 Periostitis is an inflammation of the periosteum, which is a complication of dental diseases.
Periostitis is an inflammation of the periosteum, which is a complication of dental diseases.
In the absence of treatment for periodontal inflammation, the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, the infection penetrates through the periodontal gap and affects the periosteum.
Content
- Varieties disease
- acute and chronic forms
- disease causes and risk factors
- Clinical picture
- Symptoms of acute periostitis
- Signs of chronic disorders
- Therapy disease
- Danger near
- Preventive measures
Varieties
disease, the following course of periodontitis are distinguished depending on the intensity of inflammationjaws:
- acute;
- chronic.
The classification is based on the participation of pathogenic microflora in the inflammatory process:
- purulent;
- aseptic.
By the nature of exudate periostitis happens:
- exudative;
- is proliferative( practically without exudation).
The form of the disease is:
- simple;
- serous;
- fibrous;
- ossifying;
- is otogenic;
- is hematogenous;
- purulent.
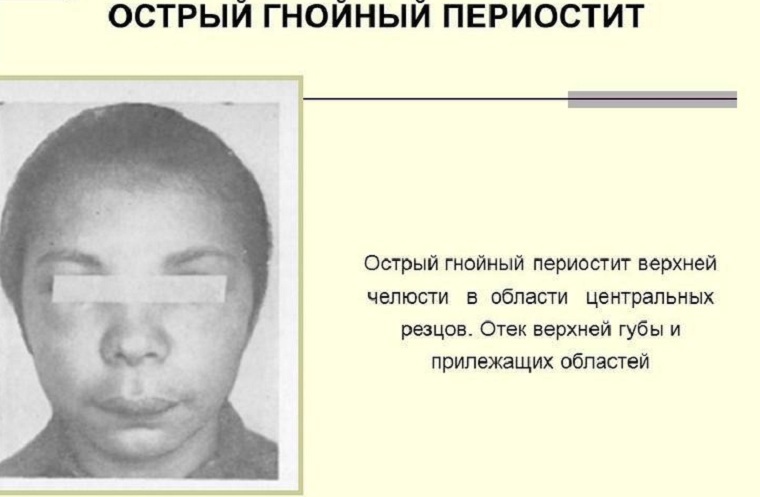
Acute and chronic form of the disease
Acute form of periostitis - suppurative inflammation of the periosteum of the jaw. Most often the periosteum of the alveolar process is inflamed. In rare cases, an abscess of the palatine or sublingual fold is diagnosed.
The cause of the development of pathological processes in the lower jaw are often molars. In acute inflammation of the upper jaw, the infection penetrates through incisors, fangs, wisdom teeth.
Chronic periostitis is rare. Inflammatory processes occur more often in the lower jaw. This course of pathology is observed in patients with immunodeficiency states.
After the abatement of acute inflammation and pain, the abscess may spontaneously emptied. As a result of chronic recurrent processes, bone compaction remains. Chronic course is observed more often in adolescents and children.
Causes and risk factors
Purulent acute processes result from the penetration of streptococcal and staphylococcal infections. Acute inflammation is a complication of recurrent inflammation of the periodontal disease.
Pathology can develop against the background:
- of complex teething;
- of purulent inflammation of cystic growths;
- inflamed non-erupted teeth;
- periodontal disease( periodontitis);
- tumors of dental tissues;
- after tooth extraction.
Adverse adverse factors include:
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- fatigue;
- injury;
- decreased immunity.
In acute and recurrent chronic periodontitis, pus can not freely penetrate outside. In this connection, the contents of the abscess begin to penetrate the lymphatic vessels into the periosteum.
In this violation, the integrity of the tissues is impaired. This determines the inadequacy of cellular immunity to fight infection.
Features of the clinical picture
When the inflammation develops, the periosteum thickens due to swelling and detachment from the bone. In the affected area due to spasm of blood vessels may form hemorrhages. Around the periosteum are small infiltrates, edema of connective tissue is observed.
The inner surface of the periosteum begins to melt rapidly in a purulent process. Exudate begins to accumulate between the bone and the inner layer.
Symptoms of acute periostitis
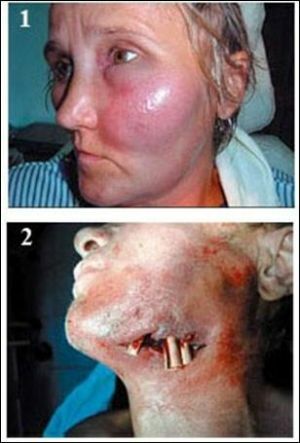
Severe form of periostitis
As a result of local immunity reactions, small abscesses begin to appear, which eventually merge with each other.
The large mass of pus contributes to an even greater delamination of the periosteum.
The result of necrosis necrosis is a violation of the integrity of the exfoliated periosteum and the breakthrough of the contents under the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
In the area of suppuration, small vessels are destroyed and thrombosed. In a few days, the abscess can break into the mouth.
The symptomatology of a purulent process depends on the location and duration of the inflammatory process.
Symptoms of acute form of periostitis of the jaw are multifaceted:
- Patients complain of pain, swelling in the area of inflammation of .
- During acute inflammation of , the temperature of rises, weakness and malaise appear. At the onset of inflammatory processes, edema is small. Within two days, the symptomatology rapidly increases.
- The patient has pains throughout the jaw, the area of the eye, ear, temple. After thermal procedures, inflammation is aggravated. Cold for a while helps to stifle the pain.
- Patients note that first appears pain in the tooth , and later there is a swelling of the face on the affected area. After the appearance of puffiness, the intensity of the pain symptom decreases.
Acute purulent periostitis of the jaw has its signs:
- When purulent inflammation of the jaw in the area of lesions of appears edema .When the upper incisor is inflamed, the upper lip and the wings of the nose swell.
- When the infection spreads, the edema seizes a large area of the face. With inflammation of the molars on the upper jaw, the zygomatic and parotid regions swell, the cheek, the lower eyelid.
In acute periostitis, which was caused by inflammation of the lower incisors, the lower lip, chin swells. The spread of infection contributes to edema of the lower region of the cheeks and corners of the mouth.
Inflammation of the molars on the lower jaw swells the cheek, parotid and submandibular areas. In this case, patients have pain syndrome and limited mobility of the joint due to contracture of the muscles.
Acute process is accompanied by regional inflammation of the lymphatic vessels, swelling of the mucous membrane in the area of the affected tooth, a painful infiltration.
After the breakthrough of the abscess into the submucosa, the pain syndrome subsides, the puffiness decreases. Pus often radiates through the mucous areas of the mouth. Sometimes the abscess breaks into the mouth. After the release of pus, the inflammation subsides.
When inflammation of the lingual surface of the alveolar process in the area of the lower jaw, patients complain of pain while swallowing, movement of the tongue and jaw.
On examination, redness and swelling of the palate are noted. If the alveolar process of the upper jaw is inflamed, a palatal abscess occurs. Patients with enlarged submandibular lymph nodes.
When the abscess increases, the folds in the sky are smoothed. When the infection spreads, the soft palate and the soft pharyngeal arch are affected.
Patients experience pulsatile pains, which are aggravated when the jaw moves. After a week, pus can break through into the mouth.
Symptoms of chronic disorder
In chronic inflammation, the periosteum increases due to the growth of connective tissue. Depending on the age of the patients and  , the state of immunity is observed, the formation of the cava tissue at different stages of maturation is observed. First, coarse-fibrous plates are formed, later a lamellar bone is formed.
, the state of immunity is observed, the formation of the cava tissue at different stages of maturation is observed. First, coarse-fibrous plates are formed, later a lamellar bone is formed.
The disease is characterized by a prolonged course with periods of exacerbation. The patient may suffer from chronic periostitis for several years.
When examined, the dentist discovers minor changes in the structure of the face, notes the painful compaction of bone and lymph nodes in the submandibular region. In the oral cavity there is a swollen reddened mucous membrane.
Therapy of the disease
With acute periostitis, complex treatment is performed. The patient is uncovered an abscess, after which a conservative therapy is prescribed.
In the initial stage of inflammation( serous inflammation), treatment begins with the creation of conditions for the outflow of exudate. The patient is exposed to the cavity of the tooth, the decay products are removed from the channels.
In more advanced cases, the patient is removed a tooth, which was the cause of the development of periostitis. All the manipulations the doctor conducts under local anesthesia( local anesthesia).Usually, after such activities, the inflammatory process is stopped.
In acute periostitis of the upper jaw urgent surgical care is indicated. Patients are uncovered by a purulent focus, treated with a wound and  creates conditions for the outflow of the contents of the abscess. Such operations are usually performed in the department of maxillofacial surgery under local anesthesia. In the wound after the opening of the abscess, rubber drainage is introduced to drain the exudate.
creates conditions for the outflow of the contents of the abscess. Such operations are usually performed in the department of maxillofacial surgery under local anesthesia. In the wound after the opening of the abscess, rubber drainage is introduced to drain the exudate.
In the postoperative period, mouth rinsing with antiseptics and washing the wound with Chlorhexidine, Etacridine, Dimexide solution with Oxacillin are shown.
Drug treatment consists in the administration of:
- nitrofuran drugs( furadonin);
- sulfonamide preparations( Sulfadimezin);
- antibiotics( oletetrin, oxacilin, lincomycin);
- analgesics;
- antihistamines( Suprastin);
- vitamins.
After the removal of the abscess and the cessation of acute inflammation, the patient is shown physiotherapy procedures:
- a sunflower-lamp;
- UHF;
- laser therapy;
- Microwave.
In chronic inflammation, treatment consists in removing the focus of infection, prescribing physiotherapy procedures. With a long course of the disease and inefficiency of treatment, bone formations are removed.
Danger next
Due to pathological processes, the cortical layer of the jaw becomes thin, which can lead to the formation of defects. Sometimes, with a strong detachment of the periosteum, secondary osteomyelitis occurs with massive infiltration.
If the abscess under the periosteum is located on the periphery, a periosteal neoplasm can develop. In case of inaccuracies in treatment and non-compliance with the doctor's recommendations, the infection can spread to the bone and lead to osteomyelitis of the jaw, phlegmon or abscess.
Preventive measures
Prevention of acute periostitis is the timely treatment of odontogenic inflammation. To prevent chronic forms of  pathology should be attached to preventive measures, correction of immunity.
pathology should be attached to preventive measures, correction of immunity.
Timely treatment of acute periostitis results in complete recovery. Already on the fifth day the patients become able-bodied.
In chronic processes, as a result of adequate therapy, recovery occurs. In advanced cases, patients may develop chronic cortical osteomyelitis.
