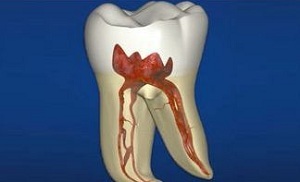
 Pulpitis is a fairly common disease, which is manifested in the development of inflammation and further destruction of internal dental tissues. The pulp is the material by which the tooth contacts the nerve endings, the blood and lymphatic vessels. Thanks to it, an active metabolism takes place, an immune response to viruses and irritants is realized, the tooth receives some protection from mechanical damage, and enamel and dentin feed on useful substances.
Pulpitis is a fairly common disease, which is manifested in the development of inflammation and further destruction of internal dental tissues. The pulp is the material by which the tooth contacts the nerve endings, the blood and lymphatic vessels. Thanks to it, an active metabolism takes place, an immune response to viruses and irritants is realized, the tooth receives some protection from mechanical damage, and enamel and dentin feed on useful substances.
In people with inflammation of the pulp, in most cases, the person experiences painful symptoms, among which there is a great sensitivity to a sharp temperature drop( or just too hot / cold), as well as periodic pain of a pulsating nature.
Sometimes problems with pulp are not accompanied by painful symptoms, but this should not be an excuse for ignoring the problem. Most often pulpitis develops as a consequence of untimely treatment of caries. If it is not treated, then the inflammation can go to the jaw tissue, in people with low immunity, sepsis is possible. Chronic pulpitis in a neglected state leads to loss of the entire tooth.
Contents
- The importance of the classification
- Classification by EM Gofung
- Systematization By EE Platonova
- System Ivanova VS
- Classification Yavorskoy ES
- System proposed by Vinogradova TF
- International classification of pulp diseases
- WHO systematization
- Description of the main types of
- Acute and chronic course of
The importance of systematization of
Classification plays a very important role in the diagnosis of pulpitis and in the appointment of adequate treatment. For today, 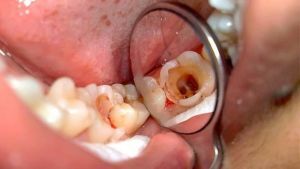 knows more than 20 different classifications of pulp diseases. This diversity is connected, first of all, with the complexity of the disease itself, as well as various approaches to its treatment: some experts try to distinguish between pulpitis among themselves on etiology, while others pay more attention to the clinic and pathomorphological features, as well as other nuances.
knows more than 20 different classifications of pulp diseases. This diversity is connected, first of all, with the complexity of the disease itself, as well as various approaches to its treatment: some experts try to distinguish between pulpitis among themselves on etiology, while others pay more attention to the clinic and pathomorphological features, as well as other nuances.
It is very difficult to create a single classification, also because when investigating pulp lesions, far from the most sophisticated methods are applied, which allow a certain number of inaccuracies and errors. With the external similarity of symptoms and signs with some one of the pulpitis, in fact, according to other criteria, it can belong to a completely different species.
Consider the most common dental classification of pulpitis, as well as the main types of disease in more detail.
Classification by EM Gofung
This classification was one of the first, developed in 1927 and is actively used even in our time. The author divides all variants of pulpitis into the following large groups, including various forms of the disease:
- with acute leakage, which can be: partial type, general and purulent general;
- is a chronic type of affliction, divided into the following varieties: simple, hypertrophic type and gangrenous type.
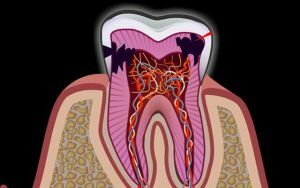 Gofung considered here only those types of disease that can be diagnosed by clinical methods. With its popularity and prevalence, its system has a number of shortcomings, among which the use of non-medical terms, and the fact that many forms of Gofung disease do not reflect the actual clinical and actual state of the pulp. Also, this classification releases from attention the cases of acute variants of the disease.
Gofung considered here only those types of disease that can be diagnosed by clinical methods. With its popularity and prevalence, its system has a number of shortcomings, among which the use of non-medical terms, and the fact that many forms of Gofung disease do not reflect the actual clinical and actual state of the pulp. Also, this classification releases from attention the cases of acute variants of the disease.
Systematization According to EE Platonov
Platonov tried to take into account the flaws developed by Gofung system and offered his own, more complete. It looks like this:
- pulpitis with acute course, - this form of the disease can be diffuse or focal;
- with a chronic course, this includes: a fibrinous type disease, hypertrophic, gangrenous;
- cases of exacerbation in the chronic course of the disease.
The classification of pulpit Platonov is now very popular. It is, in its relative completeness, most understandable to a wide range of doctors. The advantages of this system is that the author tried to take into account not only the pathological processes in the tooth itself, but also other important nuances: the localization of the arising pains, the nature of the course of the disease.
When using this classification system, dentists do not need to go into the details of studying the painful process.

System Ivanova VS
This systematization was developed in 1984 by a group of specialists led by Ivanov VS and very well answers the practitioner's dentist's requests. It takes into account such forms of pulpitis:
- acute, which includes focal serous-purulent, diffuse and purulent;
- is a chronic course that happens to be simple, proliferative, gangrenous;
- exacerbation of chronic course.
Purulent and serous varieties of the disease are included in one item because the serous form of the disease passes into the purulent in just one day, doctors diagnose it extremely rarely and therefore to distinguish serous pulpitis in a separate form there is no special meaning( according to Ivanov, V.S.and his colleagues).
Classification Yavorskoy ES
Developed in 1964, widely used and continues to be used in Ukraine, some other CIS countries. Its main feature is the possibility of using such treatment options for pulp that retain its viability. Systematization of pulpitis according to Yavorskaya and Urbanovich looks like this:
- is an acute type that is divided into the following types: pulpal hyperemia, traumatic, limited type, diffuse or serous type, purulent variant;
- chronic course, which has the following forms: fibrous, hypertrophic, gangrenous;
- exacerbation of chronic;
- aggravated by the presence of focal periodontitis.
The system proposed by Vinogradova TF
Vinogradova TF in 1987 presented a rather wide classification of the types of pulpitis observed in children. This issue requires special attention due to its diversity and complexity. It looks like this:
- pulpitis of infant teeth acute: serous, purulent, with the inclusion of periodontal or lymph nodes;
- acute for permanent teeth: partial serous type, serous total, partial purulent, general purulent;
- is a chronic variant of the disease of the two previous types: simple, proliferative, hypertrophic proliferative, gangrenous.
- to the fourth category refers to a chronic type of disease in the acute form of temporary and permanent teeth.

International classification of pulp diseases
The main principle of the international classification is that only such forms of the disease are included that are well studied, namely their diagnosis, clinical manifestation, variants of preventive treatment and treatment. The international classification of pulpitis of the 10th revision of ICD-10 is as follows:
- initial;
- acute type of disease;
- purulent variant( pulpal abscess);
- chronic;
- ulcerative chronic;
- pulpal polyp( hyperplastic chronic);
- refined of a different type;
- , unspecified.

Systematization by WHO
Another common system adopted in 1997.It looks like this:
- entry-level disease;
- acute form;
- purulent;
- chronic;
- is chronic and ulcerative - two in one;
- is hyperplastic chronic.
Description of the main types of
These types of diseases, which are used in almost any classification, need to be decoded. It is worth remembering that in some systems, by different names, one and the same disease is meant.
There are 4 main types of pulpitis depending on the etiology:
- Infectious .The most common case that arises from inflammation of the vascular-neural beam of the pulp due to the penetration of any microorganisms. Harm brings both the bacteria themselves, and the products of their vital functions. Most often, infection occurs according to a standard scenario - the microbes enter the inside of the tooth due to in time not cured caries. Less often, microbes directly enter an open cavity.
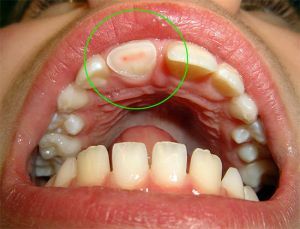
- Traumatic .The resulting trauma to the tooth leads to the fact that the roots penetrate the bacteria from the human mouth. In the normal state, it was completely protected from them. By itself, the trauma becomes only an initial impulse for the development of the disease, very quickly in the tooth the above-mentioned pulpitis of the infectious type develops.
- Concreting .This type of disease is not a consequence of the development of microbes in the structure of the tooth. Concremental pulpitis is the result of poor metabolism occurring in the tissues of the tooth. This happens most often for the reason that the vessels in the tooth are compressed by denticles and petrification. This leads to poor circulation of blood in them, stagnant processes and the appearance of inflammation and edema. After a while, this swelling turns into a full-fledged pulpitis.
- Chemical or pharmaceutical .This variant of the disease is rarely singled out as a separate species, as in practice it occurs more and more rarely, but sometimes it also has a place to be. The essence of the drug pulpitis is that the roots of the tooth are disrupted directly at the dentist's office because of mistakes made by the doctor when using strong substances, this is the same ether or alcohol;with violations of the technique of filling;when using drugs that can get into the pulp through the cement of the root or apex hole. Usually such cases are noticed after some time by the attending physician and helps the patient to cope with the problem that has arisen through his fault.
Acute and chronic course of
Acute and chronic pulpitis are divided into the following types:
- acute focal - the disease is in the initial stage of development, only part of the tissues is prone to inflammation;
- acute diffuse - in this case the entire pulp is inflamed, including its root canals;
- chronic fibrotic - a frequent case that can be the result of the development of acute inflammation, sometimes disappears under an already established seal;
- chronic hypertrophic - its main feature is the connection of the inflamed chamber with the carious area of the tooth;
- chronic gangrenous is an extreme type of disease characterized by destruction of the pulp.
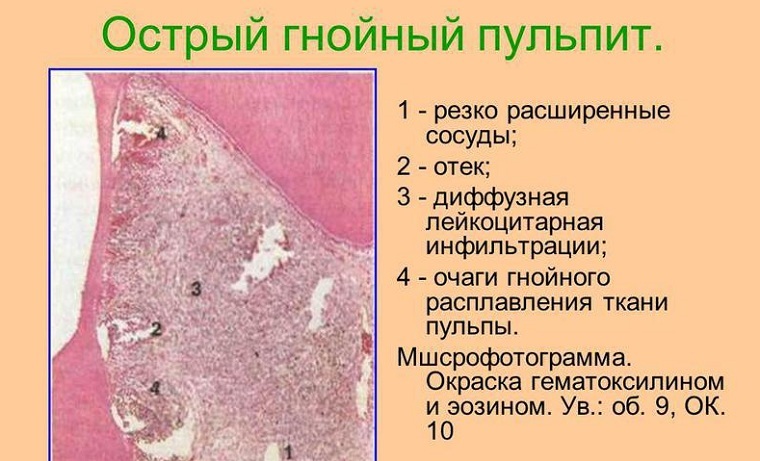
As a conclusion it should be noted that the most widely used classification of pulpit in Russia is the Platonov system, which, with relative simplicity, is able to give the most complete picture of the changes occurring in the pulp. It is quite simple, but at the same time it covers almost all variants of the disease and is excellent for practicing doctors. Also, the international classification considered above is often of practical use.
