 Many people are accustomed to postpone the problems with the oral cavity, without paying attention to such symptoms as pain, excessive sensitivity and even bleeding.
Many people are accustomed to postpone the problems with the oral cavity, without paying attention to such symptoms as pain, excessive sensitivity and even bleeding.
Such negligence can lead to complications such as a chronic form of pulpitis, which poses a danger not only to the teeth, but also to other organs.
Content
- The course of chronic pulpitis
- Fibrioznaya form - a common and very dangerous
- hypertrophic pulpitis
- gangrenosum form of violation
- the diagnosis
- complex therapeutic measures
- acute cases
- emergency assistance
- Possible complications
- Preventive measures
The course of chronic pulpitis
Chronic pulpitisIs a disease that is accompanied by inflammation of the neurovascular bundles of the tooth, which leadsto severe pain and tooth decay( sensitivity increases, caries and inflammation of neighboring tissues develop).
This disease is most often experienced by people between the ages of twenty and fifty.
This disease can be a consequence of an earlier acute form, or develop independently.
The main insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that its symptoms are often ignored by the patient, and he turns to the doctors at the stage when it is impossible to save the tooth, and the inflammation passes to adjacent tissues.
There are several main types of chronic pulpitis.
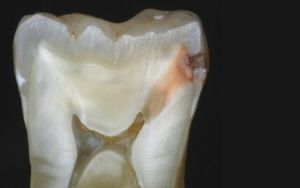
Fibriosis is frequent and very dangerous.
Chronic fibrous pulpitis is the most common form, which is an increase in the connecting 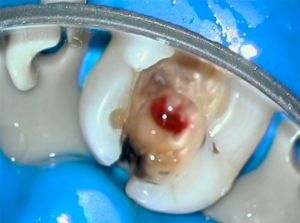 tissues inside the tooth.
tissues inside the tooth.
Upon examination, the doctor observes carious destruction, in the cavity of which dentin and plaque accumulate, as well as food residues.
A damaged tooth responds too sensitively to the slightest pressure and impact. Occurs as a consequence of the course of acute pulpitis, and without it.
Causes of the development of the disorder:
- acute pulpitis;
- untimely treatment of caries;
- poor cleaning of coronal channels;
- regular hygiene non-compliance.
Main symptoms:
- feeling of heaviness inside the tooth and pressure on the gum;
- bad smack and smell from the mouth;
- discomfort during eating hard, cold, hot;
- formation of carious deformation;
- stretching pain that gives in the ear and neck.
Hypertrophic pulpitis
 Complicated form of fibrous pulpitis, often called the polyp of the pulp. In this case, the tooth cavity collapses, exposing the pulp, which every day is exposed to harmful effects during chewing food, drinking hot and cold and from the bacteria that develop in the mouth.
Complicated form of fibrous pulpitis, often called the polyp of the pulp. In this case, the tooth cavity collapses, exposing the pulp, which every day is exposed to harmful effects during chewing food, drinking hot and cold and from the bacteria that develop in the mouth.
Bared pulp delivers a lot of discomfort, because it reacts too much to external stimuli. The patient is not able to chew the damaged tooth, because of which bacteria, caries and plaque accumulate there, which contributes to worsening of the patient's condition. Very often, teenagers and children suffer from hypertrophic form.
Reasons for the violation:
- crown destruction;
- poor-quality caries removal;
- accumulation of plaque;
- Crown injury;
- infection.
Symptoms:
- a painful polyp comes out, which reacts painfully to irritants;
- slight bleeding, despite the absence of mechanical damage;
- pain during eating;
- bad breath, as a consequence of the congestion of microbes;
- inability to chew all teeth;
- prolonged aching pain, which can provoke cold, hot or hard.
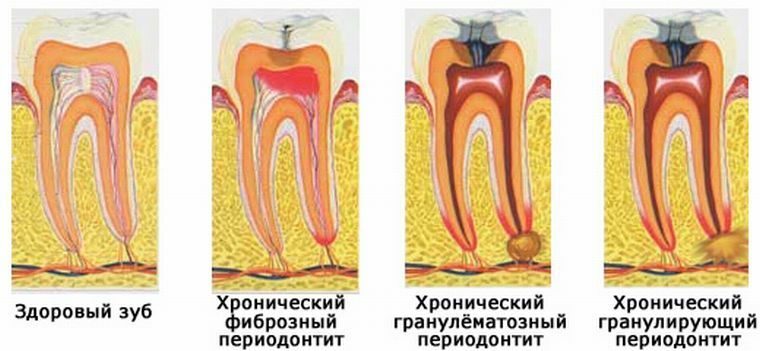
Gangrenous form of disorder
Chronic gangrenous pulpitis is accompanied by deformation of the root pulp, which subsequently leads to its destruction and necrosis of the tooth tissues.
Represents a neglected form of chronic pulpitis. Most often, lower teeth are subject to destruction, since they suffer much more often from plaque formation and caries.
In some cases, it flows into the apical periodonitis.
Causes of the disorder:
- penetration into the internal tissues of harmful microbes and bacteria, which provokes a purulent process;
- diseases of neighboring teeth;
- pathological diseases of dental tissues;
- launched caries;
- rendering of substandard dental services;
- ignoring the acute pulpitis;
- a general decrease in immunity and infectious infection.
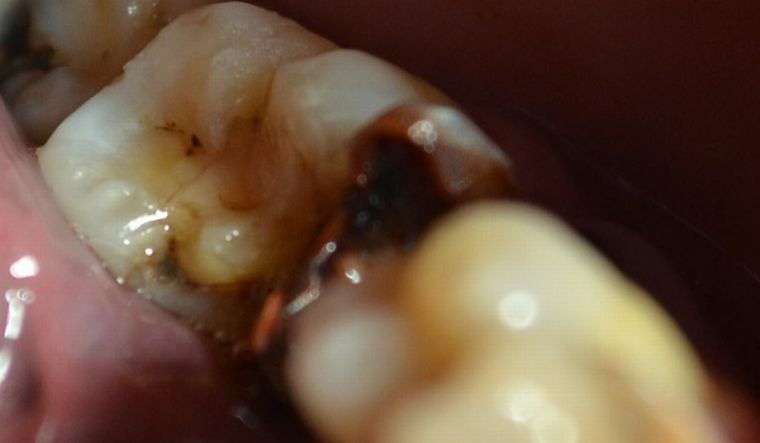
Chronic pulpitis of this form has such symptoms:
- smell rot from the mouth;
- fracture and partial deformation of the crown part;
- enamel gets an unnatural gray appearance;
- around the affected area swollen gum;
- presence of lymphatic nodules on the gum;
- painful sensations on chemical, thermal and mechanical stimuli.
Diagnosis of
Reliable diagnosis is the most important stage in the treatment of chronic pulpitis. The main criterion in the study of the patient are his personal feelings and observations. Inspection includes such steps:
- The doctor asks about the condition of the patient and compiles a report based on his complaints.
- When examining , attention is drawn to the condition of the gums ( there is silt, redness and bleeding);the state of the tooth itself, its shakiness and color;for the presence of caries and open pulp.
- The next step is the determination of the degree of deformation of the crown, root, nerve endings and bone , as well as the state of the tooth canals and vessels. For this, an X-ray is taken, on which all affected areas are visible.
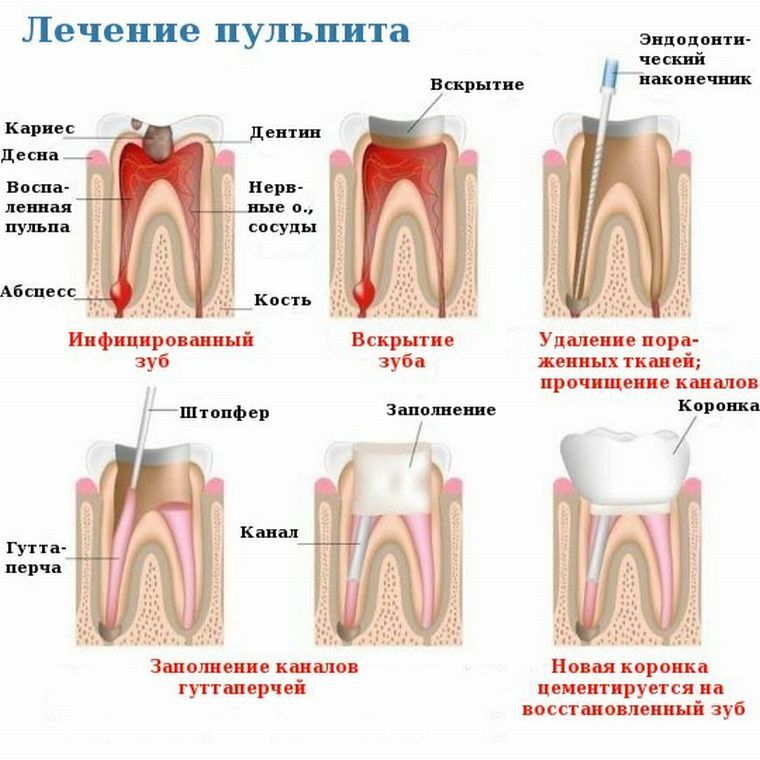
Complex of therapeutic measures
The main goal of the treatment is neutralization of infected areas and preservation of the tooth. The doctor cleans the coronal channels and heals the caries, and then restores the lost parts of the tooth, if there are none due to necrosis.
Such methods of treatment of chronic pulpitis form are applied:
- Traditional therapy of is used in case the patient has applied at the first stages, and irreparable damage has not occurred yet. In this case, the treatment is somewhat reminiscent of caries removal - the tooth is cleaned and treated with medications that act as antiseptics and pain medications.
- Biological method - used in the detection of disease during treatment of caries. A cavity is formed between the pulp and the upper crown, which can be filled with a soft cloth, and presses on the tooth and tears it from the inside. To prevent this from happening, the hole in the tooth is filled with the help of building hard tissues with the help of special liners, which contain calcium. This method is suitable for young people, with good regeneration - up to 30 years.
- Surgical method - involves the complete or partial removal of pulp. The first method is used in case the tooth is too much destroyed, and it is impossible to save it. The second method is used to treat temporary or milk teeth: only the upper part of the pulp is removed, and the lower fascicles remain, which helps form the coronal tissue.
Cases of exacerbation
Occasional chronic pulpitis reminds of itself during attacks of severe pain, the reasons for such exacerbations can be a lot, more often it is a whole complex of catalysts:
- Mechanical damage to the tooth .As a rule, it is enough to bite something hard, be it caramel or nuts.
- temperature - hot or cold food acts as an irritant for a sore nerve. The pain does not pass even a few hours after irritation.
- Reduced immunity to .If the body is weakened, all old sores "come out".Most often this happens in winter and spring, when the body lacks vitamins and minerals.
- Postponed infectious diseases can trigger an exacerbation of chronic pulpitis.
- Operations .
- Stressful situations .
- Bad mouth hygiene promotes the development of bacteria, which irritates the damaged tooth.
Sudden attacks of discomfort can be so strong that the patient loses the ability to eat and talk normally. It can happen at any time of the day, but most often it happens early in the morning or late at night. It can be short-term and prolonged pain.
Emergency care for
The first thing to do is take analgesics that will relieve pain and inflammation. Dentists recommend Ketanov, Nimesil,  Analgin and Diclofenac.
Analgin and Diclofenac.
Also it will not be superfluous to rinse the mouth with solutions of warm water and sage, hydrogen peroxide, salt or soda.
The procedure should be performed every two to three hours. The optimum temperature is not more than 40 degrees.
Possible complications of
If the situation is triggered, tooth loss is not the only problem to be feared. It is worth remembering that the inflammation of the nerve is very difficult, so the damage can go not only to other teeth, but also to the facial nerve and even the brain.
There is also a risk of infecting the dental bone, in this case periodontitis develops, which leads to tooth loss. The difficulty lies in the fact that even a poor-quality treatment can provoke this violation - for example, an improperly sealed tooth or poor cleaning of the root canals.
Preventive measures
Any disease is easier to prevent than cure. As long as possible to preserve the appearance and health of the teeth: 
- do not subject them to strong mechanical effects - many have a habit of cracking candies or cracking nuts, it is strictly prohibited;
- carefully observe oral hygiene: brush your teeth twice a day, use a thread and rinse aid;
- visit the dentist twice a year;
- do not expose the teeth to thermal damage.
These tips will insure not only from pulpitis, but also from many other diseases of the oral cavity.
