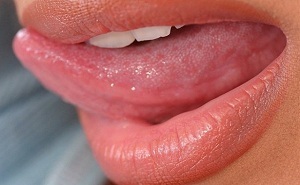
 Language is an indicator of the health of the body, and glossitis is an inflammatory process that affects the tongue.
Language is an indicator of the health of the body, and glossitis is an inflammatory process that affects the tongue.
The disease occurs as a result of traumatism of the tongue, damage by its microorganisms or as a condition accompanying other ailments.
Contents of
- Inflammation can be different. ..
- Causes and mechanism of development
- Complex diagnostics
- Red dots in language
- Therapy of disease
- How to calm inflamed papillae?
- Preventive measures
- Possible complications of
Inflammation can be different. ..
In medical practice, there are many types of inflammation of the tongue. Each type of glossitis has its signs and symptoms, which are used to diagnose:
- Acute .His symptoms are bright and intense. The cause may be parasitic and bacterial infections, as well as pathological processes in the body, for example, allergies. Symptoms: severe swelling of the tongue, pain, redness.
- Chronic .Diagnosed with a recurrent nature of the course of the disease and the inability to establish the cause of the onset. The patient suffers from spasmodic pains, there is weakness, loss of appetite, tongue swollen and can make breathing difficult. Often the inflammation passes to the entire oral cavity, lymph nodes, then to the chin and neck.
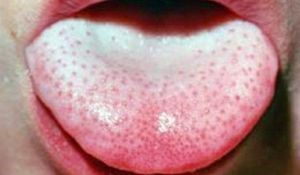
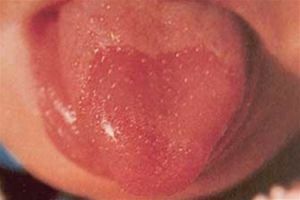
On the photo red dots in the tongue caused by stomatitis
- Desquamative .Outwardly it resembles a geographical map because of the black furrows and lines projecting on the surface, the burning of the tongue and pain during the meal are felt. Serves as a sign of other diseases, for example, liver and blood diseases, metabolic dysfunction.
- Diamond-shaped .The index of problems of the gastrointestinal tract, a frequent companion of gastritis with low acidity. On the back side of the tongue, the epithelium grows in the basal area, reddening appears, sometimes with a bluish tinge, reminiscent of an oval or a rhombus, tongue appears jaggies, mushroom-shaped mounds, furrows.
- Gunter .Its development means lack of folic acid and vitamin B12, resulting in anemia. The tongue becomes bright crimson, shiny, "polished", a small burning sensation in the mouth.
- Catarrhal .The dermal tongue is covered with a thick coating, its movement during conversation and food intake is difficult. It occurs with candidiasis, stomatitis, superficial injuries, accidental thermal and chemical burns. The disease affects only the surface layer of the mucosa, it does not penetrate into the deep layers.
- Slight .In the back of the tongue appear dark threadlike papillae, similar to multi-colored hairs. Common causes: thrush of the oral cavity, smoking, exposure to drugs, trauma to the tongue. Treatment consists of plucking the threadlike papillae with forceps and processing the tongue with a copper sulfate solution.
- Interstitial .Symptom of syphilis. The tongue is contracted due to the transformation of the muscular tissue into a connective tissue, becomes grooved, uneven. In the absence of treatment, the development of cancerous tumors is possible.
- Folded .The disease is congenital with the formation on the back of the tongue of deep folds and grooves. The language functions remain unchanged.
- Mycotic .A prerequisite for the development of ailment is the prolonged use of antibiotics. If the immune system fails, Candida fungi multiply, the tongue becomes swollen, its surface and the back are whitish, and the transverse and longitudinal furrows are pronounced.
- Yeast .Especially does not bother the patient because there is no painful symptomatology, there is only a touch of dirty white and a persistent stench from the mouth. The disease occurs due to lack of oral hygiene, frequent use of alcohol, smoking, an unbalanced diet.
- Atrophic .The disease accompanies people with chronic viral, infectious and fungal diseases,
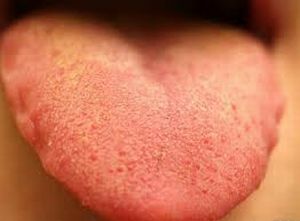 hypovitaminosis( deficiency of vitamins A and E).Characteristic signs are: dysfunction of taste buds, puffiness and hyperemia of the tongue, atrophy of lingual muscles, pain. In the early stages of symptomatology is barely noticeable, which complicates the diagnosis of the disease. When there is discomfort in the oral cavity, the process is considered to be neglected and can not be fully treated.
hypovitaminosis( deficiency of vitamins A and E).Characteristic signs are: dysfunction of taste buds, puffiness and hyperemia of the tongue, atrophy of lingual muscles, pain. In the early stages of symptomatology is barely noticeable, which complicates the diagnosis of the disease. When there is discomfort in the oral cavity, the process is considered to be neglected and can not be fully treated. - Ulcerative .It arises as a consequence of an untreated catarrhal form. The disease is characterized by the appearance of small ulcers - aft, minor bleeding, tongue edematic, with puffiness progressing and pain increasing, motor activity of the tongue decreases.
- Allergic to .It manifests itself as a response to an external irritant-allergen. The reason for the development can serve as a drug, some food products, toothpastes, mouthwashes, denture material.
Causes and mechanism of development of
Inflammation of the tongue and its papilla can provoke:
- bacteria;
- viral infections;
- fungal lesions;
- alcohol and nicotine;
- wearing dentures and braces;
- thermal and chemical burns;
- reception of antibiotics and other medicines;
- allergic reaction of the body;
- tongue injury: shock, sharp tooth edge, dry food with sharp edges;
- ignoring the rules of individual hygiene;
- carious teeth.
Inflammation of the papillae of the tongue may also occur due to such disorders and diseases:
- deficiency of vitamins;
- reduced immunity;
- diphtheria;
- anemia;
- scarlet fever;
- measles;
- is a red lichen planus;
- worm infestation;
- stomatitis;
- rheumatism;
- is lupus erythematosus.
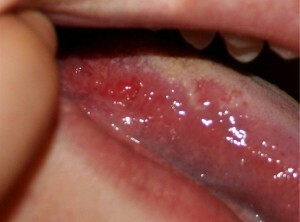 In rare cases, glossitis develops independently, in most cases it is a symptom of a common disease.
In rare cases, glossitis develops independently, in most cases it is a symptom of a common disease.
First there is plaque, the tongue swells and its mobility becomes limited, the saliva production process is broken, burning sensation is felt in the affected area, and a stench comes from the mouth.
The tongue becomes bright red or crimson, it can cause ulcers, erosions and mushroom-like outgrowths, the taste buds are disrupted, food and breathing problems may occur, the body temperature often rises, body defenses decrease, signs of intoxication appear, lymph nodes increase.
Integrated Diagnosis
Inflammation of the tongue does not pass asymptomatically. The dentist performs the initial diagnosis using special mirrors, examining the oral cavity. It can detect:
- changing the size, shape and color of the language;
- injuries and foreign bodies( small fish bones, etc.);
- edema - when the mirror is pressed on the tongue back, a hole remains;
- determine the sensitivity;
- presence of raids, red pimples, rashes, ulcers, abscesses;
- gum bleeding;
- assess the condition of the teeth and oral cavity.
A dentist, in addition to the examination, can refer the patient to additional studies to determine the tactics of treatment:
- a smear from the affected surface of the tongue to determine the causative agent of the disease;
- drug sensitivity test;
- histological examination of tissues after dissection of the abscess;
- general blood test - for evaluation of immunity, stage and type of inflammation;
- biochemical blood test - for assessing the liver and kidneys;
- blood test for AIDS, syphilis, hepatitis, viral and bacterial infections.
The doctor, if necessary, can send for consultation:
- to the otorhinolaryngologist - if changes in the upper respiratory tract are detected;
- to the gastroenterologist - in the presence of signs of pathology of the digestive system;
- to an allergist - with a weighed allergic status and the presence of desquamative glossitis;
- to the immunologist - with villous and candidal inflammation;
- to rheumatologist and therapist - with changes from the side of connective tissue;
- to a dermatologist and infectionist - if there are rashes on the skin.
Red dots in
The red dots in the language are a bright sign of glossitis. At the same time the oral cavity is painful, the tongue is swollen, in the neglected state the red dots turn into large mushroom-like outgrowths.
The main reasons for the appearance of red dots are the defeat of the herpes virus, allergoreaction to external pathogens, alcohol abuse, smoking and malnutrition.
Therapy of the disease
The earlier the anti-inflammatory therapy is started, the better the chances of recovery. If it is ignored, serious breathing difficulties and an increase in the tumor of the tongue are possible.
Treatment is aimed at excluding damaging factors or eliminating the underlying disease. It is necessary to undergo a course of treatment, adjust immunity, restore the balance of hormones, replenish the supply of vitamins and trace elements.
Principles of therapy of inflammatory processes of the tongue depending on the glossitis variety are:
- catarrhal - in professional sanitation of the mouth, elimination of painful symptoms by treatment of the lingocaine with the linguistic surface, daily antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity;
- ulcerative - in cleansing the surface of ulcers from necrotic plaque, processing the tongue with solutions of antiseptics: chlorhexidine, furacilin;
- purulent-reflux - treatment is exclusively surgical, surgical intervention provides excision of abscess,
 and then antibiotic therapy is prescribed;
and then antibiotic therapy is prescribed; - desquamative - the oral cavity undergoes sanation with hexitidine, Hexaspreeem, lidocaine and novocaine are used for analgesia;
- diamond-shaped - no special treatment is required, but with the progression of the disease it is necessary to remove the damaged area surgically;
- atrophic - it is necessary to conduct antibiotic therapy, to fill the vitamin deficiency with multivitamin complexes, the pains are eliminated with the help of sanitizing the mouth with anesthetics;
- Gunther - is treated with Iruksol( a drug based on antibiotic and promoting tissue regeneration of the enzyme), Nystatin( antifungal agent), Chlorhexidine and vitamin A.
At home, at the first signs of glossitis and the appearance of inflamed red papillae in the tongue, the oral cavityantiseptic or broth of wild rose with the addition of a few drops of propolis.
For the preparation of rinses for rinsing the herbs are widely used: sage, chamomile, calendula. But such therapy acts only as an additional treatment.
How to calm inflamed papillae?
Treatment includes the use of drugs: anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, immune medications. In addition, the affected area should be lubricated with antiseptics.
Vitamin complexes will increase immunity and accelerate recovery. Do not forget to rinse your mouth with broths of herbs, brush your mouth with a suitable toothpaste and cleanse the interdental spaces with dental floss.
Preventive measures
Timely treatment of major and associated diseases and the implementation of preventive actions can protect a person from the disease:
- it is necessary to observe the hygiene of the mouth
 ;
; - eliminate bad habits;
- to limit the intake of coarse, spicy and hot food;
- visit the dentist regularly;
- treat chronic ailments leading to inflammation of the tongue and the appearance of red pimples and papillae on its surface.
Possible complications of
In most cases, glossitis occurs without significant complications, but in neglected cases, there are possible: asthma attacks, tumors, abscesses, phlegmon, high fever.
An inflamed tongue signals "malfunctions" in the organs and systems of the body. Prevention of the disease is simple enough and if you follow its principles, you can avoid the development of an unpleasant illness.
