 Hereditary disorders of tooth development affect enamel and dentin. In the first case, it is a disease such as imperfect amelogenesis, in the second - imperfect dentiogenesis.
Hereditary disorders of tooth development affect enamel and dentin. In the first case, it is a disease such as imperfect amelogenesis, in the second - imperfect dentiogenesis.
Each of the anomalies is characterized by its own characteristics. In this case, hereditary disorders develop in several types.
The similarity between the two indicated abnormalities is that with each of them an abnormal development of the teeth occurs. In addition, both pathologies are also united by the fact that they are caused by a hereditary factor.
Contents
- Imperfective dentinogenesis
- Provoking factors
- Forms of abnormal dentin formation
- Symptoms depending on the form of the disorder
- Dental care
- Hereditary enamel dysplasias
- Provoking factors
- Type of enamel dysplasia
- Features of the symptomatology
- What does modern medicine offer?
- Stenton-Capdepone Syndrome
- Aggression Factor
- Nature of Symptoms
- Therapy Methods
Imperfect dentinogenesis
This disease occurs in about one person for every seven thousand people. Imperfect dentinogenesis develops only if one of the closest relatives of the patient has also been diagnosed with this pathology. It manifests itself at the stage of formation of the fetal bone structure.
More common disease occurs in men. It affects both dairy and permanent teeth.
The provoking factors
The main cause of the development of the anomaly is a violation of the formation of dentin at the time when the formation of the bone structure, blood vessels and kidneys.
This violation leads to the fact that the dental tissues acquire amorphous character and do not have an exact arrangement. In particular, in a person with imperfect dentinogenesis, there are areas where dentinal tubules are completely absent.
Forms of abnormal dentine formation
There are 3 types of this pathology: 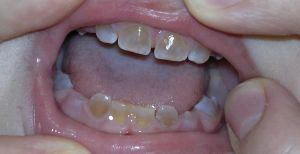
- The first type of is characterized by a deficiency of collagen.
- The second type disease occurs more often than others. Pathology arises from the mutation of the dentin-sialo-phosphoprotein gene, denoted by the DSPP index. The process of forming the matrix protein depends on it.
- The third type arises from the violation of the dentine matrix of phosphoprotein 1.
In the first type of disease, dysplasia of hard tissues near the dental roots is formed, while the second type is formed in the crown area. Regardless of the form of pathology, the tissues that form the surface layer of dentin retain a normal structure.
Symptoms depending on the form of the disorder
Symptoms of imperfect dentinogenesis are determined by its type. Among the characteristic features indicative of abnormal development of dentin, the following phenomena:
- teeth acquire a blue tint, which eventually turns into a gray-brown color;
- local bleeding;
- increased brittleness of the bone structure;
- violation of the shape of the middle ear.
The first type of abnormal development is characterized by the following features;
- the enamel surface retains its normal shape;
- narrowing of the dentinal tubules;
- lack of collagen;
- mobility of the dentition;
- the shape of the crowns takes on the onion form( in rare cases);
- abnormal abrasion of the teeth;
- hypomineralization of dental tissues.
The second type of dentinogenesis( Stanton-Capdepone syndrome) is characterized by the appearance of a number of symptoms:
- destruction and thinning of enamel;
- gradual destruction of dental cement;
- the structure of dentin differs heterogeneity;
- decrease in the content of minerals contained in the affected tissues;
- active calcification of the pulp chamber.
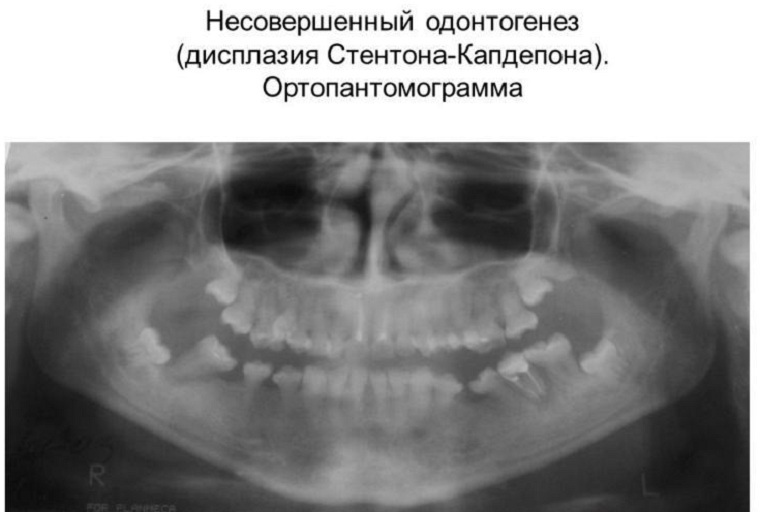
The third type of dentinogenesis can be detected by the following symptoms:
- fibrotic lesion of the dentine matrix;
- increase in the size of the pulp chamber;
- crowns take the form of a bell;
- multiple pulp chamber dissections;
- heterogeneity of dentin tissues located near the pulp.
As the disease develops, the color of the enamel and dentin can change to dark shades. Destruction of the enamel leads to the denudation of the dentin. Because of this, the sensitivity of the teeth to external stimuli increases.
Dental care
Due to the fact that imperfect dentinogenesis is a genetic disease, it can not be completely cured. In the treatment of pathology, a comprehensive approach is indicated, which presupposes a procedure for remineralization of the teeth. The following methods are also used:
- preparations containing fluoride and calcium;
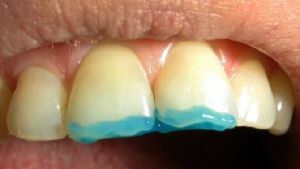
- covering of problem teeth with artificial crowns;
- installation of removable dentures, they allow to eliminate or prevent further deformation of the surface;
- restoration using composites;
- use removable caps, they restore the height of the bite.
With early diagnosis of the disorder, it is often possible to maintain the integrity of the dentition.
Hereditary dysplasia of enamel
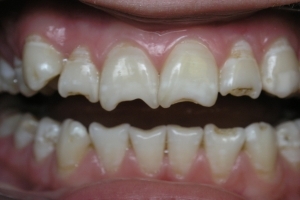 Under imperfect amelogenesis is meant a genetically determined pathology, in which the structure of the enamel is broken. The disease develops at the stage of laying ectodermal sheets, from which the bone structure, blood vessels and a number of internal organs are subsequently formed.
Under imperfect amelogenesis is meant a genetically determined pathology, in which the structure of the enamel is broken. The disease develops at the stage of laying ectodermal sheets, from which the bone structure, blood vessels and a number of internal organs are subsequently formed.
Imperfect amelogenesis is more often diagnosed in women. This fact is due to the fact that abnormal development of teeth of this type provokes a violation of other structures, resulting in the death of the male fetus.
For the first time the anomaly is manifested in children when the growth of infant teeth begins. The latter have an uncharacteristic structure with a thinned enamel, which acquires a yellow or brown tinge.
Aggravating factors
Imperfect amelogenesis develops by transferring a mutated material( an amelogenin gene) via an X chromosome or an autosome. These changes lead to the formation of thin crystals, from which the tooth enamel is subsequently formed.
The development of dysplasia of the enamel is also affected by mutations of other genes. In particular, because of the imperfection of MMP-20, fermentation of calcium-dependent proteinase is disrupted. The latter is responsible for the formation of the enamel matrix.
Type of enamel dysplasia
In medical practice, it is common to distinguish four types of amelogenesis:
- Hypoplastic .It occurs even at the stage of laying the dental tissues. Hypoplastic type is characterized by a violation of the functions of ameloblast.
- Hypomaturation .It occurs against the background of a violation of the process of formation of enamel. In this case, the normal thickness of tooth enamel remains. However, there is a lack of mineral substances in it.
- Hypocalcification .It develops due to the failure of the process of mineralization of tooth enamel. This type is characterized by active growth of crystallites. As a result, this anomaly leads to a decrease in the volume of minerals in the enamel.
- Hypomaturation with hypoplasia .The intensity of the symptomatology is determined by summation by the sign of both pathologies.
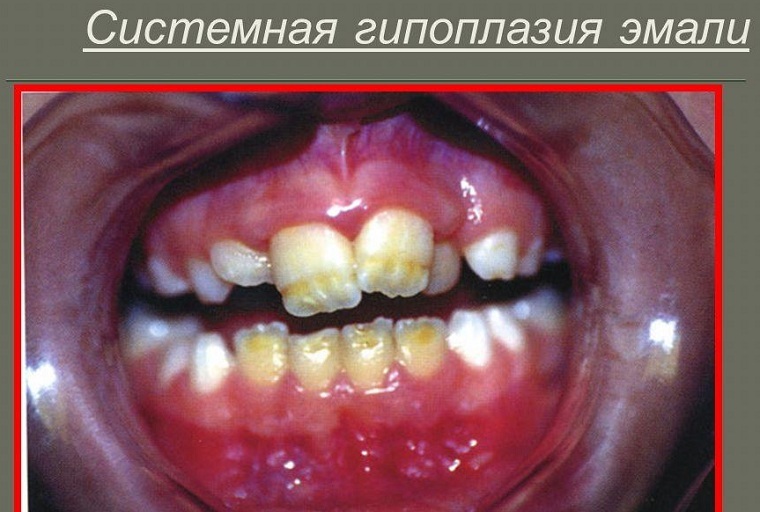
Symptoms of
Regardless of the type of disease, it is accompanied by the following manifestations:
- thinning of the enamel;
- darkening of its surface;
- formation of depressions on the teeth located near the cheeks;
- partial or complete erasure of enamel and dentin.
Hypoplastic type of disease is characterized by:
- darkening of the enamel surface;
- delay in teething;
- decrease in the height of the bite;
- by the displacement of the head related to the temporomandibular joint.
In the hypomaturative type,
- shows a low X-ray enamel density, caused by a low content of minerals in it;
- the upper parts of the tooth are covered with small dots or stripes.
The hypocalcification type is accompanied by the following phenomena:
- enamel becomes soft, which results in its peeling;
- appearance of frequent chipping on the surface of the teeth;
- is lost shine of teeth.
Due to the fact that amelogenesis leads to thinning of the enamel, due to its gradual destruction, the teeth acquire various abnormal forms.
What does modern medicine offer?
The treatment of imperfect amelogenesis takes about one year. In this disease, 
- applications with preparations containing fluoride and calcium are shown, this procedure is repeated every three months;
- application of casein phosphoprotein and amorphous calcium phosphate;
- restoration and prosthetics of teeth in case of diagnosis of significant damage.
Achieving a positive effect also allows timely treatment, during which problem teeth are covered with crowns.
Stenton-Capdepona Syndrome
Stenton-Capdepone Syndrome is a hereditary disease in which dysplasia of enamel and dentine occurs. In the presence of this pathology, one of the parents with a probability of 50%, it will manifest itself in the child.
The disease affects both sexes equally. The syndrome is characterized by a change in the color of the enamel and rapid abrasion of the teeth.
Aggressive factor
Researchers claim that this syndrome develops due to the mutation of the dentin-sialo-phosphoprotein gene, which is why the formation of the matrix protein is disrupted. This occurs even at the stage of the initial formation of the fetus inside the womb.
With such a disease there is no strong connection between the solid tissues of the tooth. In most cases, because of a genetic anomaly, the layer of preentin does not develop.
Symptom of
The main sign of hereditary opalescent dentin is the abnormal abrasion of dairy and permanent teeth. The disease is characterized by other signs:
- darkening of tooth enamel;
- thinning of the enamel, which leads to frequent cleavage and exposure of the dentin;
- decrease in the height of the occlusion, which is the reason for the decrease in the size of the lower part of the face;
- increased sensitivity of teeth( rarely detected).
Syndrome does not affect the process of teething.
Methods of therapy
The basis of the treatment of the syndrome is remineralizing therapy, which is aimed at preventing further erasure of the teeth.
Fluorine and calcium-containing preparations, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed for this purpose.
In case of serious damage to the teeth, crowns are installed or prosthetics is performed.
