 The root is a name that is not suitable for all teeth, but only for those where it is one, for teeth cutting and piercing.
The root is a name that is not suitable for all teeth, but only for those where it is one, for teeth cutting and piercing.
Food, pinned to the fangs, securely fixed in the mouth, and from it cutters - biting-sawing movements - are separated small pieces that go further, for grinding-chewing teeth more impressive.
Contents
- A brief anatomical educational program
- Why do the roots hurt?
- Inflammatory process
- Other diseases
- What symptoms accompany pain syndrome
- Is it worth mindlessly "tearing" teeth?
- Approach to therapy
- What causes "guerrilla" - complications and consequences
A brief anatomical educational program
Why are chewing teeth called indigenous? Because, unlike incisors and canines - teeth with a single stem root, these are real multi-rooted "oaks".With roots widely spread in the "soil" of the gums, with multiple roots( number from two to four or more), due to which they firmly "sit" in the gum.
Teeth are "sitting", and not hammered into the gum, like nails in a tree. Due to the special arrangement of the jaws and their roots, the teeth have the
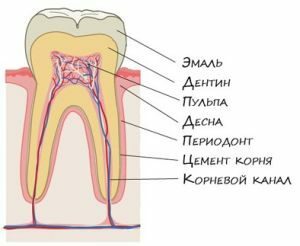 certain freedom of movement in the gingival hole: left-right, forward-backward, and even( in a small volume) - around its vertical axis.
certain freedom of movement in the gingival hole: left-right, forward-backward, and even( in a small volume) - around its vertical axis. "Sitting", they periodically "get up", and therefore the processing of food is somewhat like playing on the piano( or typing on the keyboard): the food squeezed by the jaws, presses on the teeth - and they drown slightly in the gum, then return back, like keys(although not so noticeably).
So when chewing is carried out a natural gum massage, in the thickness of which there are vascular "nervous" "mains" feeding the teeth, each of which includes the nerve, artery and vein.
From the large vascular bundle the bunches depart thinner, each of which penetrates into the tooth through a tiny hole at the top of each of its roots, which grows downward on the lower jaw( like the roots of an ordinary tree), and on the top - tops up.
But, regardless of the position taken by the roots, the circulation in the tooth is not disturbed for a minute. Neither in them, nor in the tooth pulp - the pulp, enclosed in the cavity of the tooth, which is protected from the impact from the outside by multilayered armor of dentine, cement and enamel.
When the massage of teeth and gums with food, which gives them elastic resistance, stops, malfunctions in the work of the vessels and nerves that ensure the life of the pulp begin - and the tooth begins to die slowly. But before he collapses to the ground and turns into a rotten stump, he begins to ache.
Why do the roots hurt?
Toothache( like pain in general) is a condition of ischemia, or oxygen starvation( a lack of oxygen to feed tissues in the blood flowing to them).
And lead to ischemia of dental tissues can:
- vascular causes;
- infectious diseases;
- dental abnormalities;
- is a nervous or mental pathology;
- toxins;
- tumors;
- metabolic diseases( endocrine);
- blood disease;
- injury.
Inflammatory process
 Because the roots of the tooth - not only the "anchors" that hold it in the gum, but also the hollow tubes that conduct blood into it, an infection can penetrate through the holes in their apexes into the dental cavity with the bloodstream.
Because the roots of the tooth - not only the "anchors" that hold it in the gum, but also the hollow tubes that conduct blood into it, an infection can penetrate through the holes in their apexes into the dental cavity with the bloodstream.
And then pulpitis develops - an inflammation of the soft core around the root of the tooth, in which it is not only incomprehensible where the tooth hurts( in the crown part or in the thickness of the gum), but also what kind of toothache it hurts. Especially if the pulpitis is purulent, causing irreversible damage in the cavity of the tooth.
In case of restriction of inflammation by the region of the cavity of the tooth root, apical periodontitis develops( apex is the apex of the tooth).
Other diseases
But the pain in the roots of the tooth( acute or chronic) is not necessarily a symptom of inflammation of the roots.
With the blood flow to the tooth can get not only an infection, but also a toxic substance-toxin, which does not cause the death of the pulp. Gradually, it is neutralized by the body, and then the pain goes away without consequences.
Granuloma( a compact purulent foci similar to a tumor, enclosed in a "pouch" of periodontal disease), settled near the opening-entrance to the tooth and mechanically transmitting a neurovascular bundle, can also cause pain in the roots. 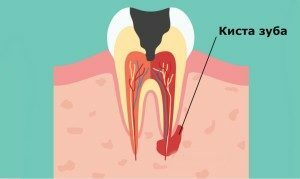
Exactly the same effect can create any tumor( both benign and malignant) or a cyst - a cavity formed in the tissue.
Since the roots carry not only blood to the tooth, but also nervous energy, the "faulty electrical wiring" passing to them can also cause considerable suffering to the owner of the problem tooth.
A general damage to the nervous system and mental illnesses, and the resulting injury to the jaw with damage( more often - with pinching) of the nerve can lead to damage on the line.
In diseases of the metabolism or blood to the ischemia of the tooth tissues, the pathology of the blood itself or the toxic substances contained therein results. But this is ischemia already chronic, with periodic exacerbations.
A special case of pain in the roots is the beginning of the eruption of a permanent tooth, which grows to replace a dairy tooth.
What symptoms accompany the pain syndrome
If you get into the cavity of the root of the tooth infection and the development of inflammation in it( with acute apical periodontitis), it is possible not only the appearance of pain, but also other symptoms.
Their severity depends not only on the type and properties of the causative agent, but also on the fact that the process takes place in a narrow cavity that does not allow infection to spread freely - and it has to "gnaw" hard dental tissues, more precisely, to melt them.
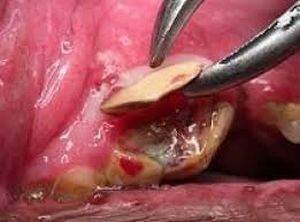
This triggered inflammation of the root of the tooth, as in the photo, can cause sepsis
Therefore, in addition to increasing pain( initially constant, aching and clearly localized, then pulsating-ripping and diffuse), excessive sensitivity, caused by pressure( nipping) on the patienttooth or its vertical percussion, in the absence of visual changes surrounding the tooth tissue.
Entry into the exudative phase, except for severe pain( even with a brief touch of the tongue with the tongue), causes the effect of the "grown tooth" and its mobility in the jaw.
In addition to the swelling of the soft tissues, the symptoms of involvement of the nearest( regional) lymph nodes appear in this stage, the body responds to the microbial invasion with an increase in body temperature( from 37 to 38 ° C), and the blood - with leukocytosis and an increase in ESR.
Radiography of periodontal changes in the acute phase of periodontitis does not reveal.
In a chronic slow process in the root of the tooth, it is possible to change its color( darkening) or the formation of a fistula( pus, melted solid tooth tissues and paved its way out - into the mouth).
Is it worth mindlessly "tearing" your teeth?
Fans of tooth extraction at the slightest pain in them often remain completely without teeth, and pain, as they were, remain - there is no diagnosis.
Therefore, considering that the root pain( in the roots) of the tooth is not yet indicative of their disease, it is first of all necessary to find out the cause of this syndrome.
And only a specially trained professional is able to do this - a dentist who has taken on an ally another professional - a radiologist. And for the establishment of the diagnosis, a variety of research methods are used.
Approach to the therapy of
In establishing the diagnosis of apical periodontitis, which most often affects the root of the tooth, treatment( in general terms) includes 3 stages:
- creating access to the focus of infection;
- treatment-disinfection( cleaning of the tooth from dead and infected tissues);Sealing of the tooth( sealing).
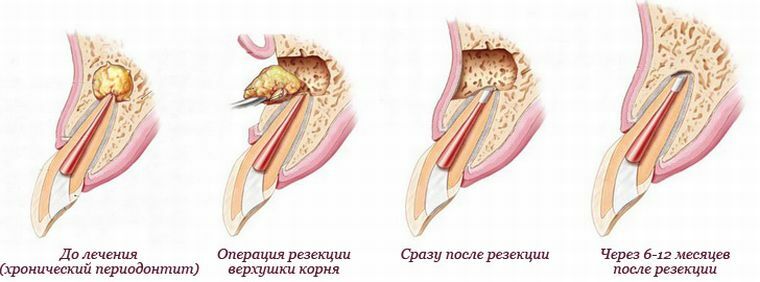
Resection of the root of the tooth
But even with professional healing, complete healing can be achieved only in 85% of cases of periodontitis, sometimes it is necessary to resort to resection of the tip of the tooth root, and only in the most extreme case, the affected tooth is removed.
After elimination of the immediate threat, a long-term multi-stage restoration of health, both general and local, involving physiotherapy and other methods of influence, is carried out.
First aid at home is to persuade the patient to entrust their health and life to a professional dentist.
Application of rinses, warming up and various "miracle means" for the speedy healing and restoration of general health is possible only after professionally conducted treatment and only with the permission of a dentist.
What causes "partisanship" - complications and consequences of
When a late application for dental care( or an attempt to "treat" the inflamed tooth roots itself), the process started in the root of the tooth can cause: 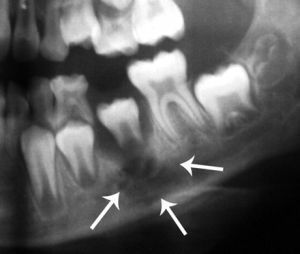
- osteomyelitis;
- formation of fistula of the tooth or jaw;
- cyst formation;
- intoxication of the body;
- sepsis - lead to complications both local and general.
In the "local" case it is the possibility of purulent fusion of not only the tissues of the aching tooth, but of the entire jaw( osteomyelitis) - the fistula formation in this case saves the situation, for the pus finds a way out. To local complications is the formation of cysts.
To preventive measures( preventing the development of pathology of the teeth and oral cavity) is regular( at least every six months) visits to the dentist and the implementation of his recommendations, as well as maintaining the body's health at a proper high level.
