 There are a lot of diseases in dentistry that can not only bring a lot of discomfort, but also significantly worsen the appearance. One of such pathologies is adentia.
There are a lot of diseases in dentistry that can not only bring a lot of discomfort, but also significantly worsen the appearance. One of such pathologies is adentia.
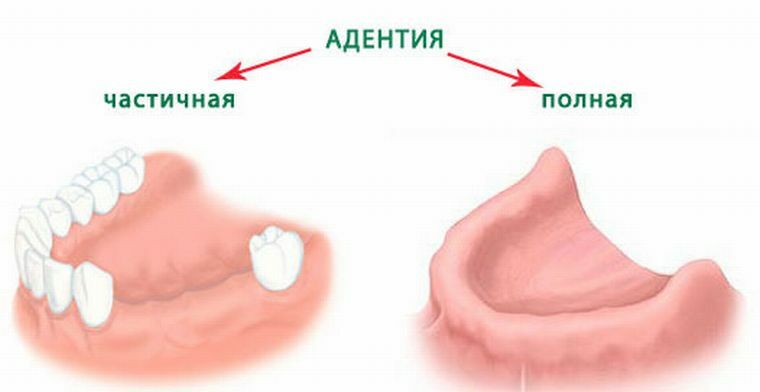
The disease is characterized by a lack of teeth, depending on the shape it can be partial or complete loss of teeth. A specialist can only diagnose the form of the violation. At the same time, the examination, palpation examination, orthopantomography and targeted intraoral radiography are performed.
In the treatment of adentia, rational prosthetics are most often performed with the use of complete and partial removable and non-removable prostheses, or dental implantation.
Adentia, in which there is a complete congenital tooth loss is rare, a partial form of pathology develops a little more often. Against this background, there is a change in the social behavior of a person and psychological maladjustment.
Contents
- Classification of missing teeth
- Causes and provoking factors
- Features of symptoms depending on the form
- Diagnostic criteria
- Modern dental practice
- Preventative measures
Classification of missing teeth
In dentistry, the primary, i.e., congenital, and secondary, otherwise acquired adentia, is different. It depends on the time and reasons for the disease. In addition, there is an adentia of permanent and temporary teeth.
True congenital pathology is diagnosed if there is no tooth rudiment. At the same time, a complicated form of the disease is characterized by a delay in the timing of eruption and fusion of neighboring crowns.
Adentia occurs in the following forms:
- The primary is extremely rare in patients with , which is a consequence of developmental disorders even at the embryo stage. In this case, the fetus may be partially or completely absent dental rudiments.
- Secondary form of the disease is typical for people in old age and is a consequence of tooth decay due to diseases or mechanical trauma.
- Complete lack of teeth is a rare occurrence, but if implant placement is required on both jaws, specialists often remove all remaining teeth.
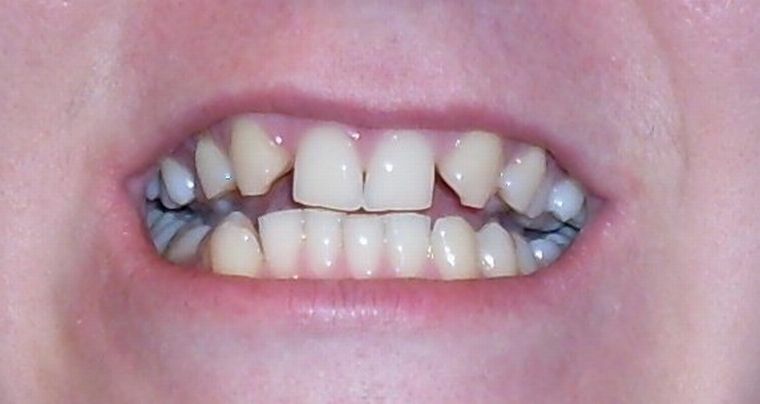
- The most common form is the partial adentia, it is observed in all children during the period of the change of milk teeth and in adults in the case of neglect of the rules of oral hygiene. And also in the absence of prevention and timely treatment.
The number of missing teeth depends on the diagnosis of partial or complete adentia. In this case, the latter is characterized by a complete loss, and with a partial individual or group loss of up to 10 teeth. If the volume is more than 10, then the multiple form is diagnosed. When one of the jaws falls to 15 teeth, a partial secondary form of the disease is noted.
In medicine secondary partial adentia also has several classes:
- for the first is characterized by the presence of a bilateral end-point defect;
- at the second one-sided terminal defect is observed;
- with a third one-sided included defect;
- the fourth class is diagnosed in the case of a frontal defect included, which is characterized by the absence of anterior teeth.
Often classes and subclasses are combined. In addition to the above classes, there is an asymmetric and symmetrical loss of teeth.
Causes and provoking factors
It is very difficult to name the exact cause of the disease development, since the disease has not been fully studied to date. There is a version that the origin of pathology begins as early as the period of fetal formation, actually at this moment the roots of the teeth are formed and the development of the ectodermal layer is disturbed.
There are cases when adentia appears against the background of intrauterine diseases of the endocrine system and the hereditary factor.
Much more often there is a secondary form of the disease, and it can manifest itself in several ways. According to statistics, tooth loss can provoke:
- development and non-treatment of caries ;
- untimely or complete absence of treatment of other diseases responsible for the destruction of the dentition( most often periodontal disease and periodontitis );
- pathologies that contribute to the overall deterioration of the human and the reorganization of the body's work;
- is often the cause of the age factor of , despite the fact that by the age of 60 many people have a lot of health problems, including teeth;
- is the most common mechanical factor , so the loss of teeth can be triggered by a strong blow;
- and of course, the important role is played by the hereditary factor .
Features of the symptomatology depending on the form of
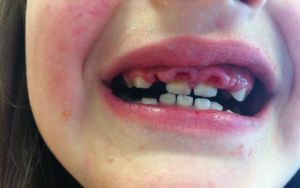 It is quite easy to diagnose the development of the anomaly yourself, as it is simply impossible to miss the loss of teeth. In addition to the visual characteristic pattern, there may also be a broken bite, wrinkles in the oral cavity, uneven teeth, and gaps between them.
It is quite easy to diagnose the development of the anomaly yourself, as it is simply impossible to miss the loss of teeth. In addition to the visual characteristic pattern, there may also be a broken bite, wrinkles in the oral cavity, uneven teeth, and gaps between them.
If the teeth fall out from the front, then later, the cheek and upper lip may fall. Also, the development of pathology can cause serious problems with speech.
In general, for each form of adentia there are inherent symptoms, as the following clinical picture is noted:
- When the partial form is missing several teeth, with masturbation, discomfort, speech problems, biting and chewing problems and active spatteringsaliva.
- With the complete form of the disease, all teeth are missing. In this case, a change in the shape of the face is observed, a whole network of wrinkles appears around the mouth, and a change of speech is noted. There is also a thinning of the bone tissue and the patient has to give up solid food, and this leads to a shortage of vitamins in the body.
- Currently, the is also allocated by the dentists with a relative complete adentium, with some teeth remaining in their places, but are subject to complete removal due to severe damage to the common row.
- Complete primary form is characterized by a malfunction in the mucosa. On x-rays, even with the full form of the disease, even the rudiments of the teeth are not visible. If any teeth are cut, there are large gaps between them. Often the symptom of this form is the formation of a non-incised tooth hidden in the jawbone or covered gum.
- The secondary is manifested as a partial or complete fallout. At the same time there is a change in the skeleton of the face, there are problems with chewing and biting food. Secondary form is accompanied by a worsening of diction. If partial adentia is observed, then the remaining teeth begin to shift, bone tissue is depleted, and when eating too cold or hot food, discomfort appears.
Diagnostic criteria
Adentia is a serious enough problem and only specialists can diagnose this pathology using modern methods. Identify the problem and find a way how to get rid of it can therapists, surgeons, orthopedists, implantologists,  orthodontists and periodontists.
orthodontists and periodontists.
For the diagnosis requires the collection of anamnesis, examination by a specialist, palpation and comparison of dental and chronological age.
If there is a local defect at the time when the eruption has already expired, specialists resort to sight intraoral radiography.
In case of suspected multiple or full form, orthopantomography or panoramic radiography is performed. Also, if necessary, the patient undergoes a CT scan of the temporomandibular joint or radiography.
Modern dental practice
In order to cure the partial form of adentia, specialists use non-removable and removable dentures.
Prosthesis is the main method of correction of the dentition. This method is used when one tooth is missing. If there is a loss of several, then the procedure is much more difficult. In this case, one or another orthopedic construction is used.
The method of prosthetics is also used in the complete absence of teeth. At the same time used are also used, both fixed and removable models of prostheses. In the case where the first option is used, immediately before the procedure it is required to install implants, which will serve as a kind of support.
Removable plastic plates are used for complete secondary adentium. This correction method is often used for people from the older age group. The use of plates is quite convenient, because they can be removed and cleaned. Prosthetics can be performed for children from the age of four, but this can provoke a disruption in the development of bone tissue.
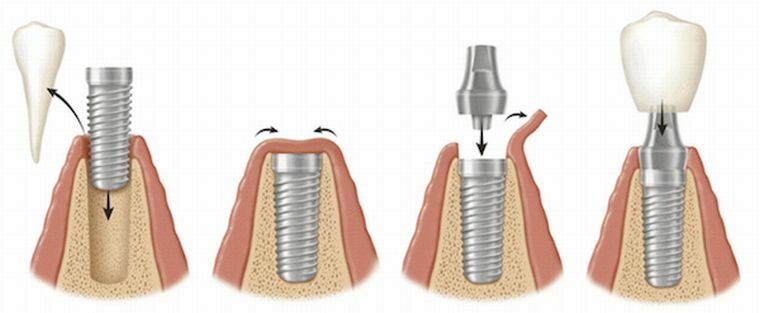
In some cases, there may be some difficulties. For example, if there are abnormalities in the development of bone tissue, fixation for the prosthesis will be insufficient. In addition, some patients have an allergic reaction to the materials that are used during prosthetics. In such cases, modern dental implantation is used.
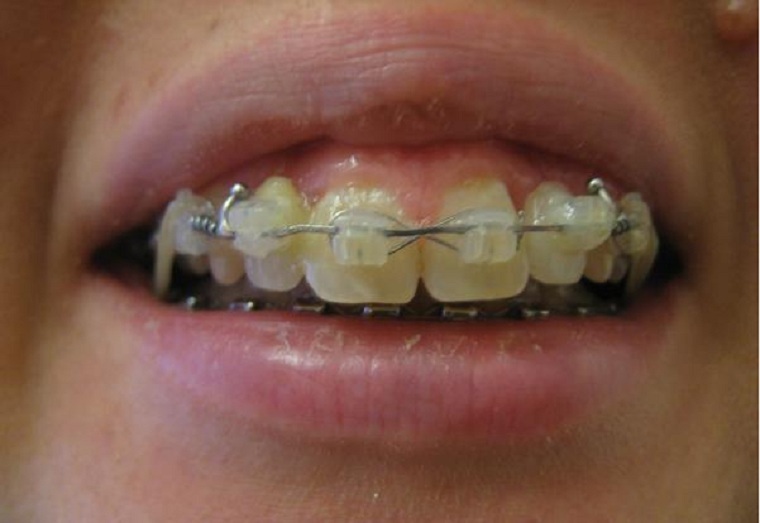
At the beginning of the twenties, braces are initially installed to form the place for the implant
Currently, several methods of implantation are different:
- Classical two-stage implantation is a method that is used for partial and complete tooth loss. The procedure is possible even if the teeth are missing for a long time. It may be necessary to build up bone tissue, restore it for several months and then perform temporary implantation. Only after implants have taken root, a permanent structure is established. This method has been around for quite some time.
If movable or destroyed teeth are observed, one-stage classical implantation is used. But this procedure is not possible in all cases, it may require a monthly course of treatment. - Express implantation implies the use of a whole complex of technologies for restoration of teeth. In this case, implants are used. Often this method is used with the full form of adentium. Since it is possible to install the implant at an angle, this makes it possible to bypass the atrophied sections of bone tissue and fix the structure as reliably as possible. But, despite the low level of traumatism, a permanent implant can not be installed immediately, first a temporary bridge is used for 2 or 3 years and only after that a permanent one, which has reliability and aesthetics.
- Despite the fact that the mini implant is inferior to the previous methods, it has its advantages. This option is used to ensure that the detachable structure is secured more reliably. In this case, thin and small unilateral implants are used, fixation of which occurs by puncture of tissues, the level of traumatism in this case is minimal. With time, prosthesis subsidence occurs, therefore the period of their operation does not exceed 10 years.
Preventive measures
To avoid the development of adentia in children, first of all favorable conditions should be created at the embryo stage. In addition, it is important to ensure that the timing of teething is not increased. To identify pathology at an early stage, you must visit the dentist at least once every six months.
To avoid the development of a secondary form of impairment, it is also necessary to constantly check with a specialist and observe all hygiene standards. With partial loss of teeth, prosthetics is necessary, such a measure will allow to stop tooth loss in the future.
