 Salivation, or salivation, is a process that provides the ability to chew and swallow food. Saliva is produced by the corresponding glands - large and small, located in the mucous membrane of the cheeks.
Salivation, or salivation, is a process that provides the ability to chew and swallow food. Saliva is produced by the corresponding glands - large and small, located in the mucous membrane of the cheeks.
In addition to physical processing of food, salivation provides its chemical treatment, as well as flushes the substances rejected by the body, has a bactericidal effect, promotes the formation of the food lump and ensures the subsequent swallowing. Disturbances in saliva production complicate these processes and negatively affect the condition of a person.
Contents
- Salivation and Violations
- How does the "Desert" arise in the mouth
- Causes of the disorder
- Clinical picture
- Approach to treatment
- What is the danger of abnormal dryness in the mouth?
- Preventive measures
Salivation and its disturbances
Salivation is the process of saliva production and separation. Salivation of large glands is a reflex action, the performance of which is associated with irritation of the nerve endings of the oral cavity with incoming food, as well as conditioned stimuli-its odor, appearance.
 The task of small glands is the constant secretion of saliva, which ensures moistening of the mucous membrane.
The task of small glands is the constant secretion of saliva, which ensures moistening of the mucous membrane. The process of saliva secretion is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, and the centers of this process are located in the medulla oblongata.
Disturbances of salivation, manifested in a decrease or a pronounced increase in the production of saliva, are associated with various pathologies and phenomena: diseases of the salivary glands, organic lesions of the vegetative centers, acute inflammatory processes occurring in the oral cavity, poisoning by certain substances during ingestion, disturbance of the tone of the vagus nerve, an overabundance or a lack of vitamins in the body.
How the "desert" arises in the mouth
 Hyposylvania is a violation of the separation of saliva from the glands, which consists in a decrease in its secretion. A similar pathology is also known as hyposialia, oligotypism or oligosyalya.
Hyposylvania is a violation of the separation of saliva from the glands, which consists in a decrease in its secretion. A similar pathology is also known as hyposialia, oligotypism or oligosyalya.
Deviation causes discomfort in the patient due to such unpleasant symptoms as regular dryness in the oral cavity, a burning sensation, painful sensations when eating solid food.
Oligosyalya is characterized by the presence of three stages, the last of which can become an impetus to the process of destruction of the mucosa and teeth.
- The initial stage of oligochtism is expressed in the fact that a decrease in saliva secretion occurs usually during a conversation. Some patients note that there is no dry mouth, but they have pain in the area of the tongue. Another category of people with this deviation feel discomfort associated with dry mouth, as well as eating or talking. At the initial stage, the saliva has a normal color and normal viscosity, its amount is within the normal range or slightly lower.
- When the stage is severe, dryness is observed regularly and interferes with the patient. He notes the soreness in the tongue and the burning sensation after a long conversation, and also during a meal. Saliva in the oral cavity at a pronounced stage of hyposalization remains very small.
- In the late stage of , the mucous membrane of the mouth is constantly dry, burning sensation is regularly felt in this area. Upon examination, the membrane is really completely dry, with free saliva completely absent in the oral cavity.
Reducing the secretion of saliva causes a violation of the swallowing process, the appearance of an unpleasant odor, outgoing from the mouth, dental and gum disease.

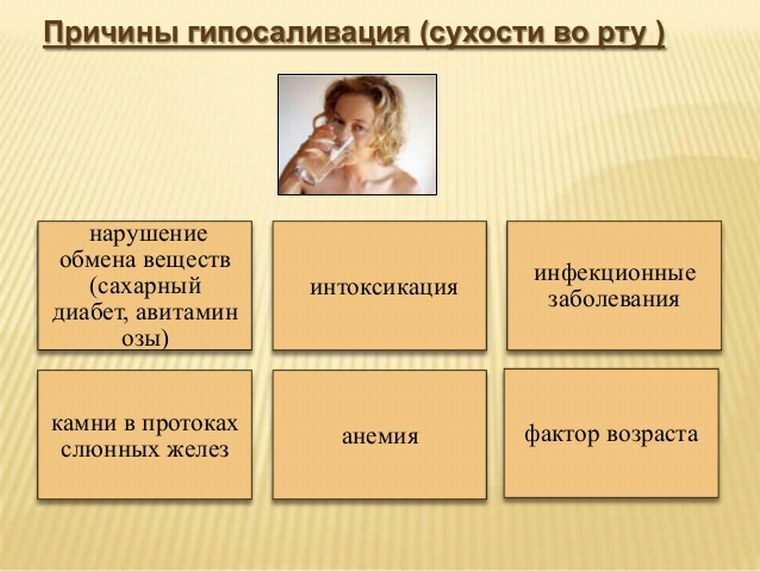
Reasons for violation of
The main causes that contribute to the development of the disease are:
- lack of vitamins A, B, E in the body;
- of salivary gland disease;
- smoking, frequent reception of alcoholic beverages;
- hormonal imbalance associated with impaired functioning of the endocrine system;
- deficiency of iron in the body, which disrupts the process of hemoglobin formation;
- scale dehydration in case of excessive stress or diarrhea;
- presence of diseases - diabetes, lupus;
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- disease of infectious genesis( dysentery, hepatitis);
- pathology of the central nervous system( cerebrosclerosis);
- taking medications from the atropine group.
Clinical picture
Hyposalivation causes a number of unpleasant symptoms. The patient feels dryness and burning sensation in the mouth, roughness of the mucous membrane, pain when eating with a firm consistency. Other signs characterizing this deviation are:
- insufficient moisture of the mucosa or its dryness, which are noted during visual inspection;
- minimum amount of saliva;
- formed saliva has a thick foamy consistency;
- inability to swallow food without parallel water intake.
Approach to treatment of
 To eliminate the symptoms of reduced salivation, it is necessary to identify the true cause of such a deviation and treat a provoking disease.
To eliminate the symptoms of reduced salivation, it is necessary to identify the true cause of such a deviation and treat a provoking disease.
Symptomatic treatment is performed to increase salivation and eliminate the discomfort experienced by the patient.
To this end:

Galvanization of the salivary gland region
- prescribes the intake of vitamins - A, B1, B2, C, E;
- galvanize the area of the location of large salivary glands;
- impose lysozyme applications on the oral mucosa;
- is recommended to lubricate the oral cavity with sunflower oil;
- prescribe the use of special gels for stimulation of salivation.
Also, when hyposalizing, you should increase the amount of fluid consumed and thoroughly rinse the mouth with acidic liquids that stimulate the saliva production process.
What is the danger of dryness in the mouth?
The danger of oligotypism is that serious disruption occurs under such conditions:
- mucous membrane becomes more vulnerable to injury and damage if it is not moist enough;
- the process of chewing and swallowing food is difficult, which worsens digestion;
- is broken taste perception;
- there is an increased accumulation of plaque, which eventually becomes a solid structure - dental calculus;
- slows down the natural process of remineralization of tooth enamel;
- the tongue can not move freely in the oral cavity, which makes it difficult to talk;
- slows the transport of nutrients to the mucosa.
Hyposylvania provokes abnormalities that make swallowing difficult, and also contribute to stool disorders and diseases of teeth and gums. These problems affect the emotional state of a person, make him irritable.
The process of reducing the secretion of saliva can ultimately lead to problems with the psyche and a constant state of stress along with the existing problems in the functioning of internal organs.
Preventive measures

It is also important to observe the water balance of
In most cases, hyposalization is the result of diseases of internal organs and systems.
Therefore, the universal council for the prevention of the development of this deviation is as follows: it is necessary to always monitor the health status, promptly treat pathological processes and undergo the necessary examinations.
Also it is necessary to look after the oral cavity correctly and regularly, to visit the dentist for preventive examinations.
The prognosis for this deviation is favorable, but only on condition of active treatment and compliance with all recommendations given by the doctor.
