
Humming and tinnitus - or tinnitus, is a subjective sensation of sound, while objective sound stimuli are absent. An independent ailment is not a rumble, but merely points to a disturbance in the mechanism of perception of sound.
Contents
- 1 Reasons for
- 1.1 Nature of noise
- 1.2 Causes of tinnitus
- 2 Treatment of
Reasons for

Tinnitus is very diverse - from squeak and rustle to monotonous non-stop buzz. Unfortunately, there are a lot of reasons for the phenomenon. Moreover, in some cases, the truth can not be established even after the most thorough investigation.
The mechanism of formation of nonexistent noise is generally the same. The main role here is played by auditory cells with hairs, which transform sound vibrations into electrical impulses transmitted to the brain. When the frequency of the vibrations of the hairs coincides with the frequency of oscillation of the sound wave, the sound is transmitted without distortion.
If the hairs oscillate chaotically for various reasons, the electrical impulses entering the brain become disordered and are perceived as a permanent unidentifiable noise. There are often no objective sources of sound at all.
Nature of noise
There are several types of hum in the ears. To a certain extent, the nature of the noise makes it possible to establish the true cause of tinnitus.
- v Objective - that is, existing in reality. In this case, it is necessary to speak only of the painful sensitivity of the auditory nerve.
- v Subjective - squeak, noise, creak, hum and other, which are audible only to the patient.
The most characteristic and easiest to identify in this category is the circulatory noise and heart beat, as it is clearly correlated with cardiac tremors.
v Vibration - sound is reproduced by the hearing organ or surrounding structures. To some extent, this sound can be heard and the doctor. There are several subspecies:
- central - the hum is felt not so much in the ears as in the head;
- peripheral - the source of noise is felt by the hearing organs;
- permanent - most often a consequence of an operation on the hearing organ;
- periodic - occurs with diseases of the ears, inflammation, for example;
- single-sided - sound is heard only in one ear;
- bilateral - both organs of hearing are affected.
v Non-vibrational - this sound generates pathological excitation of the inner ear, irritation of the nerve endings and even the incorrect operation of certain brain cells responsible for identifying sounds.
 What drops in the ears with purulent otitis are the most popular, is described in this article.
What drops in the ears with purulent otitis are the most popular, is described in this article.
How effective are the drops in the ears of Danzil, and how to use them, is described in this article.
And what is the price of the Otof drops, and where they are applied, is described in this article: http: //prolor.ru/u/ lechenie-u / otofa-ushnye-kapli-instrukciya-po-primeneniyu.html
Perhaps you will also be interested in learning how to useear drops. Candybiotic.
Causes of tinnitus
According to statistics, at least 20-30% of people occasionally hear hum and noise, which in fact do not exist. Hearing disorders are observed equally in men and women from 3 to 80 years. However, more often such a hearing damage occurs in people engaged in the respective industries, where the sound and vibration loads are the norm.
Tinnitus provokes a decrease and loss of hearing, causes headaches, nausea, dizziness, may be accompanied by secretions from the auricle. The loudness of the rumble is sometimes so great that the patient is not able to hear real sounds.
The factors that lead to pathological changes in the functioning of the auditory organ are numerous, so the diagnosis of such seemingly "obvious" violations is actually very complicated.
External ear injuries: 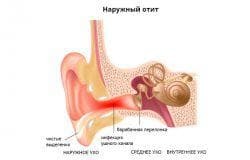
- external otitis media;
- foreign body is a very common cause in patients of childhood;
- sulfur plug( and here's how to remove the ear plug at home and how to do it, see this article)
Middle ear lesions:
- exudative otitis - swelling of the eustachian tube leads to the inability of a normal outflow of exudate - serous or purulent. The movement of the exudate in the cavity is felt as a noise and a splash of water in the ear. It is accompanied by stuffy nose;but what drops with purulent otitis should be used.is indicated in this article.
- trauma , tumors and other injuries of the tympanic membrane - most often due to excessive sound load;
- otosclerosis - abnormal bone growth in the middle ear. The reasons are unknown. Most often observed during pregnancy, menstruation, during lactation.
Injuries to the inner ear:
- Meniere's disease is an increase in the volume of fluid in the cavity of the inner ear. It is accompanied not only by tinnitus, but also by a noticeable loss of balance and dizziness;
- neuritis of the auditory nerve - swelling of the tissue just causes the appearance of chaotic signals creating a non-existent noise;
- tumor of the auditory nerve;
- presbyacusis - age-related changes in auditory cells;
- l abirintitis - inflammation of the inner ear, usually occurs after otitis.
In the video - buzzing in the ears:
In most cases, these ailments are a consequence of inflammation of the middle and inner ear and are called complications after a flu or ARVI.
The state of the ears is to a large extent medicated with a so-called ototoxic effect. Against the background of their reception, noise appears regularly.
The list of them is quite extensive:
- drugs that affect the condition of the central nervous system - caffeine, euphyllin, haloperidol;
Haloperidol
- antibiotics of the aminoglycoside series - gentamicin, amikacin;(and here what antibiotics to treat a purulent sore throat, it is told in given article).

Amikacin
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - diclofenac, indomethacin;
Indomethacin
- loop diuretics, similar to furosemide;
- cardiovascular drugs - digitalis.
There are a number of systemic ailments that can cause a buzzing in the ears of varying degrees of intensity.
Here the diagnosis is even more complicated:
- atherosclerosis is a chronic artery disease;
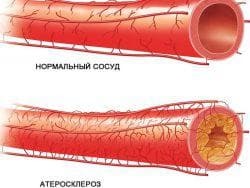
- hypertension - with increasing pressure, a sudden change in the patient's blood flow and heart beats very clearly;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine - leads to a violation of the circulation of the head and is accompanied by the same painful sensation of blood flow;
- tumor - neuroma, swelling of the tympanic membrane;
- ailments associated with metabolic disorders - diabetes, hypoglycemia, thyroiditis;
- carotid artery stenosis - narrowing of the working vascular lumen.
Noise can also be caused by causes not related to damage or ailment:
- fluid in the ear - certainly creates noise, is eliminated purely by mechanical means;
- stress - often has a narrowing effect on the vessels, which causes pressure drops and, accordingly, noise and hum;
- head trauma - hum can be associated with both circulatory disorders and malfunctioning of brain cells;
- poisoning - toxic substances used in production, in addition to other symptoms cause and a strong buzz in the ears.
Treatment of
Noise in the ears can be associated with both the disease of the organ itself and with completely different ailments, so timely and competent diagnosis is so important.
If the occurrence of a buzz in the ears is caused by excessive sound loads - at work, when listening to loud music, the only method of treatment is to eliminate the stimulus. The easiest way to do this is by reducing the volume of the sound or using ear plugs.
On the video, constant buzzing in the ears:
Treatment in all other cases is more complicated.
- Otitis of any kind requires medication. Used anti-inflammatory, sometimes - with purulent forms, antimicrobial drugs.
- Quite simply eliminates the sulfur plug - the ear is washed with furacilin or saline.
If noise is an accompanying factor, then you can get rid of it only by curing the primary disease.
- For disorders in the circulation of the brain, a variety of nootropics are prescribed: cortexin, cerebrolysin. Be sure to include in the course of drugs vasodilating, improving blood flow - Cavinton, cynarizin, betaserk.
Cavinton
- If the noise arose against the background of osteochondrosis, then the first thing that the patient will have to do is restore the normal mobility of the joints and relieve muscle spasms. For the latter, muscle relaxants are prescribed in severe cases - sirdaluth, midolmeal .As anti-inflammatory drugs are used nimesulide, meloxicam. If the pain syndrome is very strong and the noise is not possible to endure, the pain is stopped with non-narcotic analgesics - the catadolone, for example.
Sirdalut
Treatment of this disease is impossible without the patient's own efforts. Only physical activity can restore normal blood circulation and compensate for changes in the condition of the vertebrae.
And here's what to do, when lays the ears for a cold and what can be the reasons, will help understand this article.
What drops you can cure otitis media, and how to choose them correctly, is described in this article.
- If hum is caused by a tympanic injury or is associated with age-related changes, nothing can be done. In these cases, the only method is hearing care.
Drug therapy is supplemented by methods of physiotherapy. Excellent effect gives pneumomassage, electrophonophoresis, electrostimulation and other types of procedures.
Noise in the ears is caused by a mass of different causes - from simple water ingestion to systemic diseases requiring long-term treatment. It is possible to get rid of the rumble only by correctly ascertaining the cause of the ailment.
