Effective struggle with the Colorado potato beetle is possible both with the use of chemical poisoning agents, and with the help of non-toxic natural substances.
Contents of
- Where in Russia is the Colorado beetle?
- What does the Colorado beetle look like, what is it afraid of, what are the harms of the larvae?
- Stages of development of the Colorado beetle with complete transformation: photo
- Natural enemies and scarlet-repeller beetles: plants, flowers, birds
- Are guinea fowl eating Colorado beetles?
- Planting potatoes and combating Colorado potato beetle with
- preparations Prestige from Colorado beetle - instructions for use
- How to get rid of the Colorado beetle by folk remedies?
- Video: Colorado beetle, 8 ways to remove without chemicals
- Mustard with vinegar from Colorado beetle: recipe
- Video: Cleaner for combating Colorado potato beetle
- Effective treatment for Colorado potato beetle and eggplant
- Video: Fighting Colorado beetle. Acura
Colorado beetle is a lot of trouble for truck farmers. To protect the potato crop from this voracious pest, one must use a variety of methods of struggle, including chemicals and folk remedies.
However, it is not possible to completely destroy Colorado beetles due to their stamina and vitality. It remains only to restrain the growth of the number of these insects in order to minimize the threat of damage to the fallow crop.
 Colorado beetle
Colorado beetle Where in Russia is the Colorado beetle?
The Colorado beetle received the name and began its march through the potato fields in 1859.It was then that in the American state of Colorado, pests that spread from the north of Mexico devastated huge plantations of nightshade crops. At the same time, their numbers have multiplied many times, and the speed of distribution across the United States has increased several times.
Speed of Colorado beetle traffic in America in the 18th century was 200 km per year.
In 1876 on the imported potato the Colorado beetle got to Europe. For more than 70 years, these leaf beetles caused serious damage to the agriculture of European countries, and after the end of World War II, they reached the borders of the former USSR.
In 1949, beetles attacked the potato fields of Ukraine, and from there, in 1953, they reached Belarus and Russia. In the Urals, beetles came from the Ukrainian SSR in haymaking cars in 1975, and in 2000 appeared in the Primorsky Territory.
 Potato leaves
Potato leaves damaged by Colorado beetle larvae The unusual persistence of these insects contributes to the widespread distribution of Colorado beetles. They do not sink in the seas and rivers, successfully traveling on the water, move on all types of transport for long distances, fly in the wind. In the absence of food Colorado beetles fall into diapause, falling asleep for a period of several days to three years, and when approaching danger - they pretend to be dead.
What does the Colorado beetle look like, what is it afraid of, what damage does the larvae bring?
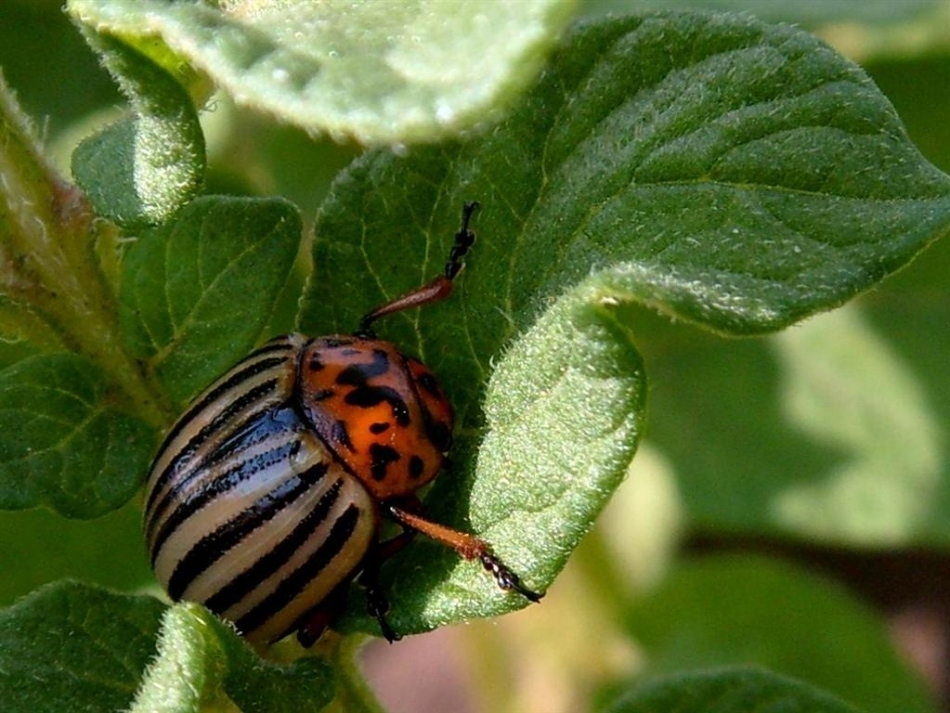
The size of the Colorado beetle is about 1 - 1.2 cm in length and 0.6 - 0.8 cm in width. Soft orange body and tender insect wings are hidden under stiff striped elytra.
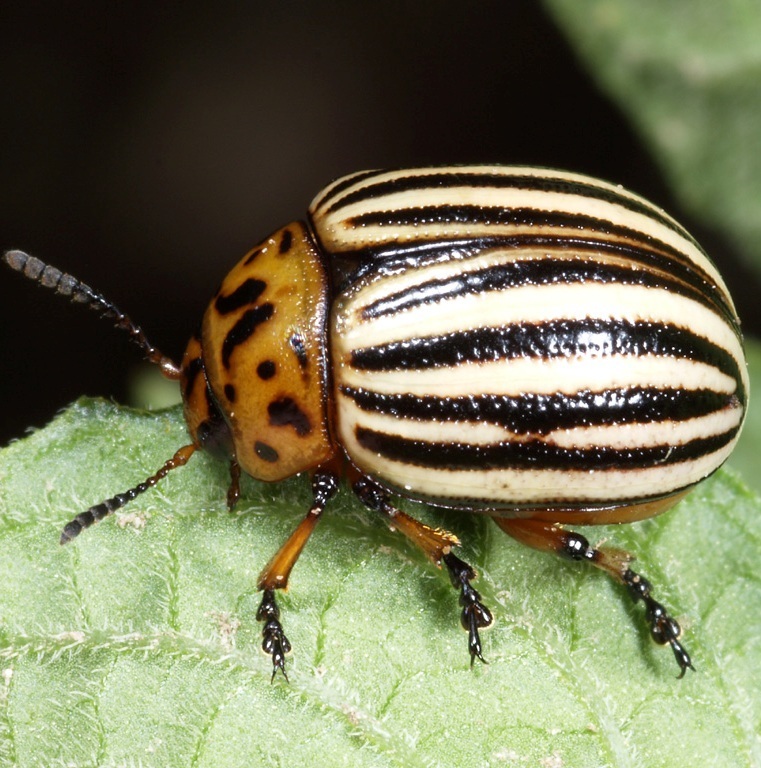 How the Colorado Beetle Looks
How the Colorado Beetle Looks Ten light stripes( five on each) are clearly visible on the light colored wings of the Colorado beetle. Hence the first name of the pest is "decemlineata", which means "ten-tyule".
In flight Colorado beetles are able to develop a speed of about 8 km / h. For a season the beetle can make a way in tens kilometers.
Colorado beetles actively multiply. On the lower part of the leaves of the nightshade plants, the females lay orange oblong eggs, from which, after 1 to 2.5 weeks, soft-bodied larvae appear.
Before turning into beetles, the larva passes through 4 stages of growth. The older they become, the greater the harm is caused by the bushes of the nightshade: once they only gnaw out the flesh of the lower part of the leaves, gradually pass to the upper part and the tips of the shoots.
Before burrowing into the ground for pupation, adult larvae creep along neighboring, not damaged earlier, bushes.
IMPORTANT: During the season one female of the Colorado beetle may lay 300 to 1,000 eggs. Fertility depends on weather and climate.
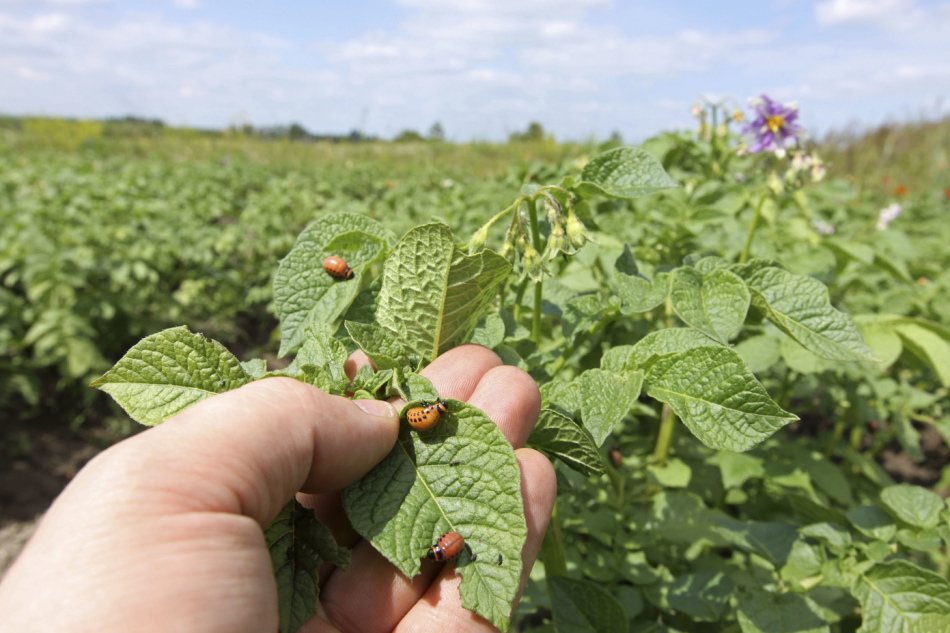
The Colorado beetle and its larvae quickly develop immunity to most of the poisons used. Only the use of systemic insecticides in the struggle gives good results. If the site is small enough to quickly get rid of the Colorado potato beetle, it is best to collect by hand and destroy adult individuals, their eggs and larvae.
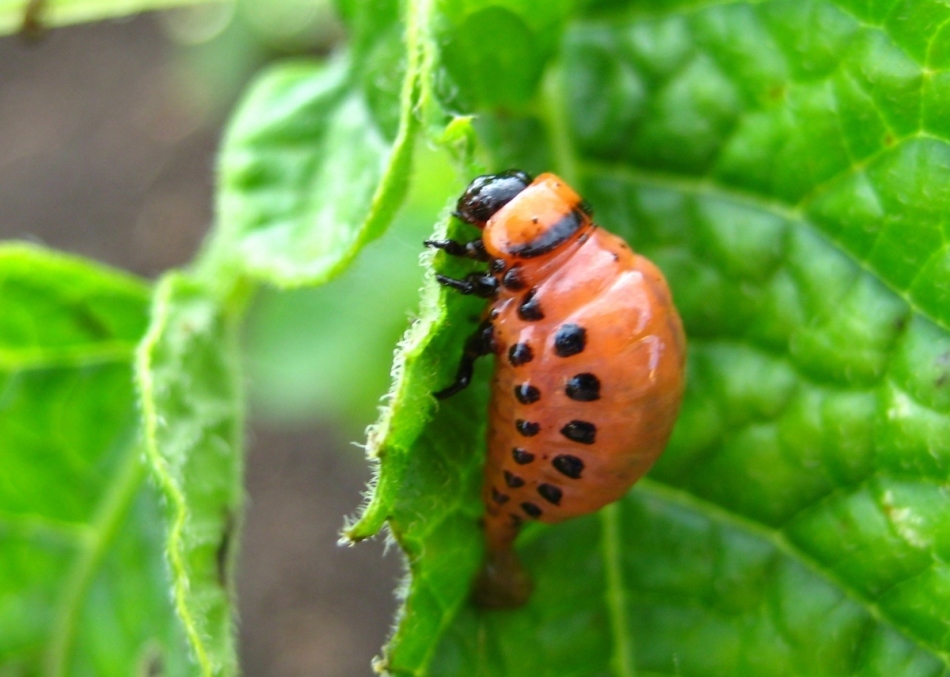 Larvae of Colorado beetle do great harm
Larvae of Colorado beetle do great harm Colorado beetles have few natural enemies, as they accumulate toxic substances in their bodies.
Scare off a Colorado beetle can smell rotting onions. Buckled along with potatoes, onion cleaning will help to keep young shoots from attacking these pests.
Stages of development of the Colorado beetle with complete transformation: photo
In the spring, when the potato beetles ready for breeding begin to get out from under the ground, their first pairings take place. Typically, beetles with the greatest readiness for mating come out of the ground when it warms up to 12 - 15 ° C.
The result of a massive awakening of Colorado beetles is the numerous eggs laid by the females. Egg is the first stage of development of insects.
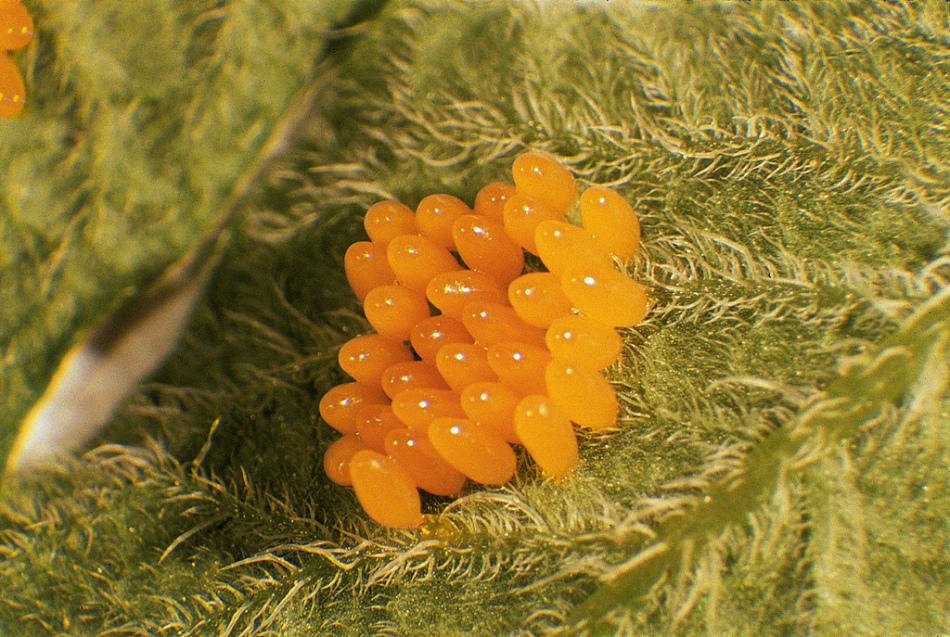 Colorado beetle eggs
Colorado beetle eggs The second stage is the larvae .They devour thin shells of eggs, from which they hatched themselves, as well as eggs that do not have time to be pierced. A few days the larvae gain strength by parasitizing only on the underside of the leaves, then move to the upper parts. To grow stronger, the larvae need to eat hard, which they do, leaving only potted stems and veins from the potato bushes.
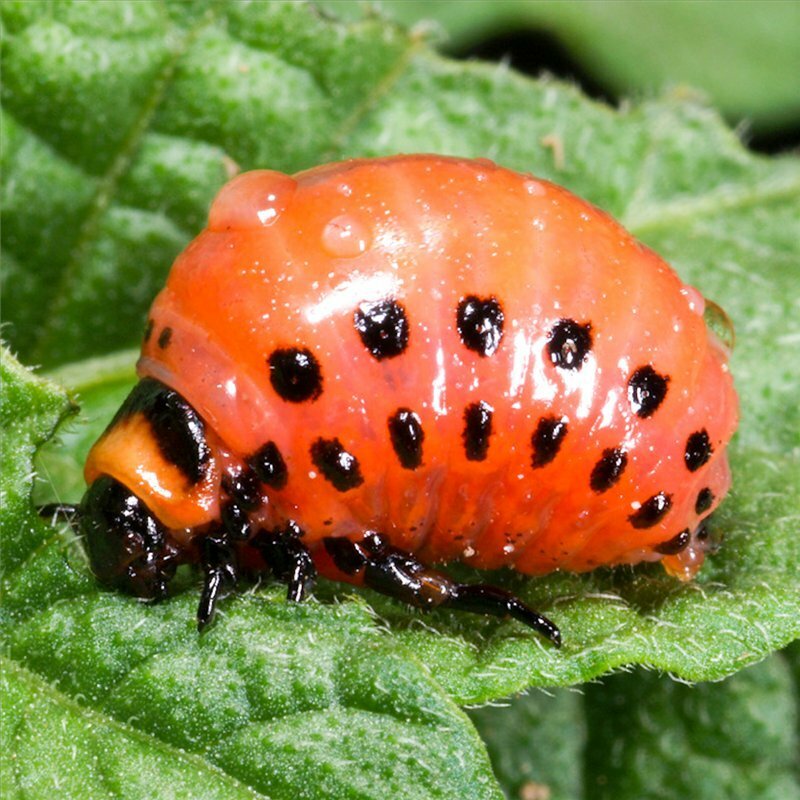 Larva of the Colorado beetle
Larva of the Colorado beetle Adult larvae, ready for pupation, burrow into the ground. There, at a depth of 10-15 cm, they turn into pupae , which is the third development stage of .In this form, they spend 10 - 20 days.
Pupae of the Colorado potato beetle do not harm the harvest. They "close" and remain inactive all the time while they are underground.
Fourth stage of development - adult beetles , which by their appearance from the ground declare readiness to reproduce and repeat the cycle.
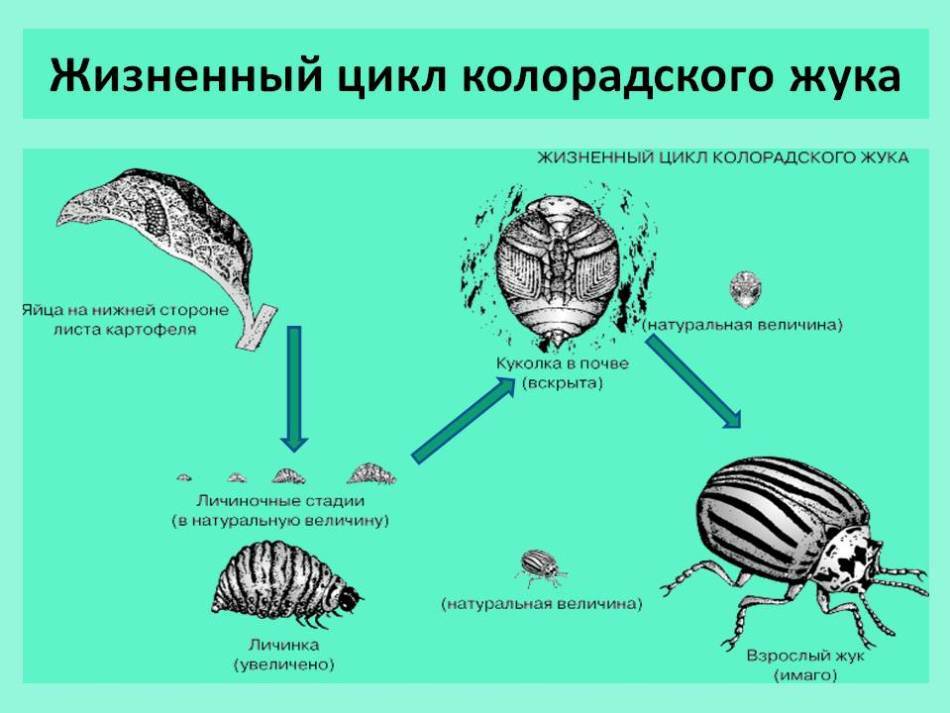 Stages of development of the Colorado beetle
Stages of development of the Colorado beetle Natural enemies and scarlet repellent of the Colorado beetle: plants, flowers, birds
There are few natural enemies in the Colorado beetle. Only a few species of insects can help gardeners in the fight against potato pests:
- ladybug - eats eggs and newly hatched larvae, but does not harm adult beetles
- lace-eyed - feeds on egg-laying and small larvae of Colorado beetle
- flies-syrphids -destroy eggs
Also Colorado beetles eat guinea fowl, turkeys and pheasants .However, in order to accustom these birds to hunt for striped pests, it is necessary to regularly mix them with food for eggs and larvae of Colorado beetles, as well as dead adult individuals.
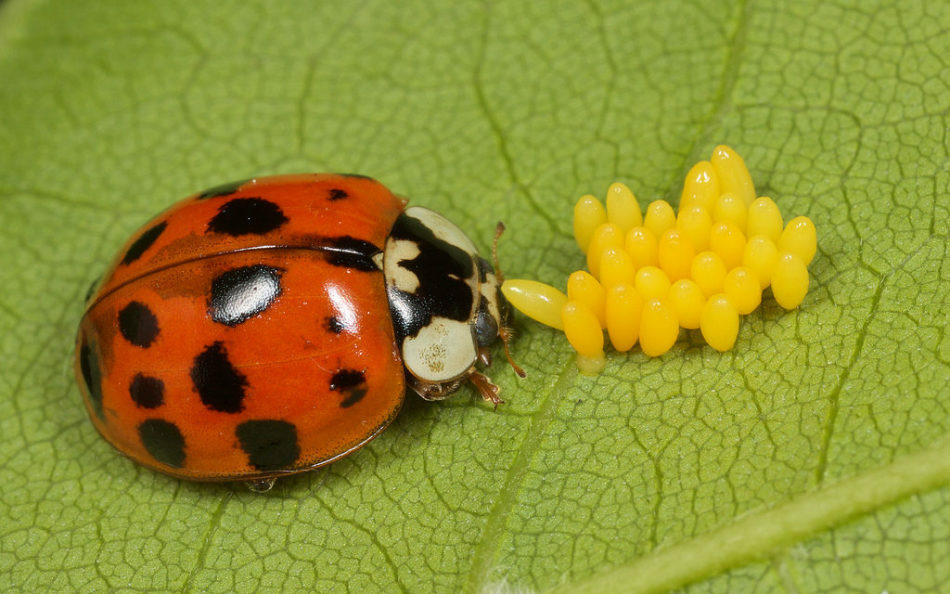 Ladybird is a natural enemy of the Colorado beetle
Ladybird is a natural enemy of the Colorado beetle Seeded along the perimeter of the site with potatoes calendula, night violet, tagetis or legumes scare off beetles with its odor. Also, striped robbers will refuse potatoes processed with decoction of celandine.
IMPORTANT: Multiple attempts of native biologists to bring from Mexico and to settle the natural wreckers of the Colorado beetle by Russian fields have not been successful. Unlike its striped fellow countryman, heat-loving insects perish when the first frosts come.
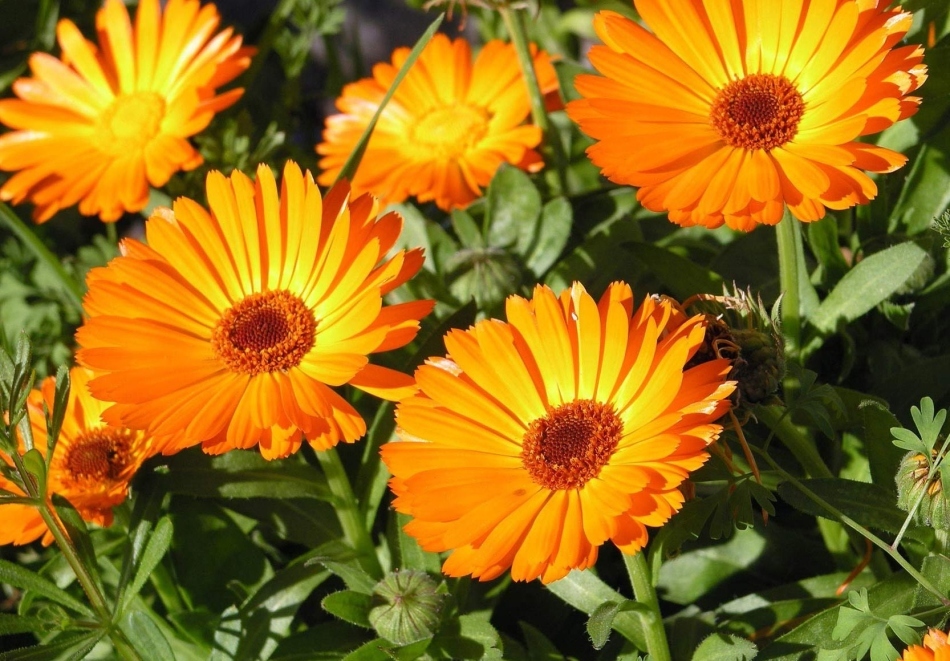 Calendula discourages Colorado beetle from potato beds
Calendula discourages Colorado beetle from potato beds Do guinea fowl eat Colorado beetles?
Guinea fowl successfully eat Colorado beetles right on the bed when they get used to this "delicacy".The protein and proteins contained in beetles and their larvae are necessary for guinea fowl and must necessarily be present in their daily diet.
First of all, the birds will select and destroy all the eggs laid by the Colorado beetles on the reverse side of the leaves of the nightshade cultures. This will lead to a significant reduction in the number of pests. Then they will gradually destroy the growing larvae and adult beetles.
IMPORTANT: To successfully combat the Colorado beetle in the 10 to 15 hectare area, it is enough to release 3 to 4 guinea-fowl per day on the garden.
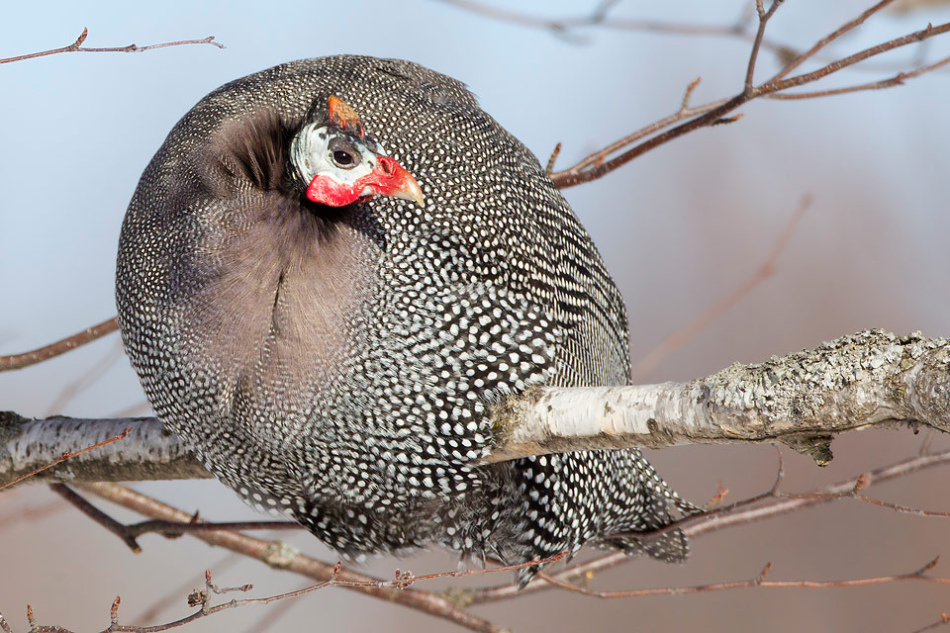 Guinea fowl eating Colorad beetles
Guinea fowl eating Colorad beetles Planting potatoes and combating Colorado potato beetle with
Preparations with potato tubers before planting, as well as spraying sprouts, have an extremely adverse effect not only on the state of beetles, but also on human health. The fight with the Colorado potato beetle is carried out only when it is not possible to destroy pests in another way. The following tools can be used:
- Iskra, Vesta, Taran, Tsitkor, Mavrik, Arrivo are pyrethroids with insufficient efficiency.
- "Bancol" is a highly effective neuristoxin, safe for human and other warm-blooded venom, derived from marine worms. It acts on the central nervous system of insects, blocking the main reflexes. Beetles stop taking food, multiply, move and soon die after poisoning.
- "Regent" - phenylpyrazole, an insecticide of a new generation of long-acting. The first poisoned beetles die within a few hours, and a week later the potato beds are completely cleared of parasites.
- "Commander" - chlornicotinil, is effective both when applied to the soil during planting of potatoes, and when sprinkling greens. It acts on leaf-eating pests at any stage of their development. It is enough 1 - 2 treatments per season to completely protect the potato crop.
- "Confidor", "Mospilan", "Aktara" - neonicotinoids of rapid action with a long period of active damage to insects. For the season will need 2 - 3 treatments.
IMPORTANT: The Colorado beetle quickly becomes accustomed to poisons, so repeated use of drugs of the same action is ineffective.
 "Bancol" - a remedy for the Colorado beetle
"Bancol" - a remedy for the Colorado beetle Prestige from the Colorado beetle - instructions for use
Inexpensive, easy-to-use preparation "Prestige" provides a long-lasting result and protection of potatoes not only from harmful insects, but also from pathogens. This agent is a suspension consisting of imidacloprid and pencicuron.
IMPORTANT: "Prestige" is classified as moderately dangerous poisons( grade 3).After 50 days from the application, the preparation loses its protective properties and decomposes without forming poisonous compounds.
Use "Prestige" to strictly follow the instructions:
- Dilute the preparation with water from the ratio 1:10( per 1 bucket of planting potatoes it will take 10 g of poison and 100 g of water).
- The potatoes should be carefully processed, after pouring on the oilcloth, and leave to dry.
- Potatoes must be planted no earlier than 2 hours after treatment.
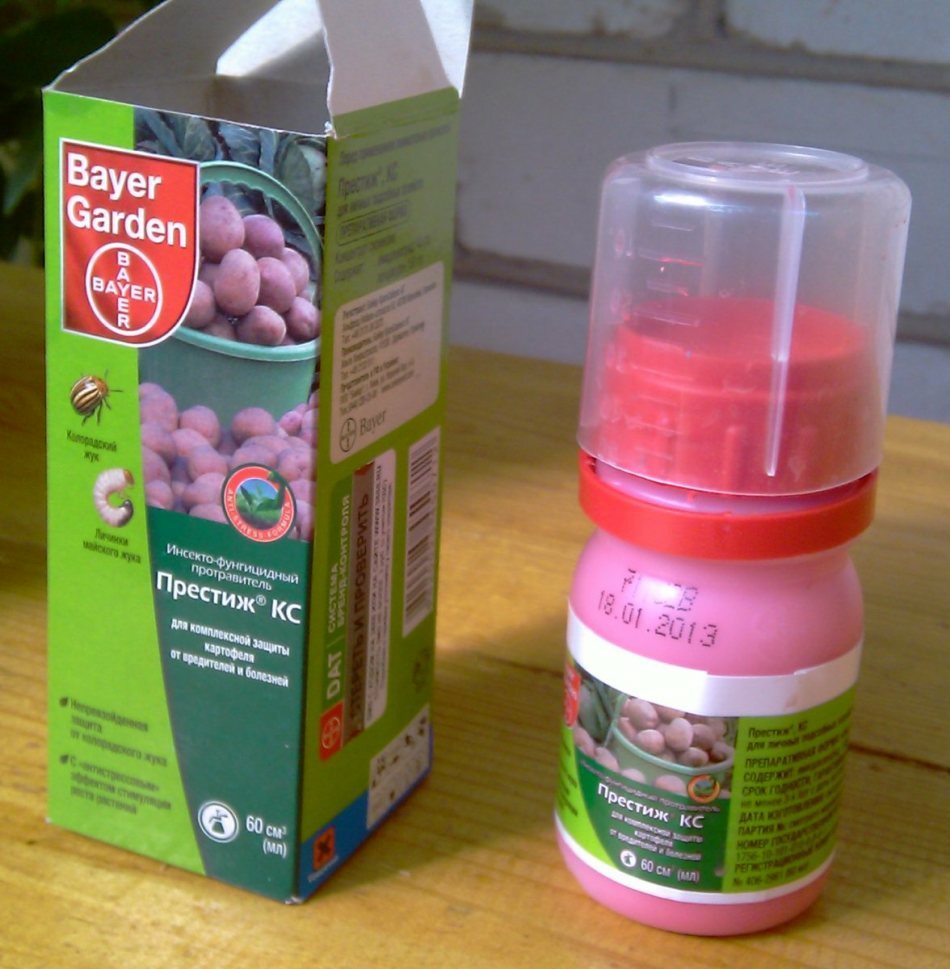 "Prestige" from the Colorado Beetle
"Prestige" from the Colorado Beetle How to get rid of the Colorado beetle by folk remedies?
Folk methods of combating the Colorado potato beetle even take a lot of time and energy, but they are absolutely harmless to human health. The most popular among truck farmers are:
- Mechanical bleeding from the bush with a broom. After the beetles are falling, they are collected and immersed in kerosene or brine.
- Next to the potato beds are poured large piles of fresh potato peelings. These Colorado beetles are quickly collected for these heaps. When a lot of harmful insects are trapped, they simply ignite a bunch, previously doused with kerosene.
- When the first potato shoots appear from the ground, new tubers - baits are planted nearby. Beetles prefer fresh young shoots, so they will quickly crawl from older bushes to young ones.
- Regular thorough spraying of potato bushes with infusions of garlic, onion, celandine, wormwood. The effectiveness of this type of treatment depends on the weather - in the sun the effect of infusions is weakened, and the rain completely neutralizes their effect. In order to scare off pests from the bed, spraying should be done at least once a week.
- The wood ash treatment is started during planting, when it is poured into each well along with potato tubers. In the future, spray the bushes with a concentrated infusion of ash.
IMPORTANT: The more popular methods of combating the Colorado beetle are used simultaneously, the better the result will be.
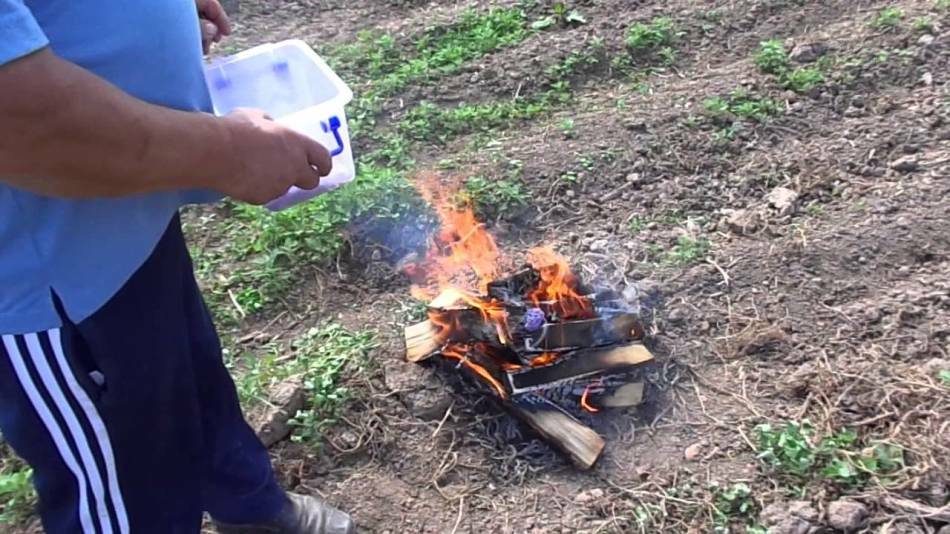 Destruction of Colorado beetles
Destruction of Colorado beetles Video: Colorado beetle, 8 ways of removal without chemistry
Mustard with vinegar from Colorado beetle: recipe
One of the most popular and effective folk remedies that discourages the Colorado beetle and its larva from eating potato leaves is mustard-aceticsolution. There are several options for its preparation:
Recipe No.1
Ingredients:
- Mustard powder( 2 to 3 tablespoons)
- Water( 1 L + 1 sour)
- Vinegar( 100 ml)
Preparation:
- Mustard put in a deep container
- Pourwater( 1L)
- Leave for 48 hours
- Dilute with water( 1 pail)
- Add vinegar
- Mix
- Use for spraying bushes
Video: Ecologically clean agent for combating Colorado beetle
Recipe No. 2
Ingredients:
- Water( 1 bucket)
- Vinegar( 100 ml)
- Mustard powder( 3 items)
- Turpentine( 50 ml)
- Infusion of onion husks( 300 ml)
- Wormwood infusion( 300 ml)
- Infusion of garlic( 300 ml)
Preparation:
- Put all the ingredients in a deep garden container
- Fill with water
- Mix
- Use in the evening to spray the potato bushes
 The scent of mustard repels the Colorad beetles
The scent of mustard repels the Colorad beetles Recipe No.3
Ingredients:
- Mustard powder( 6 table spoons)
- Laundry soap( 50 g)
- Vinegar( 100 ml)
- Water1l + 1 bucket)
Preparation:
- Mustard powder with water( 1L)
- Leave for 2 days
- Dilute with remaining water( 1 bucket)
- Add greased soap
- Add vinegar
- Mix well
- Use for spraying potato bushes
IMPORTANT: To the mixture of mustard and vinegar from Colorado beetlesthe immunity is developed, therefore the given agent can be applied repeatedly on the same site.
 Mustard powder from Colorado beetles
Mustard powder from Colorado beetles Rules for preparation and use of mustard-acetic solutions for effective control of the Colorado potato beetle:
- Spray the bushes as carefully as possible, do not be afraid to "go too far."Abundant processing is guaranteed to bug potato beetles.
- Treat the beds in a calm, non-lighter evening.
- Avoid draining into the ground solutions with the addition of vinegar, make sure that the bulk of it remains on the leaves.
- If you use a mustard solution for processing without adding vinegar, you can also use it for watering.
- Do not use the solution after 2 hours from the date of preparation.
- Do not use the solution in the heat - in the sun, it instantly loses its properties.
- Stop spraying 20 days before harvest.
Effective tool for processing potato and eggplant potatoes from the Colorado potato beetroot and
. So that the time spent for combating the Colorado beetle, the means and efforts were not in vain, you must carefully approach the choice of the method of treatment.
 Treatment of potato beds from the Colorado beetle
Treatment of potato beds from the Colorado beetle It is pointless to call any specific type of poison or method. Colorado beetles are accustomed to all chemical drugs that are applied repeatedly on the same site and, developing immunity, continue to live and multiply on poison treated bushes.
Therefore, it becomes obvious that the preparations for the treatment of beds will have to be changed from time to time.
Only Colorado beetles do not get used to folk remedies. They are always scared off by the smells of onion and garlic, and the intolerance of the taste of mustard and vinegar is also constant.
To keep the crop of the potato intact, completely exterminating the plot of the Colorado potato beetle, its larvae and eggs, every grower can do it. To do this, it is sufficient to select a chemical preparation for the treatment of bushes and apply it in combination with folk methods of struggle.
