 Diseases of the teeth can occur in both pronounced and latent form. Hidden diseases are diagnosed already in extremely acute dangerous complications of the current. This pathology is granuloma.
Diseases of the teeth can occur in both pronounced and latent form. Hidden diseases are diagnosed already in extremely acute dangerous complications of the current. This pathology is granuloma.
The granuloma of the tooth has the form of a rounded inflammatory formation of a small size with clear contours. The place of localization is the tip of the root of the tooth.
content
- Details about the problem
- formation mechanism
- Symptoms and signs of
- problems Conservative therapy
- Sealing
- Antibiotics
- Treatment surgical methods
- resection root apex or cystectomy
- tooth Hemisection
- tooth removal
- Treatment folk remedies
- Possible complications
Details of the problem
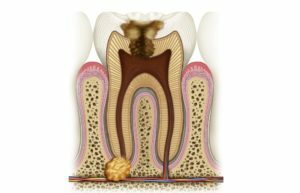
 Components of the tooth are the crown and root protruding above the gum. When the granuloma develops, the pathological process takes place outside the visibility zone, under the gum.
Components of the tooth are the crown and root protruding above the gum. When the granuloma develops, the pathological process takes place outside the visibility zone, under the gum.
As a result, a cavity surrounded by dense walls of connective tissue is formed, in which deceased cells, including bacterial cells, accumulate. Thus, the granuloma is a nodule of dead and inflamed tissues with purulent contents.
This formation is a hotbed of infection, so without treatment it can provoke the development of severe disorders of various organs and systems of the body.
Mechanism of formation
By the nature of origin, granuloma can be considered proliferative( with the growth of the endometrium) stage of development of inflammation, which becomes a protective reaction of the body to attack pathogenic bacteria. The resulting dense capsule from connective tissue serves as a barrier that isolates healthy tissues from infection.
The mechanism of granuloma formation involves three stages:
- The presence of a started dental disease , which causes the collection of microbes in the pulp of the tooth. The pulp becomes inflamed and begins to die. The breakthrough of the capsule is due to the weakening of the immune defense. As a result, the tooth acquires mobility, and its roots are denuded.
- Further propagation of microbes causes infection to enter bone tissue and form a neoplasm around the inflamed area, which is then converted directly to the granuloma.
-
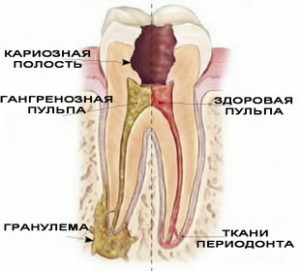
 Simultaneously with the retreat of the bone from the focus of infection, a dense capsule is formed from the connective tissue of , inside which the immune cells interact with bacterial cells. Gradually dying off as a result of the struggle, bacterial cells become purulent.
Simultaneously with the retreat of the bone from the focus of infection, a dense capsule is formed from the connective tissue of , inside which the immune cells interact with bacterial cells. Gradually dying off as a result of the struggle, bacterial cells become purulent.
The last stage is diagnosed with acute granuloma, which is characterized by active growth of pathological tissue and the replacement of dead cells.
Pathology manifests itself in hypothermia, after suffering stress or cold, physical overexertion. If at the third stage the histological examination gives a positive result, ascertain the cyst on the root of the tooth.
Symptoms and signs of the presence of the
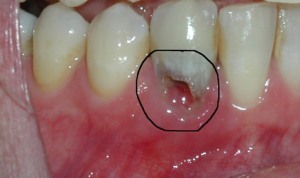
problem As already noted, the granuloma can be asymptomatic for a sufficiently long period of time, which significantly complicates its diagnosis. Often it grows to such a size that it becomes visible during visual inspection. As a rule, as the disease progresses, the patient notes the following changes:
-
 swelling of the gums;
swelling of the gums; - severe toothache;
- development of flux or phlegmon;
- darkening of the affected granuloma tooth;
- purulent discharge in the space between the tooth and gum;
- temperature increase;
- headache and general weakness.
Suspected granuloma at the first stage of its formation can be due to acute pain that occurs in the gum area near the affected tooth after waking. Also, there may be a slight swelling. When going to the next stage, one of the characteristic signs of the disease becomes transient fever with a jump-like increase and a decrease in temperature.
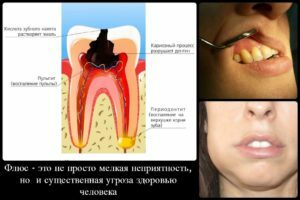
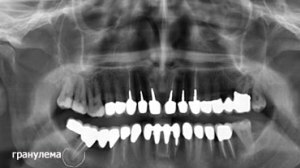 An accurate diagnosis can be made only on the basis of an X-ray or radiovisiographic examination. In the first case, the picture clearly shows the darkened area near the root of the tooth.
An accurate diagnosis can be made only on the basis of an X-ray or radiovisiographic examination. In the first case, the picture clearly shows the darkened area near the root of the tooth.
Radiovisiography is also a type of X-ray study, but it is performed with minimal body irradiation( the results are output directly to the computer monitor, so this survey is called digital).
It is effective to cure granuloma and save the affected tooth only at an early stage of the disease, so it is important to contact a specialist if you have even the slightest suspicion of this pathology. Treatment can be carried out both therapeutic and operative way. Strengthen the effect of therapeutic herbs. The choice of method of treatment depends on the size of education, the state of dental tissues and the presence of complications.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment of granulomas includes sealing and the use of antibacterial drugs to eliminate inflammation.
Sealing
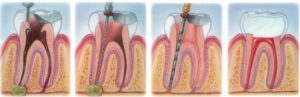 This type of treatment is performed by an endodantist, which specializes in dental canals.
This type of treatment is performed by an endodantist, which specializes in dental canals.
First, the inflamed canal is cleaned of the contents, disinfected, and then tightly sealed( good results can be achieved using the method of vertical condensation).
As a result, the source of infection is completely neutralized, and the affected tissues of bone and gums begin to gradually recover.
Reception of antibiotics
 Filling of the tooth canal is usually preceded by treatment with the introduction directly into the granuloma of antibacterial drugs. Usually in such a situation a combination of sulfonamide and antibiotic is used.
Filling of the tooth canal is usually preceded by treatment with the introduction directly into the granuloma of antibacterial drugs. Usually in such a situation a combination of sulfonamide and antibiotic is used.
The choice of specific drugs is carried out only by a doctor who assesses the severity of the pathological process and the prevalence of granuloma.
In most cases, the treatment of granulomas is carried out using Doxycillin, Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin or Azithromycin.
The use of antibiotics can stop the spread of inflammation and prevent its re-development.
Surgical treatment
 Surgical treatment is indicated if conservative therapy is ineffective or the process is sufficiently started.
Surgical treatment is indicated if conservative therapy is ineffective or the process is sufficiently started.
In the course of surgical intervention, it may be necessary to open the gums with the purpose of its subsequent drainage for the exit of pus( the duration of the procedure is a maximum of 3 days).
Surgical treatment is carried out with the simultaneous administration of antibacterial drugs, the appointment of antiseptics and analgesics.
Also, rinses using herbs are shown. It is quite widely used chemist's tincture of celandine, connected with glycerin or vegetable oil, and Romazulan( previously diluted in water).Solutions are applied to cotton swabs, which are then applied to problem areas.
Qualitative granuloma surgery without complete tooth extraction allows to significantly facilitate further prosthetics.
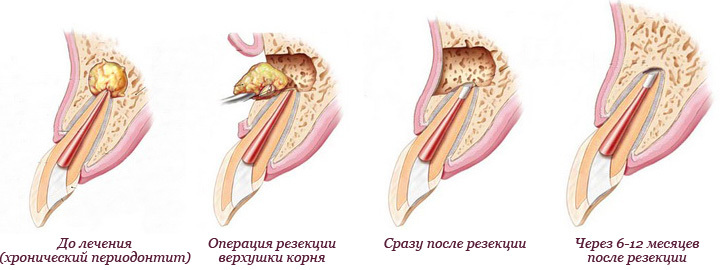
Resection of the apex of the root or cystectomy
The procedure is as follows:
- tooth dissection;
- high-quality cleaning of the channel and its filling with a special solution;
- removal of granuloma and infected apex of the root of the tooth;
- insertion into the cleaned cavity of artificial fabric;
- tooth filling.
Hemisection of the tooth
It is usually done if the granuloma affects the multi-rooted tooth, and it is not possible to completely preserve the root. Consists of the following measures:
-
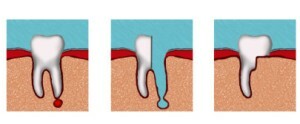 removal of the root of the tooth and the adjacent crown part;
removal of the root of the tooth and the adjacent crown part; - filling the formed cavity with special material;
- crown setting;
- follow-up of the condition of the tooth by X-ray examination.
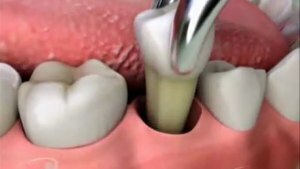
Tooth extraction
Is an extreme measure if the above measures are already ineffective. Indications for removal are:
-
 late stage of the development of the disorder;
late stage of the development of the disorder; - development of periodontitis with the formation of a gingival pocket;
- vertical root crack;
- obstruction of the root canals;
- numerous perforations( integrity violations) of the root;
- apparent tooth decay.
After removal of the tooth, the granuloma dissolves, as pathogenic purulent contents completely exit through the open cavity.
About modern methods of treatment of cysts and granulomas will tell the dentist:
Treatment with folk remedies
 Among the dentists recommended traditional medicine can be noted infusions of ayr and propolis. To prepare, you need 500 grams of vodka and 30 grams of plant ingredients.
Among the dentists recommended traditional medicine can be noted infusions of ayr and propolis. To prepare, you need 500 grams of vodka and 30 grams of plant ingredients.
For qualitative infusion of a container with filled contents, it is necessary to put it in a dark place for a couple of weeks.
Then the infusions are filtered and used for rinsing, combining in a 1: 2 ratio. The duration of one rinse is 3 minutes.
Possible complications of
Untimely treatment of granuloma can result in a variety of complications:
- Quite often there is a complete tooth loss due to the destruction of its root. In addition to an aesthetic defect, an actively growing granuloma becomes involved in the inflammatory process surrounding the affected tooth soft tissue, in which necrosis develops with the formation of purulent contents.
- The spread of pus leads to the development of such severe pathologies as osteomyelitis of the jaw , formation of the tooth cyst, which can eventually degenerate into the malignant cancer tumor .
- In addition, untreated granuloma is a source of constant infection of the body, resulting in the development of various diseases of internal organs, including pyelonephritis, sinusitis, infectious myocarditis .
- If purulent contents enter the maxillary sinuses, and from them into the skull, symptoms of of encephalitis, meningitis appear, peripheral nerves become inflamed. When the tissues of the heart are affected, the risk of death is significantly increased.
- Also, it is possible the development of of the migrating granuloma - a painless protrusion on the skin of the face, which is connected by a dense strand with the affected tooth. The disease proceeds with the formation of fistulas and abscesses, which "move" - after healing of one, immediately another arises in a new place.
An urgent visit is required if any suspicious symptoms appear, as in the case of granuloma it is important not only to stop the pathological inflammatory process in time, but also to keep the tooth as much as possible, which is achieved only at the first stages of the disease development.
