articular part of the lower jaw back to the articular bed.
Blechman's method
The technique can be performed in one of two ways:
- , after groping the coronal processes in the oral cavity, the doctor presses them downwards and backwards simultaneously, which leads them to return to the joint;
- coronal processes are pushed from the outside and return in the same manner to the joint fossa by the same movement.
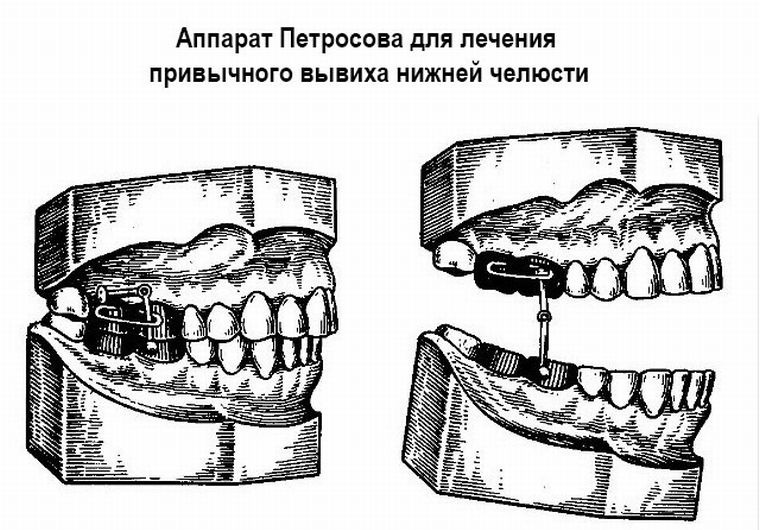
At the risk of relapse of dislocation, as well as in chronic processes, special tires are used, performing the role of prosthetics. Their main task is to prevent an overly wide opening of the mouth. One of these prostheses is the apparatus of Petrosov, the essence of which lies in the imposition of crowns on the lower and upper jaw, connected by a special limiter, which prevents the opening of the mouth.
Operative methods of treatment
There are also operative methods of treatment used for long-lasting dislocations, when joint structures had a pathological modification, as well as with degenerative joint changes associated with chronic diseases.
Lindemann's method
The task of such an operation is to increase the size of the articular tubercle by splitting it and introducing Teflon with fixation by a metal suture.
You can also make a deepening of the joint fossa, which is achieved by moving the articular disc in a vertical position anterior to the fovea. This method allows to ensure reliable fixation of joint structures with the exception of the possibility of relapses.
The Rauer Method
The essence of manipulation is to increase the articular tubercle with the use of a transplant. In this operation,  uses the costal cartilage, which is injected under the periosteum of the tubercle, which allows to increase its volume.
uses the costal cartilage, which is injected under the periosteum of the tubercle, which allows to increase its volume.
As an upgrade of the method, an additional reduction of the joint capsule is used, an improvement in fixation by suturing the fascia to the ligamentous apparatus, and suspension of the lower jaw by means of a transplanted tendon.
After the dislocation was corrected, the first time the jaw must be fixed in order to avoid a repeated case of traumatism with relaxed muscles.
Prevention is to be careful when opening the mouth, avoiding wide jaw movement when eating, screaming, singing. If there is a predisposition to dislocation / subluxation, it is necessary to report this to the doctor with dental examinations or preoperative manipulations.
