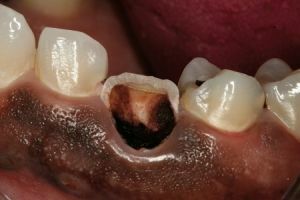
Gangrene pulp: Soot outside from heat from within
To understand independently to any person that it develops gangrenous pulpitis, it is easy. He experiences physical tortures - persistently recurring or not passing pain with an acute process in the tooth, or( in chronic course), this moral suffering is due to the indestructible smell of decay coming from the mouth, despite all the tricks to neutralize it.
And chronic gangrenous pulpitis is a mandatory staining of tissues under the enamel consistently in all shades of gray, yellow, brown and brown in the process of slowly-inevitable destruction of the crown of the tooth.
To a dentist, it is easy to diagnose a patient's face with an acute process, and one look at a sick tooth is chronic, for the picture is typical.
He will also explain to the patient: Acute gangrenous pulpitis is the slow destruction of dental pulp due to poisoning with microbial poisons, resulting in its decomposition, partial or complete, as well as softening and destruction of hard tissues. Pains in the tooth arise due to pressure on the walls of a purulent detritus mass accumulated in a limited volume of a closed pulp chamber, and irritation of the surviving pulp structures.
In chronic gangrenous pulpitis, pulp necrosis takes place in the open pit. In the "pit" the tooth cavity is transformed either when a free communication with the oral cavity created a deep caries, or after an unsuccessful past intervention by the dentist, leaving a part of his instrument in the cavity of the tooth, which causes perforation.
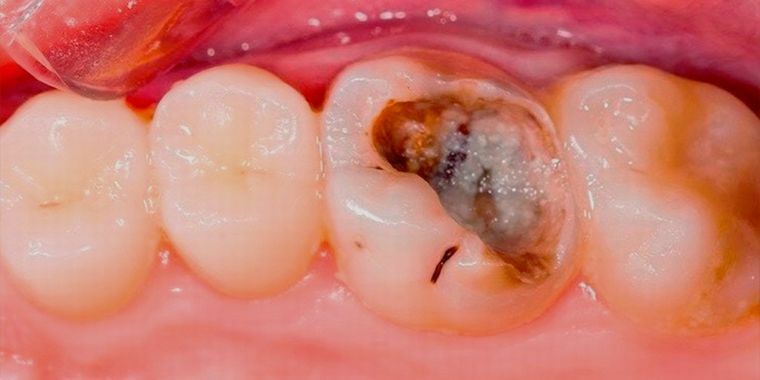
Deep caries is the direct route to necrosis of the pulp
So, gangrenous pulpitis is a serious problem, because the participation of the mouth in building relationships and career with such a disease is minimized.
Why does the tooth look like a darkened one, like a cauldron smoking from the outside, in the depths of which the heat is burning?
Contents
- About the causes and pathogenesis of
- Manifestations and clinic
- Medical history and diagnosis
- Medical care
About the causes and pathogenesis of
To start gangrene of pulp, the cause is necessary - access to it of microbial poisons of anaerobic flora. For their penetration into the closed cavity of the tooth, there are the following ways:
- through the apical channel , due to which the nerves and blood vessels providing it to the vitality enter the interior;
- through the carious cavity , deepening until the thinned bottom of it ceases to be an obstacle to getting into the pulp chamber of biologically active substances of microorganisms;
- through the channel of the dissection of the pulp chamber by the dentist .
Microbial toxins trapped inside the tooth due to the appearance of a message from the pulp chamber with the oral cavity( or due to 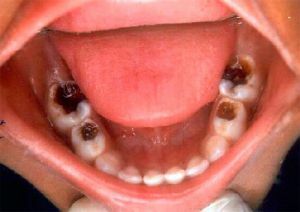 of an artificial opening with the vascular neuropathy left inside it), cause inflammation of pulp - pulpitis first, and then gangrene, when its structure undergoes irreversiblechanges.
of an artificial opening with the vascular neuropathy left inside it), cause inflammation of pulp - pulpitis first, and then gangrene, when its structure undergoes irreversiblechanges.
In the chronic gangrenous process of the pulp, the whole immediately and completely does not die - between the necrotic ulcerated coronal part of it and the state of fibrous inflammation of the root, a demarcation zone of granulation tissue is formed. And only after the complete dying of the dental pulp comes the complete loss of all kinds of sensitivity by the tooth. Risk factors for the onset of gangrene of the tooth are:
- mechanical - in the form of a fracture of the crown or root, excessive erasure, the opening of the dental chamber during dental manipulation;
- caused by acute or chronic dental-maxillary pathology - retrograde infection with a significant depth of periodontal pockets, periodontitis of the adjacent tooth, osteomyelitis of the jaw, sinusitis.
Gangrenous pulpitis is either a natural continuation of the acute or subsequent phase of the chronic course of the disease, or else the primary chronic process.
Manifestations and clinic
Symptoms of gangrenous pulpitis will be different depending on the prescription of the onset of the pathology and on the presence or absence of an oral cavity with the oral cavity. For the acute form of the disease in the intact tooth, this is predominantly a pain syndrome.
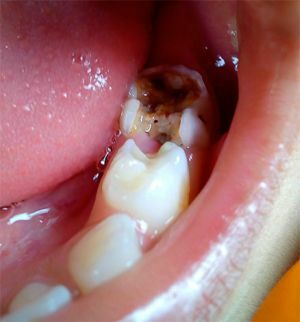
Gangrene pulp is visible to the naked eye
When the dentition is opened in the case of chronic course, biting is accompanied by moderate soreness, for everyday life it is discomfort and a feeling of heaviness in the affected organ. Characteristic is also a painful response to the difference in food temperature: if it is high, then it causes exacerbation of aching pains, and even after a long time after the termination of the effect, the sensations persist.
Gangrenous decomposition of pulp is marked by an extremely tangible putrefactive odor emanating from the patient's mouth. The affected tooth is dull with an admixture of dirty tones, a significant destruction of the crown part, the depth of the carious cavity in its center is filled with the products of decay of dentin. The pulp with normal contact and palpation is painless, the pain appears only when the cavity is deeply probed or if solid food particles get stuck in it.
With the involvement of the root apex process, the swelling and gingivia of the gums are noticeable, or the fistulous course is detected.
For a considerable period of time, the submandibular lymph nodes increase and become moderately painful.
The peculiarity of the condition in children is the absence of characteristic symptoms, due to the not formed roots of temporary teeth. However, a significant pain response is possible with a sharp change in temperature, as when entering from a cold room into a warm room. Inspection reveals a discoloration of the tooth, a considerable size cavity abundantly filled with decay products with a characteristic putrefactive odor. Percussion can cause a little soreness.
Anamnesis and diagnosis
Diagnosis of gangrenous pulpitis does not present any particular difficulties.
It follows from an anamnesis that the pains appeared in the affected tooth then decreased or stopped for no apparent reason. The complaints of the patient are dominated by indications of the appearance of pain in the night, the irradiation of them to neighboring teeth or spreading around the trigeminal nerve. During the day there is a sensation of heaviness in the tooth, the pain appears rarely, under the influence of significant stimuli in the form of extremely hot food or getting stuck in the dental cavity. 
Inspection reveals a change in the color and degree of shine of the tooth - it is a dull, dirty shade. Its center is occupied by a cavity of extensive depth and width, filled with decomposed remains of food and products of decay of tissues with a typical expressive smell.
The examination of the mouths causes pain( as opposed to painlessness in the study of the cavity), carrying out the thermal test reveals a special sensitivity with alternating hot and cold action with slow extinguishing of the sensations after the completion of the exposure.
Percutaneous reaction is usually absent, rarely slightly positive.
The electrodontodiagnostics method reveals a weakening of the degree of electrical excitability of the pulp to a level of 60-90 μA, the radiographic picture demonstrates the broadening of the periodontal gap, and, more rarely, the presence of a periapical foci of destruction.
This type of pulpitis must be differentiated from:
- caries( medium and deep);
- variants of chronic pulpitis( especially fibrous);
- of chronic periodontitis( in particular, apical).
Medical care
Treatment of chronic gangrenous pulpitis with non-surgical methods has no effect due to the necessity of mandatory extraction of necrotic pulp.
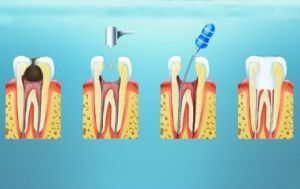
Vital pulpectomy is the only effective treatment for
. Under the influence of local anesthesia, vital pulpectomy is performed( extirpation) - extracting both parts of the pulp - crown and root, using diathermocoagulation to avoid bleeding( the method also allows to extract the whole pulp).
The algorithm for vital vituperation includes preparation of the cavity with the maximum possible opening of the mouths of the root canals, widening the channels themselves with the complete extraction of devitalized pulp and products of decomposition of dental tissues. Antiseptic treatment follows the execution of each phase of the intervention.
Subsequent steps include temporary filling of the channels with calcium hydroxide-based composition for 5-7 days and setting a temporary filling on the crown part of the tooth, and then sequentially sealing the channels under X-ray control.
The restoration treatment is completed by replenishing the volume and shape of the crown area with the help of special materials or by making and installing an artificial crown.
In the treatment of infant teeth, they are limited to vital amputation with mummification of pulp in resorcinol-formalin channels due to the unreality of full-scale cleansing of dental canals with unformed root ends.
In the absence of professional assistance in the case of development of gangrenous pulpitis, there may be consequences - full-scale necrosis of all pulp zones, including the root, the growth of periodontal destruction, which can lead to the need for prolonged conservative therapy or extraction of the tooth. Timely treatment not only contributes to the disappearance of pain and odor from the mouth, but also contributes to the restoration of enamel color and regression of temporary disorders in periodontium.
Measures to prevent the development of pulp necrosis include regular dental checkups, prevention and treatment of dental caries and pulpitis.
